上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)血液中使用的药剂 Agents used in blood

® 上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Agents used in blood nT ANGHA是IAO TON 1三
Agents used in blood

上游充通大淫 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Classification of drugs ●Anticoagulants ----Heparin,low molecular weight heparin ----Warfarin ● Fibrinolytics ●Antipletelet drugs Treatment of bleeding ----Vitamin K 1三三 Treatment of anemia ----Iron MA ----Cyanocobalamin (B12) ----Folic acid
●Anticoagulants ----Heparin, low molecular weight heparin ----Warfarin ● Fibrinolytics ● Antipletelet drugs ● Treatment of bleeding ----Vitamin K ● Treatment of anemia ----Iron ----Cyanocobalamin (B12) ----Folic acid Classification of drugs
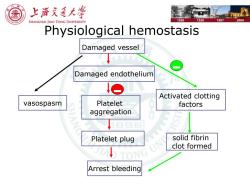
上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Physiological hemostasis Damaged vessel Damaged endothelium Activated clotting vasospasm Platelet factors aggregation Platelet plug solid fibrin clot formed ONG Arrest bleeding
Physiological hemostasis Damaged vessel vasospasm Activated clotting factors solid fibrin clot formed Platelet plug Arrest bleeding Platelet aggregation Damaged endothelium - -
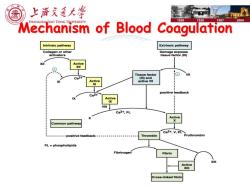
上济充通大学 SHANGHAI IIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Mechanism of Blood Coagulation Intrinsic pathway Extrinsic pathway Collagen or other Damage exposes activators tissue factor(Ill) Active XII Tissue factor Ca2+ (Ill)and Active active Vll XI Ca2+ positive feedback Active X VIn Ca2+,PL X Active X Common pathway Ca2+,V,PL ---------positive feedback------------ Thrombin Prothrombin PL=phospholipids Fibrinogen Fibrin XI Active X☒1Ⅲ Cross-linked fibrin
Mechanism of Blood Coagulation Mechanism of Blood Coagulation
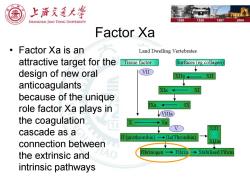
上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Factor Xa 。Factor Xa is an Land Dwelling Vertebrates attractive target for the Tissue factor Surfaces (eg collagen) ↓ design of new oral VII X anticoagulants because of the unique role factor Xa plays in IXa IX LVIlla the coagulation Xa cascade as a II(prothrombin) ◆Ila(Thrombin connection between the extrinsic and AO ibrinogen◆Fibrin)◆Stabilised Fibrin intrinsic pathways
Factor Xa • Factor Xa is an attractive target for the design of new oral anticoagulants because of the unique role factor Xa plays in the coagulation cascade as a connection between the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways

FACTORS WHICH PROMOTE BLOOD FLUIDITY Normal Hemostasis Natural Anticoagulants Protein C Protein S Antithrombin III Endothelial-Derived Anti-Platelet Substances Nitric Oxide Prostacyclin(PGl2) Fibrinolytic System "clot busters" Plasmin Plasminogen Tissue Plasminogen Activator(tPA) Department of Pharmacology Howard University College of Medicine

