上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 15_Polytropic process

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 15 Spring,2017 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG R几L E http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日G
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 15 Spring, 2017 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html
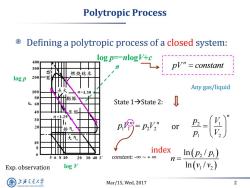
Polytropic Process Defining a polytropic process of a closed system: 400 300 燃烧结束 sgpr一nogvse ph=cnsn log p 200 点火 Any gas/liquid 100 l=1.30 膨胀 State1→State2: 40 压缩 =1.29 30 20 排气 or 大气 10 8 index 6 In(p2/p) 56810 203040V constant.-o∞~+o∞ n= Exp.observation log V In(v/v2) 上游充通大 Mar/15,Wed,2017 2 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 2 Polytropic Process Defining a polytropic process of a closed system: n pV constant constant: -∞ ~ + ∞ State 1State 2: 1 1 2 2 n n pV p V or 2 1 1 2 n p V p V log p Exp. observation log V 2 1 1 2 ln / ln / p p n v v Any gas/liquid log p=-nlogV+c index
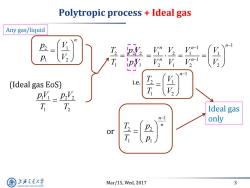
Polytropic process Ideal gas Any gas/liquid P (Ideal gas EoS) i.e. py pvz T Ideal gas n-1 only 27 n or P 上游究大学 Mar/15,Wed,2017 3 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 3 Polytropic process + Ideal gas 1 1 2 2 1 2 p V p V T T (Ideal gas EoS) 2 2 2 1 1 1 T p V T p V 1 2 2 1 1 n n T p T p 2 1 1 2 n p V p V or Ideal gas only 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 n n n n n V V V V V V V V Any gas/liquid 1 2 1 1 2 n T V T V i.e
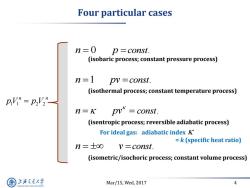
Four particular cases n=0 p =const. (isobaric process;constant pressure process) n=1 pv =const. (isothermal process;constant temperature process) p"=p2V2” n=K pv*=const. (isentropic process;reversible adiabatic process) For ideal gas:adiabatic index K =k(specific heat ratio) n=士o∞ V=const. (isometric/isochoric process;constant volume process) 上游充通大学 Mar/15,Wed,2017 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 4 Four particular cases 1 1 2 2 n n pV p V n p 0 const. n pv 1 const. n pv const. n v const. (isobaric process; constant pressure process) (isometric/isochoric process; constant volume process) (isentropic process; reversible adiabatic process) (isothermal process; constant temperature process) For ideal gas: adiabatic index = k (specific heat ratio)
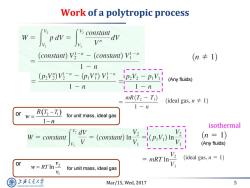
Work of a polytropic process m- w= Vn (constant)V3-"-(constant))V}-" (n卡1) 1-n (pV)Vg-"-(p,V)V-nt (Any fluids) 1-n 11-n mR(T2-Ti) (ideal gas,n≠I) 1-n or w= (T-T) for unit mass,ideal gas 1-n isothermal [v dv W constant v= V (n=1) (Any fluids) (ideal gas,n 1) or mRT In- w=RTIn for unit mass,ideal gas 上泽通大学 Mar/15,Wed,2017 5 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 5 Work of a polytropic process isothermal (Any fluids) (Any fluids) 2 1 1 R T T w n or for unit mass, ideal gas for unit mass, ideal gas 2 1 RT ln v w v or
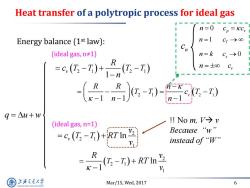
Heat transfer of a polytropic process for ideal gas n=0 Energy balance (1st law): n=1 Cr→0 (ideal gas,n≠1) n=k C→0 -区-0+-W n=±oo C -T) n-l q=△u+w !No m,V→v (ideal gas,n=1) =c (T-T)+RTIn Because“w" V instead of“W" k-g-T)+R7n兰 R 1 上游充通大 Mar/15,Wed,2017 6 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 6 Heat transfer of a polytropic process for ideal gas 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 v v R R n T T c T T n n R c T T T T n Energy balance (1st law): (ideal gas, n≠1) q u w n c 0 p v n c c n c 1 T n k c s 0 n c v (ideal gas, n=1) 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 ln ln 1 v T T v c T T RT v R v RT v !! No m, V v Because “w” instead of “W
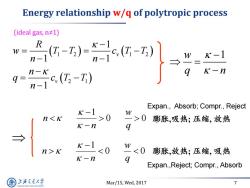
Energy relationship w/q of polytropic process (ideal gas,n≠1) R W K-1 -) K-n q=- Expan.,Absorb;Compr.,Reject K-1 W n0 >0膨胀,吸热;压缩,放热 K-n 9 K-1 n>K <0 w<0 膨胀,放热;压缩,吸热 K一n 9 Expan.,Reject;Compr.,Absorb 上游通大学 Mar/15,Wed,2017 7 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 7 Energy relationship w/q of polytropic process 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 v v R w T T c T T n n n q c T T n 0 0 1 q w n n w 1 q n 0 0 1 q w n n (ideal gas, n≠1) 膨胀,吸热; 压缩, 放热 Expan., Absorb; Compr., Reject 膨胀,放热; 压缩, 吸热 Expan.,Reject; Compr., Absorb
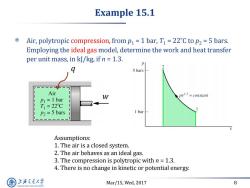
Example 15.1 Air,polytropic compression,from p=1 bar,T1=22C to p2 =5 bars. Employing the ideal gas model,determine the work and heat transfer per unit mass,in kJ/kg,if n 1.3. 5 bars Air W pul3=constant P1=1 bar T1=22℃ P2=5 bars 1 bar Assumptions: 1.The air is a closed system. 2.The air behaves as an ideal gas. 3.The compression is polytropic with n 1.3. 4.There is no change in kinetic or potential energy. 上游充通大 Mar/15,Wed,2017 8 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 8 Example 15.1 Air, polytropic compression, from p1 = 1 bar, T1 = 22˚C to p2 = 5 bars. Employing the ideal gas model, determine the work and heat transfer per unit mass, in kJ/kg, if n = 1.3. q w Assumptions: 1. The air is a closed system. 2. The air behaves as an ideal gas. 3. The compression is polytropic with n = 1.3. 4. There is no change in kinetic or potential energy
