中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)04 Mesh Parameterizations

Mesh Parameterizations Xiao-Ming Fu
Mesh Parameterizations Xiao-Ming Fu

Outline 。Definition Tutte's barycentric mapping Least squares conformal maps(LSCM,ASAP) Angle-Based Flattening (ABF) ·ABF++,LABF As-rigid-as-possible (ARAP) ·Simplex Assembly
Outline • Definition • Tutte’s barycentric mapping • Least squares conformal maps(LSCM, ASAP) • Angle-Based Flattening (ABF) • ABF++, LABF • As-rigid-as-possible (ARAP) • Simplex Assembly

Definition °A function that puts input surface in one-to- one correspondence with a 2D domain. Parameterization of a Triangulated Surface all (ui,vi)coordinates associated with each vertex vi (xi,yi,Zi ) 3D 2D
Definition • A function that puts input surface in one -to - one correspondence with a 2D domain. • Parameterization of a Triangulated Surface • all (𝑢𝑖, 𝑣𝑖) coordinates associated with each vertex 𝒗 𝑖 = 𝑥 𝑖 , 𝑦 𝑖 , 𝑧 𝑖 𝑇 3D 2 D
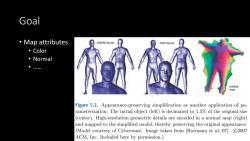
Goal ·ap attributes 290000 facets 3500 facets 。Color 。Normal map Figure 5.2.Appearance-preserving simplification as another application of pa- rameterization:The initial object (left)is decimated to 1.5%of the original size (center).High-resolution geometric details are encoded in a normal map (right) and mapped to the simplified model,thereby preserving the original appearance. (Model courtesy of Cyberware.Image taken from [Hormann et al.07].C2007 ACM,Inc.Included here by permission.)
Goal • Map attributes • Color • Normal • ……

Constraints ·Bijective The image of the surface in parameter space does not self-intersect. The intersection of any two triangles in parameter space is either a common edge,a common vertex,or empty
Constraints • Bijective • The image of the surface in parameter space does not self-intersect. • The intersection of any two triangles in parameter space is either a common edge, a common vertex, or empty
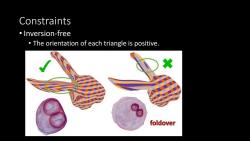
Constraints 。Inversion-free The orientation of each triangle is positive. 然 foldover
Constraints • Inversion-free • The orientation of each triangle is positive

Constraints ·Locally injective The orientation of each triangle is positive det>0. For boundary vertex,the mapping is locally bijective-> 0()>2π. 0()>2π θ()<2π
Constraints • Locally injective • The orientation of each triangle is positive → det𝐽 > 0. • For boundary vertex, the mapping is locally bijective → 𝜃 𝒗 > 2𝜋. 𝜃 𝒗 2𝜋 𝒗
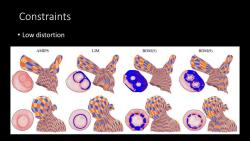
Constraints 。Low distortion AMIPS LIM BDM(5) BDM(9)
Constraints • Low distortion

Outline 。Definition Tutte's barycentric mapping Least squares conformal maps(LSCM,ASAP) Angle-Based Flattening (ABF) ·ABF+,LABF As-rigid-as-possible (ARAP) 。Simplex Assembly
Outline • Definition • Tutte’s barycentric mapping • Least squares conformal maps(LSCM, ASAP) • Angle-Based Flattening (ABF) • ABF++, LABF • As-rigid-as-possible (ARAP) • Simplex Assembly

Barycentric Mapping One of the most widely used methods. Given a triangulated surface homeomorphic to a disk,if the (u,v)coordinates at the boundary vertices lie on a convex polygon in order,and if the coordinates of the internal vertices are a convex combination of their neighbors,then the (u,v)coordinates form a valid parameterization (without self-intersections,bijective)
Barycentric Mapping • One of the most widely used methods. Given a triangulated surface homeomorphic to a disk, if the (𝑢, 𝑣) coordinates at the boundary vertices lie on a convex polygon in order, and if the coordinates of the internal vertices are a convex combination of their neighbors, then the (𝑢, 𝑣) coordinates form a valid parameterization (without self-intersections, bijective)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)03 Mesh Smoothing.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)02 Discrete differential geometry.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)01 Representation.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)积分公式——方向导数专题.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)重要的傅里叶变换对.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)利用变量代换转化为勒让德方程并求解.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)勒让德多项式的递推公式.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)捕捉分离变量法温柔气息.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)非齐次问题处理方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)探寻分离变量法心底的迷——疑难点阶段性总结.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)关于分离变量法使用条件的探讨.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)定解问题书写原则和方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)重要的物理学公式定律.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)二阶线性常系数微分方程求解——特征根法,你到底,你到底是谁.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)数理方程经典问题专题整理——函数变换法的应用.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)数理方程复习参考手册.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)数理方程复习指导(授课老师:高源).pdf
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)积分 Intergration.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)导数应用 The Derivatives in Graphing and Application.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)导数 The Derivatives.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 函数逼近.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(补充材料)第三章 函数逼近与曲线拟合.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 常微分方程数值解.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 插值(主讲:傅孝明).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 数值微分和数值积分.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十章 最优化方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 最小二乘拟合.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第零章 绪论(主讲:傅孝明).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(补充材料)绪论补充证明.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 解线性方程组的直接法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 解线性方程组的迭代法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 计算矩阵的特征值与特征向量.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数值计算方法与算法》教材教学用书(考研指定参考书,第三版,共八章).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)数值计算方法课程扩充教程(第九章 函数逼近、第十章 最优化方法).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(补充材料)迭代法收敛性补充证明.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 非线性方程求根.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《高等代数》课程教学资源(电子教案)高等代数电子教案(共六章).doc
- 上饶师范学院:《高等代数》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 线性方程组.doc
- 上饶师范学院:《高等代数》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 行列式.doc
- 上饶师范学院:《高等代数》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 矩阵.doc