上游充通大淫 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 History of Anticoagulants Jay McLean,a second year medical student at Johns Hopkins University,discovered this wonderful drug in 1916 while performing research in the laboratory of W.H.Howell,MD. W&LI 1三 In 1960,DW Barritt and SC Jordan performed the first randomized trial showing the efficacy of anticoagulant therapy in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Since then,important therapeutic advances have been made in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. .Barritt,D.W.,and Jordan,S.C.:Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism.A controlled trial.Lancet,1:1309-1312,1960.[Medlinel
History of Anticoagulants In 1960, DW Barritt and SC Jordan performed the first randomized trial showing the efficacy of anticoagulant therapy in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Since then, important therapeutic advances have been made in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. •Barritt, D. W., and Jordan, S. C.: Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism. A controlled trial. Lancet, 1: 1309-1312, 1960.[Medline] Jay McLean, a second year medical student at Johns Hopkins University, discovered this wonderful drug in 1916 while performing research in the laboratory of W.H. Howell, MD
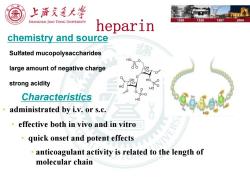
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 heparin chemistry and source Sulfated mucopolysaccharides large amount of negative charge strong acidity Characteristics administrated by i.v.or s.c. effective both in vivo and in vitro quick onset and potent effects anticoagulant activity is related to the length of molecular chain
heparin chemistry and source Sulfated mucopolysaccharides large amount of negative charge strong acidity Characteristics • administrated by i.v. or s.c. • effective both in vivo and in vitro • quick onset and potent effects • anticoagulant activity is related to the length of molecular chain
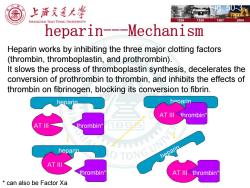
上降充通大警 SHANGHAI IIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 heparin---Mechanism Heparin works by inhibiting the three major clotting factors (thrombin,thromboplastin,and prothrombin). It slows the process of thromboplastin synthesis,decelerates the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin,and inhibits the effects of thrombin on fibrinogen,blocking its conversion to fibrin. heparin heparin AT Ill thrombin' AT III thrombin* heparin heparin AT IlI thrombin AT Ill thrombin* can also be Factor Xa
heparin AT III thrombin* AT III heparin thrombin* thrombin* heparin AT III AT III thrombin* heparin Fig. 50-3 * can also be Factor Xa heparin---Mechanism Heparin works by inhibiting the three major clotting factors (thrombin, thromboplastin, and prothrombin). It slows the process of thromboplastin synthesis, decelerates the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, and inhibits the effects of thrombin on fibrinogen, blocking its conversion to fibrin
上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Heparin Heparin is given by injection or drip into a vein (intravenously)or by injection under the skin (subcutaneously)for treatment and prevention. It is derived from porcine intestinal mucosa, standardized for anticoagulant activity. The agent also causes an increase in the 客图1 Heparin number of negatively charged ions in the Sodium Injection,S 1000 USP units/1 mL vascular wall,which helps prevent the 前mL Multiple Dose V SU6 CUTANE005峡 formation of intravascular clots
Heparin • Heparin is given by injection or drip into a vein (intravenously) or by injection under the skin (subcutaneously) for treatment and prevention. • It is derived from porcine intestinal mucosa, standardized for anticoagulant activity. • The agent also causes an increase in the number of negatively charged ions in the vascular wall, which helps prevent the formation of intravascular clots
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for Congestive Heart Failure.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心律失常药物 Anti-Arrhythmic Drug.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心绞痛药物 ANTIANGINAL DRUGS.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 8:Antihypertensive Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 5:Cholinergic Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 6 Adrenoceptor drugs(agonists and antagonists).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 4:Pharmacology of Peripheral Nervous System - Overview.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 3:Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics(2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 3:Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 2:Pharmacokinetics(2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 1:Introduction to Pharmacology、Chapter 2:Pharmacokinetics(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(八).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(七).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(六).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(五).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(四).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(三).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(二).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(一).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antipyretic-analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lipidemic modulating drugs Antiatherosclerotic agents.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Diuretics Excretion of Water and Electrolytes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Hypnotics & anxiolytics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)General anesthetics(全身麻醉药)Anti-epileptics(抗癫痫药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for psychiatric disorders.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Opioid Analgesics & drug abuse.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease & Alzheimer's disease.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Histamine &H-R blocking drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antipyretic-analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs(nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,NSAIDs).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 24:Autacoid Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 26:Drugs for Digestive Disorders.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 28:Antidiabetic Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 29:Thyroid Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)性激素类药及避孕药 Sex Hormones and Contraceptives.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Anti-bacterial drugs——general principles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)β-lactams and other antibiotics acting upon cell wall.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Aminoglycosides(氨基糖苷 类)and polymyxins 多粘菌素)Macrolides(大环内酯类)and other antibiotics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Anti-fungal drugs 抗真菌药.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antimycobacterial drugs(抗结核分枝杆菌药)and antileprotic drugs(抗麻风病药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Anti-parasitic drugs(抗寄生虫药).pdf
