西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 09 紫外吸收光谱法(Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV)

Chapter 9 Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV (紫外吸收光谱分析)
Chapter 9 Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV (紫外吸收光谱分析)

Moleaular absorption Absorbing species UV/Vis We are dealing with electronic transitions. Due to the large number of vibrational and rotational states,the spectra appear as bands

UV/Vis absorption UV/Vis absorption by organic compounds requires that the energy absorbed corresponds to a jump from a populated orbital to an unpopulated one. anti-bonding anti-bonding n non-bonding bonding bonding

Electronic transitions include three kinds of types: ● N→V transitions include →* transitions in saturated organic compounds andππ* transitions in unsaturated compounds. ● N→Q transitions: a kind of transitions arise from the electron excitation from nonbonding orbital to anti-bonding orbital. ● N→R transition: electron is excited to a higher level until it is ionized to molecular ion. ● Charge transfer transitions: charge (electron) transfers between different parts of the compound due to charge redistribution of the compound excited by a radiation
Electronic transitions include three kinds of types: ● N→V transitions include →* transitions in saturated organic compounds andππ* transitions in unsaturated compounds. ● N→Q transitions: a kind of transitions arise from the electron excitation from nonbonding orbital to anti-bonding orbital. ● N→R transition: electron is excited to a higher level until it is ionized to molecular ion. ● Charge transfer transitions: charge (electron) transfers between different parts of the compound due to charge redistribution of the compound excited by a radiation

* : anti-bond orbital
* : anti-bond orbital

UV/Vis absorption n->o*transitions The compound must contain atoms with unshared electron pairs. Compounds containing O,S,N and halogens can absorb via this type of transition. Absorptions are typically in the 150-250 nm region and are not very intense
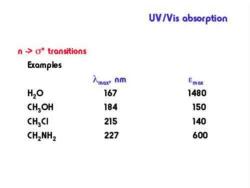
UV/Vis absorption n ->o*transitions Examples 入mox nm Emox H2O 167 1480 CHOH 184 150 CHCI 215 140 CH2NH2 227 600

UV/Vis absorption n->*and>*transitions For a orbital to be available,there must be some degree of unsaturation. multiple bonds and resonance structures These result in some of the most intense absorptions (200-700 nm region). As the degree of unsaturation increases,you typically see a shift to higher
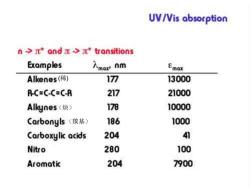
(稀) (炔) (羰基)
(稀) (炔) (羰基)
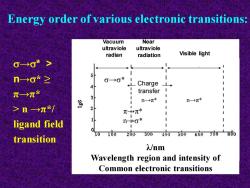
→* > n→* ≥ π→π* > n →π*/ ligand field transition Energy order of various electronic transitions: Vacuum ultraviole radian Near ultraviole radiation Visible light →* π→π* n→* n→π* n→π* Charge transfer λ/nm Wavelength region and intensity of Common electronic transitions
→* > n→* ≥ π→π* > n →π*/ ligand field transition Energy order of various electronic transitions: Vacuum ultraviole radian Near ultraviole radiation Visible light →* π→π* n→* n→π* n→π* Charge transfer λ/nm Wavelength region and intensity of Common electronic transitions
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 08 原子吸收法 Atomic absorption spectrometry(AAS).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 07 原子发射法(Atomic Emission Spectrometry, AES).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 04 电位法 potentiometry.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 03 High Performance Liquid Chromatography(HPLC).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 02 气相色谱法 Gas Chromatography(GC).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 质谱分析(Mass Spectrometry, MS).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 核磁共振波谱法(Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy,NMR).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 红外光谱法 Infrared absorption spectroscopy(IR).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 01 preface.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 06 库仑滴定法 Coulometry.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 05 伏安法 voltammetry.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第18章 核化学.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第17章 氢.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第16章 f区元素.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第15章 d区元素.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第14章 p区元素(二).ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第13章 p区元素(一).ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 s区元素.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第11章 条件电势和氧化还原滴定.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第10章 沉淀稳定常数和络合滴定.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(参考资料)Detectores Detectores.pdf
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 红外吸收光谱法(Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy, IR).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论 INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS(主讲:马永钧).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 气相色谱法.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 高效液相色谱(High Pertormance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 电位分析法(Potentiometry).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 伏安分析法(Voltammetry).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 电解与库仑分析法.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 原子发射光谱法(Atomic Emission Spectrometry, AES).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 原子吸收光谱法(Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, AAS).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 紫外光谱法(Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(参考资料)电位滴定法中终点电位的确定方法.doc
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(参考资料)potentoal titration the first and second derivatives_potentoal titration the first and second derivatives.doc
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 醇和醚.ppt
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 酚.ppt
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 醛、酮.ppt
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 羧酸及其衍生物.ppt
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 β-二羰基化合物.ppt
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 胺.ppt
- 天津科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 重氮化合物和偶氮化合物.ppt
