西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 05 伏安法 voltammetry

§5 Voltammetry §5-1 Basic principle of polarograpy Voltammetry A group of analytical methods based on determining current flow – voltage curve during electrolysis Several types of methods based on Electrode type How the potential is applied How the current is measured
§5 Voltammetry §5-1 Basic principle of polarograpy Voltammetry A group of analytical methods based on determining current flow – voltage curve during electrolysis Several types of methods based on Electrode type How the potential is applied How the current is measured
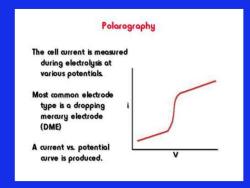
Polarography The cell arrent is measured during electrolysis at various potentials Most common electrode type is a dropping mercury electrode (DME) A current vs.potential aurve is produced
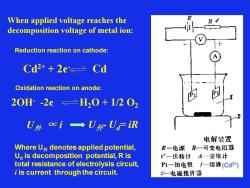
When applied voltage reaches the decomposition voltage of metal ion: Reduction reaction on cathode: Cd2+ + 2e- Cd Oxidation reaction on anode: 2OH- -2e H2O + 1/2 O2 U外 ∝ i Where U外 denotes applied potential, Ud is decomposition potential, R is total resistance of electrolysis circuit, i is current through the circuit. U外- Ud= iR (Cd2+)
When applied voltage reaches the decomposition voltage of metal ion: Reduction reaction on cathode: Cd2+ + 2e- Cd Oxidation reaction on anode: 2OH- -2e H2O + 1/2 O2 U外 ∝ i Where U外 denotes applied potential, Ud is decomposition potential, R is total resistance of electrolysis circuit, i is current through the circuit. U外- Ud= iR (Cd2+)
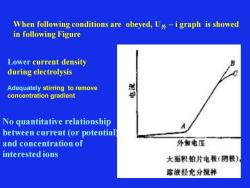
When following conditions are obeyed, U外 – i graph is showed in following Figure Lower current density during electrolysis Adequately stirring to remove concentration gradient No quantitative relationship between current (or potential) and concentration of interested ions
When following conditions are obeyed, U外 – i graph is showed in following Figure Lower current density during electrolysis Adequately stirring to remove concentration gradient No quantitative relationship between current (or potential) and concentration of interested ions

To find the analytical relationship between the current and the concentration of sought-for ions , following measurements are adopted: ●MICROPLATINUM ELECTRODE Or DROPPING MERCURY ELECTRODE ( in most common use) to insure high current density ● NO STIRRING to insure enough high concentration difference between the electrode surface and the solution bulk Then E = Eo + ln CM RT nF
To find the analytical relationship between the current and the concentration of sought-for ions , following measurements are adopted: ●MICROPLATINUM ELECTRODE Or DROPPING MERCURY ELECTRODE ( in most common use) to insure high current density ● NO STIRRING to insure enough high concentration difference between the electrode surface and the solution bulk Then E = Eo + ln CM RT nF

When the current flowed for only a short period through the electrode, ion concentration on the surface of the electrode reduce suddenly. The difference in ion concentrations between the surface and the bulk solution is equivalent to an electrochemical cell, which is called concentration polarization(浓差极化). thus, there is a voltage that is equivalent to this concentration change called concentration polarization potential(浓差电势) When a microplatinum electrode or dropping mercury electrode is used and no stirring is carried out, concentration polarization takes place soon, following polarogram is obtained Limiting current A B C D
When the current flowed for only a short period through the electrode, ion concentration on the surface of the electrode reduce suddenly. The difference in ion concentrations between the surface and the bulk solution is equivalent to an electrochemical cell, which is called concentration polarization(浓差极化). thus, there is a voltage that is equivalent to this concentration change called concentration polarization potential(浓差电势) When a microplatinum electrode or dropping mercury electrode is used and no stirring is carried out, concentration polarization takes place soon, following polarogram is obtained Limiting current A B C D

Polarograph Battery M G-galvanometer V-voltammeter Sample cell Professor Jaroslav Heyrovsky (1890-1967)and his polarograph which he first described in 1922. The output was recorded on photographic film

