同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)积分 Intergration

Chapter Six Intergration
Chapter Six Intergration

The Area Problem Given a function fthat is continuous and nonnegative on an interval [a,b],find the area between the graph of f and the interval [a,b]on the x-axis
The Area Problem ⚫Given a function f that is continuous and nonnegative on an interval [a,b], find the area between the graph of f and the interval [a,b] on the x-axis

Antiderivative ●Definition A function F is called an antiderivative of a functionf on a given interval Iif F(x)=fx) for all x in the interval
Antiderivative ⚫Definition A function F is called an antiderivative of a function f on a given interval I if F’(x) =f(x) for all x in the interval
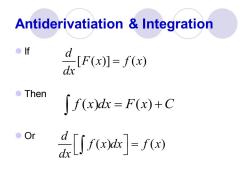
Antiderivatiation Integration ●f 2r0划0网 Then ∫f(x)dx=F(x)+C ●O ]-fo
Antiderivatiation & Integration ⚫ If ⚫ Then ⚫ Or [ ( )] ( ) d F x f x dx = f x dx F x C ( ) ( ) = + ( ) ( ) d f x dx f x dx =

Indefinite Integral Express∫f(x)k is called indefinite integral. It emphasizes that the result of antidifferentiation is "generic"function with a indefinite constant term ●“J“is called an integral sign ●“fx)”is called integrand ●“C"is called the constant of integration. odx is the differential symbol,serves to identify the independent variable
Indefinite Integral ⚫ Express is called indefinite integral. ⚫ It emphasizes that the result of antidifferentiation is “generic” function with a indefinite constant term ⚫ “ “ is called an integral sign ⚫ “f(x)” is called integrand ⚫ “C” is called the constant of integration. ⚫ dx is the differential symbol, serves to identify the independent variable f x dx ( )

Properties of the Indefinite Integral ●Theorem Suppose that F(x),G(x)are antiderivatives of fx),g(x),respectively,and c is a constant.Then OA constant factor can be moved through an integral sign: ∫cf(xdx=cF(x)+C OAn antiderivation of a sum(difference)is the sum (difference)of the antiderivatioves: [Jf(x)±g(O)]=F(x)士G()+C
Properties of the Indefinite Integral ⚫Theorem Suppose that F(x), G(x) are antiderivatives of f(x),g(x), respectively, and c is a constant. Then A constant factor can be moved through an integral sign: An antiderivation of a sum (difference) is the sum (difference) of the antiderivatioves: cf x dx cF x C ( ) ( ) = + f x g x dx F x G x C ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = +
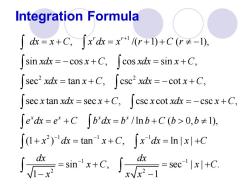
Integration Formula ∫c=x+C,∫xd=x+)+C≠-1)。 sin xdx=-cosx+C,[cos xdx=sinx+C, sec2xdx=tanx+C,[csc2 xdx =-cotx+C, secxtan xdx secx+C,cscx cotxdx =-cscx+C, edx=e+Cb'dx=b/lnb+C(b>0,b≠1), ∫1+x2)'dx=tan'x+C,「xdk=lnlx+C dx
Integration Formula 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 , /( 1) ( 1), sin cos , cos sin , sec tan , csc cot , sec tan sec , csc cot csc , / ln ( 0, 1), (1 ) tan , ln r r x x x x dx x C x dx x r C r xdx x C xdx x C xdx x C xdx x C x xdx x C x xdx x C e dx e C b dx b b C b b x dx x C x dx + − − − = + = + + − = − + = + = + = − + = + = − + = + = + + = + = 1 1 2 2 | | sin , sec | | . 1 1 x C dx dx x C x C x x x − − + = + = + − −