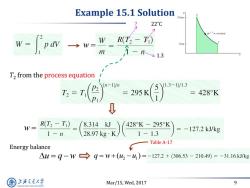
Example 15.1 Solution P s bars 22C pul3 =constant w-fow W R(T2-F 1bar m 1-31.3 T2 from the process equation (n-1)/m =295K (1.3-1)/1.3 =428K D W= R(T2-T) 8.314kJ 428K-295K =-127.2kJ/kg 1-n 1-1.3 Table A-17 Energy balance △u=9-1w→9=w+(4-4)=-127.2+(306.53-210.49)=-31.16kkg 上游充通大 Mar/15,Wed,2017 9 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 9 Example 15.1 Solution 22˚C 1.3 ? T2 from the process equation Energy balance u q w w w 2 1 q w u u ( ) Table A-17
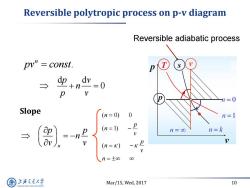
Reversible polytropic process on p-v diagram Reversible adiabatic process pv'”=const. T → dp+n dv =0 p V n=0 Slope (n=0) 0 n=1 → =-n P (n=1) n=0 n=k V p (n=K) 一K D n=±oo 00 上游究通大学 Mar/15,Wed,2017 10 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Mar/15, Wed, 2017 10 Reversible polytropic process on p-v diagram . n pv const d d 0 p v n p v n p p n v v Slope n v p n v p n n ( ) ( 1) ( 0) 0 Reversible adiabatic process
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 对流传热的理论基础 5-1 对流传热概说 5-2 对流换热问题的数学描写.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 导热问题的数值解法 §4-4 非稳态导热问题的数值解法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 非稳态导热 § 3-3 典型一维物体非稳态导热的分析解 §3-4 半无限大物体的非稳态导热 第四章 导热问题的数值解法 4-1 导热问题数值求解的基本思想 4-2 内节点离散方程的建立方法 4-3 边界结点离散方程的建立及代数方程的求解.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 2-5 具有内热源的一维导热问题 2-6 多维稳态导热的求解 第三章 非稳态导热 3-1 非稳态导热的基本概念 3-2 零维问题的分析法——集中参数法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 2-5 具有内热源的一维导热问题 2-6 多维稳态导热的求解 第三章 非稳态导热 3-1 非稳态导热的基本概念 3-2 零维问题的分析法——集中参数法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 §2-3 典型一维稳态导热问题的分析解 2-4 通过肋片的导热.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 导热基本定律及稳态导热 2-1 导热基本定律 2-2 导热问题的数学描写.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 对流传热的理论基础 5-3 边界层型对流传热问题的数学描写 5-4 流体外掠平板传热层流分析解及比拟理论 第六章 单相对流传热的实验关联式 6-1 相似原理与量纲分析.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《传热学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)传热传质学 Heat and Mass Transfer 第一章 绪论(王平阳).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《能源物理》教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 质点运动学.pdf
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 原子光谱与分子光谱.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 光学基本知识与药用光学仪器.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 量子力学基础.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 波动光学.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 振动和波.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 静电场.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 恒定磁场 第四节 磁场对运动电荷的作用、磁性药物治疗剂的临床应用.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 热力学基础.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 恒定电流与电路.ppt
- 上海中医药大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 分子物理学基础.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 16_Control volume analysis - mass conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 17_Control volume analysis - energy conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 18_Illustrations_1 Nozzles, diffusers, turbines.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 19_Illustrations_2 Compressors, pumps.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 20-21_Illustrations_3 Heat exchangers, throttling devices, System integration.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 22_Transient analysis of Energy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 23-24_Introducing 2nd law, concept of irreversibilities.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 27-28_Applying 2nd law to thermodynamic cycles, Maximum performance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 29_Carnot Cycle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 30_Clausius inequality and Entropy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 31_Retrieve entropy data.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 32_Internally reversible processes, Closed system entropy balance.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 33_Entropy increase principle.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 34_Entropy balance to open systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 35_Isentropic processes, Isentropic efficiencies.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 36_Heat transfer and Work of internal reversible, ss flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 37-38_Concept of exergy and apply to CM&CV systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 39-40_vapor power cycles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 43_superheat and reaheat.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《热力学 Thermodynamics(I)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)Lecture 44_Vapor-compression refrigeration, Heat pump systems.pdf