When applied voltage does not reach reduction voltage of metal ion, only a little current flow, called residual current produced by reduction of impurities and charging current, eg AB in the Figure Limiting current A B C D Arriving on decomposition voltage, the electrode reactions occur, the current rises rapidly with increasing voltage, BC section in the figure Cathode (DME): Cd2+ + 2e- +Hg Cd(Hg) (amalgam) Anode (calomel or pool mercury electrode with a big area): 2Hg - 2e- + 2Cl- Hg2Cl2
When applied voltage does not reach reduction voltage of metal ion, only a little current flow, called residual current produced by reduction of impurities and charging current, eg AB in the Figure Limiting current A B C D Arriving on decomposition voltage, the electrode reactions occur, the current rises rapidly with increasing voltage, BC section in the figure Cathode (DME): Cd2+ + 2e- +Hg Cd(Hg) (amalgam) Anode (calomel or pool mercury electrode with a big area): 2Hg - 2e- + 2Cl- Hg2Cl2

When it reaches C point voltage, due to concentration polarization, the current arrives at a limiting value and does not rise markedly, called limiting current, consisting of residual current and diffusion current 极谱波可以用i~ U外表示曲线表示,也可以用i ~ Ede曲线来表示,从下 面的讨论可以看出,二者是基本重合的。 U = ( ESCE -Ede ) + i R ∵ i and R are very little in polarographic electrolysis U = ESCE -Ede = -Ede( vs. SCE) To remove completely influence of iR, three electrode system is usually used
When it reaches C point voltage, due to concentration polarization, the current arrives at a limiting value and does not rise markedly, called limiting current, consisting of residual current and diffusion current 极谱波可以用i~ U外表示曲线表示,也可以用i ~ Ede曲线来表示,从下 面的讨论可以看出,二者是基本重合的。 U = ( ESCE -Ede ) + i R ∵ i and R are very little in polarographic electrolysis U = ESCE -Ede = -Ede( vs. SCE) To remove completely influence of iR, three electrode system is usually used

Very little oscillation
Very little oscillation
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第18章 核化学.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第17章 氢.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第16章 f区元素.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第15章 d区元素.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第14章 p区元素(二).ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第13章 p区元素(一).ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 s区元素.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第11章 条件电势和氧化还原滴定.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第10章 沉淀稳定常数和络合滴定.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第09章 沉淀溶解平衡和沉淀滴定.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第08章 酸碱平衡和酸碱滴定.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第07章 金属配位化合物.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第06章 氧化还原反应与电化学.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第05章 酸、碱和酸碱反应.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第04章 化学反应速率与反应动力学的初步概念.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第03章 化学热力学的初步概念与化学平衡.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第02章 化学键与分子结构.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第01章 原子结构和元素周期表.ppt
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 09 沉淀溶解平衡和沉淀滴定.pdf
- 西北大学:《无机化学与分析化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 08 酸碱平衡和酸碱滴定.pdf
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 06 库仑滴定法 Coulometry.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 01 preface.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 红外光谱法 Infrared absorption spectroscopy(IR).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 核磁共振波谱法(Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy,NMR).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 质谱分析(Mass Spectrometry, MS).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 02 气相色谱法 Gas Chromatography(GC).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 03 High Performance Liquid Chromatography(HPLC).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 04 电位法 potentiometry.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 07 原子发射法(Atomic Emission Spectrometry, AES).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 08 原子吸收法 Atomic absorption spectrometry(AAS).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 09 紫外吸收光谱法(Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry, UV).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(参考资料)Detectores Detectores.pdf
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 红外吸收光谱法(Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy, IR).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论 INSTRUMENTAL ANALYSIS(主讲:马永钧).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 气相色谱法.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 高效液相色谱(High Pertormance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 电位分析法(Potentiometry).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 伏安分析法(Voltammetry).ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 电解与库仑分析法.ppt
- 西北师范大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 原子发射光谱法(Atomic Emission Spectrometry, AES).ppt