Integration by Substitution ● Step 1 Look for some composition fg(x))within the integrand for which the substitution u=g(x), du =g'(x)dx Produces an integral that is expressed entirely in terms of u and du,(may not OK) Step 2 If OK in Step 1,then try to evaluate the resolution integral in terms of u,(may not OK) ● Step 3 If OK in Step 2,then replace u by g(x)to express your final answer in term of x
Integration by Substitution ⚫ Step 1 Look for some composition f(g(x)) within the integrand for which the substitution Produces an integral that is expressed entirely in terms of u and du, (may not OK) ⚫ Step 2 If OK in Step 1, then try to evaluate the resolution integral in terms of u, (may not OK) ⚫ Step 3 If OK in Step 2, then replace u by g(x) to express your final answer in term of x. u g x du g x dx = = ( ), '( )
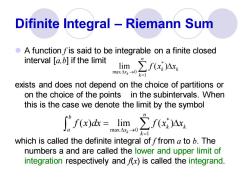
Difinite Integral -Riemann Sum A function fis said to be integrable on a finite closed interval [.if the limit limx max△xk→0 k=1 exists and does not depend on the choice of partitions or on the choice of the points in the subintervals.When this is the case we denote the limit by the symbol fx)dk=Iim,∑fx)Ax nax△xk→0 k=1 which is called the definite integral of ffrom a to b.The numbers a and are called the lower and upper limit of integration respectively andfx)is called the integrand
Difinite Integral – Riemann Sum ⚫ A function f is said to be integrable on a finite closed interval [a,b] if the limit exists and does not depend on the choice of partitions or on the choice of the points in the subintervals. When this is the case we denote the limit by the symbol which is called the definite integral of f from a to b. The numbers a and are called the lower and upper limit of integration respectively and f(x) is called the integrand. * max 0 1 lim ( ) k n k k x k f x x → = * max 0 1 ( ) lim ( ) k n b k k a x k f x dx f x x → = =

Difinite Integral-Graph Area ●Theorem OIf a function fis continuous on an interval [a,b],then fis integrable on [a,b],and net signed area 4 between the graph of fand the interval [a,b]is A=心((x)dz
Difinite Integral – Graph Area ⚫Theorem If a function f is continuous on an interval [a,b], then f is integrable on [a,b], and net signed area A between the graph of f and the interval [a,b] is ( ) b a A f x dx =
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)导数应用 The Derivatives in Graphing and Application.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)导数 The Derivatives.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)极限 Limits & Continuity.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D,PPT课件)函数.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D)习题样本.doc
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D)习题集 Calculus Exercise.pdf
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D)2008-2009学年第一学期《高等数学 D(英语)》期末考试试卷(A 卷,答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《高等数学 Advanced Mathematics》课程教学资源(高数D)2008-2009学年第一学期《高等数学 D(英语)》期末考试试卷(A 卷,试卷).pdf
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(D题库,无答案)第四章 微分方程题库.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(D题库,无答案)第二章 导数与微分.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(D题库,无答案)第三章 积分及其应用.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(D题库,无答案)第一章 函数与极限.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(A2题库,无答案)第八章 重积分题库.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(A2题库,无答案)第九章 曲线积分与曲面积分题库.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(A2题库,无答案)第七章 多元函数微分学.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(A2题库,无答案)空间解析几何题库.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(A2题库,无答案)无穷级数1.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(A2题库,无答案)微分方程1.doc
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(B2题库,无答案)第9章 多元函数微分学及其应用.docx
- 江西科技学院:《高等数学》课程教学资源(B2题库,无答案)第8章 无穷级数.doc
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)数理方程复习指导(授课老师:高源).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)数理方程复习参考手册.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)数理方程经典问题专题整理——函数变换法的应用.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)二阶线性常系数微分方程求解——特征根法,你到底,你到底是谁.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)重要的物理学公式定律.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)定解问题书写原则和方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)关于分离变量法使用条件的探讨.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)探寻分离变量法心底的迷——疑难点阶段性总结.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)非齐次问题处理方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)捕捉分离变量法温柔气息.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)勒让德多项式的递推公式.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)利用变量代换转化为勒让德方程并求解.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)重要的傅里叶变换对.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数理方程》课程教学资源(讲稿)积分公式——方向导数专题.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)01 Representation.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)02 Discrete differential geometry.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)03 Mesh Smoothing.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《数字几何处理 Digital Geometry Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲义)04 Mesh Parameterizations.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 函数逼近.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《计算方法》课程教学资源(补充材料)第三章 函数逼近与曲线拟合.pdf
