上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 19 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volume Analysis Spring,2017 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 LAAAAARA http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lecture 19 Spring, 2017 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volume Analysis http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
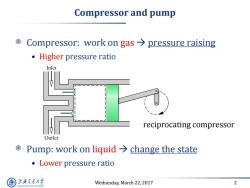
Compressor and pump Compressor:work on gas pressure raising Higher pressure ratio Inlet reciprocating compressor Outlet ©Pump:work on liquid→change the state Lower pressure ratio 上游充通大 Wednesday,March 22,2017 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 2 Compressor and pump Compressor: work on gas pressure raising • Higher pressure ratio Pump: work on liquid change the state • Lower pressure ratio reciprocating compressor
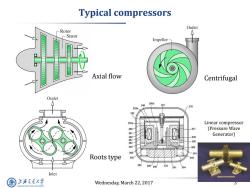
Typical compressors Outlet Rotor Stator Impeller- Axial flow Centrifugal Outlet 200d 240 231 270 252 252 252a Linear compressor 241 (Pressure Wave Generator) 230 280 242 300 200 293 Roots type 202 292 295 220 290 210 291 294 Inlet 上降通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 3 Typical compressors Axial flow Centrifugal Roots type Linear compressor (Pressure Wave Generator)
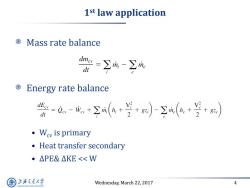
1st law application Mass rate balance =∑m-∑m: dt Energy rate balance 份-@,-成+空m(4+于+)(a+兰+) dt ·Wc is primary Heat transfer secondary ·△PE&△KE<<W 上游气通大粤 Wednesday,March 22,2017 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 4 1 st law application Mass rate balance Energy rate balance • Wcv is primary • Heat transfer secondary • ∆PE& ∆KE << W
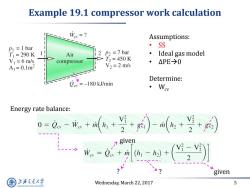
Example 19.1 compressor work calculation Wey=? Assumptions: =1 bar ·SS T =290K Air 2 p2 7 bar Ideal gas model > V=6 m/s compressor T2=450K ● △PE→0 A=0.1m2 V2 2 m/s Determine: Qev =-180 kJ/min ·Wew Energy rate balance: 0=0.-1++--+ given =-( given 上游充通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 5 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 5 Example 19.1 compressor work calculation Assumptions: • SS • Ideal gas model • ∆PE0 Determine: • Wcv Energy rate balance: given given ? ?
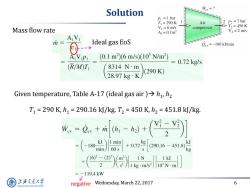
Solution Wev=? P1=1 bar T1=290K Air 2 P2=7bar Mass flow rate VI=6 m/s compressor T,=450K A1=0.1m2 V2 =2 m/s AVI m Ideal gas EoS Qcy=-180 kJ/min 1(0.1m2)6m/s)(105N/m (R/M)T 2897gR)290 8314Nm 2=0.72kgs Given temperature,Table A-17 (ideal gas air)>h,h2 T1=290K,h1=290.16k/kg.T2=450K,h2=451.8k/kg. -e.+a--(] -(-1)l+02e016-451 kJ +(:erXgndiso -119.4kW 上游充通大学 negative v Wednesday,March 22,2017 6 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 6 Solution Mass flow rate Ideal gas EoS Given temperature, Table A-17 (ideal gas air ) h1 , h2 T1 = 290 K, h1 = 290.16 kJ/kg. T2 = 450 K, h2 = 451.8 kJ/kg. negative
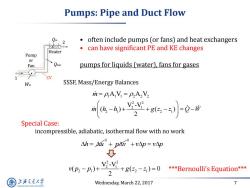
Pumps:Pipe and Duct Flow 2 often include pumps (or fans)and heat exchangers can have significant PE and KE changes Heater Pump or Fan Qloss pumps for liquids (water),fans for gases SSSF,Mass/Energy Balances i=PAVi=P2A2 V2 +s6y0-i Special Case: incompressible,adiabatic,isothermal flow with no work △h=A°+p4°+vAp=vp Wn-n+,Y+ge-)=0 ***Bernoulli's Equation*** 2 上游充通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 7 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 7 Pumps: Pipe and Duct Flow 2 Qin • often include pumps (or fans) and heat exchangers • can have significant PE and KE changes pumps for liquids (water), fans for gases Pump or Fan 1 Heater Qloss CV Win SSSF, Mass/Energy Balances Special Case: incompressible, adiabatic, isothermal flow with no work 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 V -V ( ) ( ) 0 2 v p p g z z m 1 1 1 A V A V 2 2 2 h u 0 p v 0 v p v p 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 V -V ( ) ( ) 2 m h h g z z Q W ***Bernoulli’s Equation***
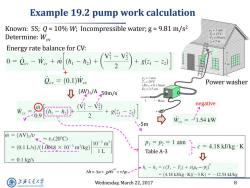
