复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)ENERGY METABOLISM & BODY TEMPERATURE

Chapter 7 ENERGY METABOLI SM BODY TEMPERATURE §l.Energy metabolism Introduction definition Substantial metabolism Assimilation metabolism Dissimilation metabolism (catabolism) Energy metabolism
Chapter 7 ENERGY METABOLISM & BODY TEMPERATURE § 1. Energy metabolism • Introduction & definition Substantial metabolism Assimilation metabolism Dissimilation metabolism (catabolism) Energy metabolism

Energy sources utilization Energy sources of living organisms Direct donator of energy:ATP Reserve form of energy:CP Energy sources:food Glucose (1 mol):aerobic glycolysis yields 38 mol ATP;anaerobic glycolysis yields 2 mol ATP Fat:1 mol 6C fatty acid yield 44 mol ATP Protein:rarely used as energy donator
• Energy sources & utilization * Energy sources of living organisms Direct donator of energy: ATP Reserve form of energy: CP Energy sources: food Glucose (1 mol): aerobic glycolysis yields 38 mol ATP; anaerobic glycolysis yields 2 mol ATP Fat: 1 mol 6C fatty acid yield 44 mol ATP Protein: rarely used as energy donator

Energy transfer utilization More than 50%transfer to heat, Less than 50%store in the ATP CP Utilization:synthesis growth never conduction muscular contraction glandular secretion active absorption etc
* Energy transfer & utilization More than 50% transfer to heat, Less than 50% store in the ATP & CP Utilization: synthesis & growth never conduction muscular contraction glandular secretion active absorption etc
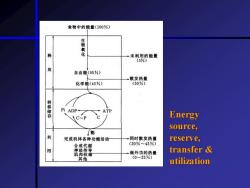
食物中的能量(100%) 氧 释 一未利用的能量 056】 放 自由能(95%) 散发热量 化学能(45%) (50%) 转移储存 Pi ADP+ ATP C-P c Energy source, 能 利 完成机体各种功能活动 同时散发热量 reserve, 合成代谢 (20%~45%) 传导 肌肉收缩 酰外沙的势量 transfer 其他 utilization
Energy source, reserve, transfer & utilization

Measuring the metabolic rate Direct calorimetry Indirect calorimetry Principle:The law of constant proportions Several related concepts Thermal equivalent of food Thermal equivalent of oxygen Respiratory quotient (RQ) Classical simple measurement O2 consumption CO2 production measuring Closed opened measurement
• Measuring the metabolic rate * Direct calorimetry * Indirect calorimetry Principle: The law of constant proportions Several related concepts Thermal equivalent of food Thermal equivalent of oxygen Respiratory quotient (RQ) Classical & simple measurement O2 consumption & CO2 production measuring Closed & opened measurement
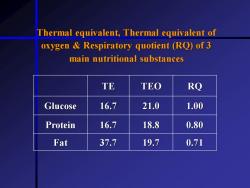
Thermal equivalent,Thermal equivalent of oxygen Respiratory quotient (RQ)of 3 main nutritional substances TE TEO RQ Glucose 16.7 21.0 1.00 Protein 16.7 18.8 0.80 Fat 37.7 19.7 0.71
TE TEO RQ Glucose 16.7 21.0 1.00 Protein 16.7 18.8 0.80 Fat 37.7 19.7 0.71 Thermal equivalent, Thermal equivalent of oxygen & Respiratory quotient (RQ) of 3 main nutritional substances
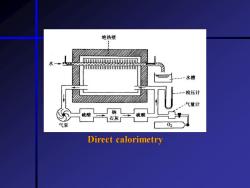
绝热壁 2auaiaeauaaaaauiaida 水 2 -水槽 检压计 气量计 硫酸 」钠 石灰 0 Direct calorimetry
Direct calorimetry

呼吸察 氧气 记纹鼓 收 呼吸活瓣 时间 Indirect calorimetry
Indirect calorimetry

Factors affecting energy metabolism Exercises Concept of oxygen debt Nervous Thinking peacefully anxious Food specific dynamic effect Environmental temperature Others:age,sex,circadian rhythm, hormones,diseases,etc
• Factors affecting energy metabolism Exercises Concept of oxygen debt Nervous Thinking peacefully & anxious Food specific dynamic effect Environmental temperature Others: age, sex, circadian rhythm, hormones, diseases, etc

Basal metabolism Basal metabolic Rate (BMR) Definition Law of body surface area Under what condition BMR can be measured? In the Early morning Arousal condition Lie down peacefully with no exercises No nervous Have a good sleep last night Fasting for over 12 h Room temperature at 20~25 'C
• Basal metabolism & Basal metabolic Rate (BMR) * Definition & Law of body surface area * Under what condition BMR can be measured? In the Early morning Arousal condition Lie down peacefully with no exercises No nervous Have a good sleep last night Fasting for over 12 h Room temperature at 20~25 ℃
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)digestion and absorption.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 血液 blood.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)BASIC FUNCTIONS OF THE CELL.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 遗传的细胞和分子基础.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 肿瘤遗传学 Cancer(Tumor)Genetics.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 医学遗传学概论.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 染色体病.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 多基因遗传与常见复杂疾病(多基因遗传的特点).ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 基因诊断 Gene diagnosis.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 基因治疗.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 基因操作.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 单基因病 Mendelian Inheritance.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 人类疾病的生化和分子遗传学——先天性代谢病.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 人类疾病的分子遗传学——血红蛋白病.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 人类基因组计划.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教学大纲_医学遗传学.doc
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)基因操作技术_医学遗传学第七章.doc
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 感觉器官的功能.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——原始信号的改善.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 群体遗传学.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Functions of the Nervous System.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Physiology——INTRODUCTION.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Physiology of Reproduction.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Physiology of the Endocrine System.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)RESPIRATION.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——从噪声中提取有用信息.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——传导(播)速度和流速测定.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——信号的时域测量.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理原则和方法——医学信号概述.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——医学图像处理基础.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 尿的生成和排出.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——散点图与双信息图.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——数字信号预处理.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——模拟信号的数字化.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——生物信号的频域分析.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)生理学信号的记录和分析——生物信号的摘取.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——生理学实验实例.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 血液循环 CIRCULATION.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)分子病与先天代谢病(2)医学遗传学第三章.doc
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)分子病与先天代谢病(1)医学遗传学第三章.doc