Example 19.2 pump work calculation Known:SS;Q=10%W;Incompressible water;g=9.81 m/s2 p2=I atm Determine:Wev T2=23℃ V2=50m/s 2=5m Energy rate balance for CV: 0=0。-成+刻+()+的-对 v=(0.1)Wev P=I atm T1=20C Power washer (AV)=0.1 liter/s ↓(ayi/A50m/s D1=2.5cm (好-嗡) negative -h2) + 0.9 2 +8(- Wev =-1.54 kW -5m m (AV)/v ≈U(20C) (0.1L/s)/1.0018×10-3m/kg) 10-3m3 P=p2=1 atm C= 4.18 kJ/kg K Table A-3 1 0.1 kg/s h1-h2=c(T-T2)+v(P-p) △h=△u+p4+vp一 = (4.18kJ/kg·K)(-3K)=-12.54kJ/kg 上降文通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 8 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 8 Energy rate balance for CV: Example 19.2 pump work calculation + -5m 50m/s (AV)1/A Table A-3 negative Power washer Known: SS; Q = 10% W; Incompressible water; g = 9.81 m/s2 Determine: Wcv h u p v 0 v p
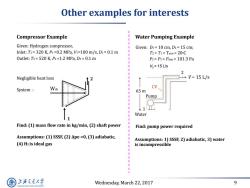
Other examples for interests Compressor Example Water Pumping Example Given:Hydrogen compressor, Given:D1=10 cm,D2=15 cm; Inlet:T1=320K,P1=0.2MPa,=100m/s,D1=0.1m T2=T1=Tatm=20C Outlet:T2=520 K,P2=1.2 MPa,D2=0.1 m P2=P1=Patm=101.3 Pa V2=15L/s 2 Negligible heat loss ÷V=15L/s System Wsh 65m Pump Water 1 Find:(1)mass flow rate in kg/min,(2)shaft power Find:pump power required Assumptions:(1)SSSF,(2)Ape =0,(3)adiabatic, Assumptions:1)SSSF,2)adiabatic,3)water (4)Hz is ideal gas is incompressible 上游充通大 Wednesday,March 22,2017 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 9 Other examples for interests Compressor Example Given: Hydrogen compressor, Inlet: T1 = 320 K, P1 =0.2 MPa, V1=100 m/s, D1 = 0.1 m Outlet: T2 = 520 K, P2 =1.2 MPa, D2 = 0.1 m Negligible heat loss 2 System : Wsh 1 Find: (1) mass flow rate in kg/min, (2) shaft power Assumptions: (1) SSSF, (2) ∆pe =0, (3) adiabatic, (4) H2 is ideal gas Water Pumping Example 2 CV 65 m Pump V 15 L/s 1 Water Find: pump power required Assumptions: 1) SSSF, 2) adiabatic, 3) water is incompressible Given: D1 = 10 cm, D2 = 15 cm; T2 = T1 = Tatm = 20oC P2 = P1 = Patm = 101.3 Pa V2 = 15 L/s

Homework: Problems:SP1,SP2 上游充通大学 Wednesday,March 22,2017 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Wednesday, March 22, 2017 10 Homework: Problems: SP1, SP2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 16_Control volume analysis - mass conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 15_Polytropic process.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 对流传热的理论基础 5-1 对流传热概说 5-2 对流换热问题的数学描写.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 导热问题的数值解法 §4-4 非稳态导热问题的数值解法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 非稳态导热 § 3-3 典型一维物体非稳态导热的分析解 §3-4 半无限大物体的非稳态导热 第四章 导热问题的数值解法 4-1 导热问题数值求解的基本思想 4-2 内节点离散方程的建立方法 4-3 边界结点离散方程的建立及代数方程的求解.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 2-5 具有内热源的一维导热问题 2-6 多维稳态导热的求解 第三章 非稳态导热 3-1 非稳态导热的基本概念 3-2 零维问题的分析法——集中参数法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 2-5 具有内热源的一维导热问题 2-6 多维稳态导热的求解 第三章 非稳态导热 3-1 非稳态导热的基本概念 3-2 零维问题的分析法——集中参数法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 §2-3 典型一维稳态导热问题的分析解 2-4 通过肋片的导热.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 2-1 导热基本定律 2-2 导热问题的数学描写.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 对流传热的理论基础 5-3 边界层型对流传热问题的数学描写 5-4 流体外掠平板传热层流分析解及比拟理论 第六章 单相对流传热的实验关联式 6-1 相似原理与量纲分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer 第一章 绪论(王平阳).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《能源物理》教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 质点运动学.pdf
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 原子光谱与分子光谱.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 光学基本知识与药用光学仪器.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 量子力学基础.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 波动光学.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 振动和波.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 静电场.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27-28_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 29_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 30_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37-38_Concept of exergy and apply to CM&CV systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 45_Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 46_Diesel cycle and dual cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 47_Compressor, compression with intercooling.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 48_Review and Final Exam.pdf
