上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 3:Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics(2)

Chapter 3: Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics (2) Prof.R.D.Ye 2012-09-19
Chapter 3: Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics (2) Prof. R.D. Ye 2012-09-19
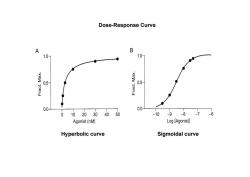
Dose-Response Curve A B 1.0- 1.0- 0.5- 0.5 0.0- 0.0- 0 102030 40 50 -10 8-76 -9 Agonist(nM) Log [Agonist] Hyperbolic curve Sigmoidal curve
Dose-Response Curve Hyperbolic curve Sigmoidal curve

Dose-response relationship The relationship between the concentration of a drug at the receptor site and the magnitude of the response is called the dose- response relationship.Depending on the purpose of the studies,this relationship can be described in terms of a graded (continuous) response or a quantal (all-or-none)response
Dose‐response relationship • The relationship between the concentration of a drug at the receptor site and the magnitude of the response is called the dose‐ response relationship. Depending on the purpose of the studies, this relationship can be described in terms of a graded (continuous) response or a quantal (all‐or‐none) response
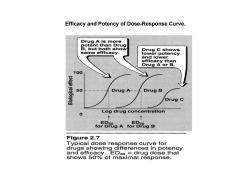
Efficacy and Potency of Dose-Response Curve. Drug A is more potent than Drug B,but both show Drug C shows same efficacy. lower potency and lower efficacy than Drug A or B. 100 50 Drug A Drug B Drug C Log drug concentration ↑ 1 foB8 O A fOr Di积gB Figure 2.7 Typical dose response curve for drugs showing differences in potency and efficacy.EDso drug dose that shows 50%of maximal response
Efficacy and Potency of Dose-Response Curve

Relationship of Affinity and Efficacy of Drug and Potency and Efficacy(maximum activity)of Dose-Response Curve. 100- 1007 A 50 B 50 Potency xeW 88 Intrinsic activity f(Efficacy and Affinity) f(Efficacy) 0 2 -1 0 -1 0 Log ([Agonist]/KA) Log ([Agonist]KA) Drug A is more potent than Drug B,and they both have the same efficacy Drug C is less efficacious;it probably has the same affinity as Drug B
Relationship of Affinity and Efficacy of Drug and Potency and Efficacy (maximum activity) of Dose-Response Curve. Drug A is more potent than Drug B, and they both have the same efficacy A B C Drug C is less efficacious; it probably has the same affinity as Drug B

K =(Equilibrium)Dissociation constant(unit:M) Kd=k2/k1 K1 K3 R+D士RD→Effect K2 Low K=high affinity difficult to dissociate,nM to pM High K=low affinity quick to dissociate,mM to uM Kd is equal to the concentration of the agonist that makes 50% receptor bound with agonist
Kd = (Equilibrium) Dissociation constant (unit:M) Low Kd = high affinity = difficult to dissociate, nM to pM High Kd = low affinity = quick to dissociate, mM to M R + D RD Effect k1 k2 k3 Kd = k2/k1 Kd is equal to the concentration of the agonist that makes 50 % receptor bound with agonist

Occupational Theory of Drug action A B 1.0- 1.0- xeW 0.5- 0.5- 0.0- 0.0- 0 102030 40 50 -10 -9 -8-7 -6 Agonist(nM) Log [Agonist] In occupational theory of drug action,fraction of receptor binding was assumed to be equal to the fraction of max effect. However,it was demonstrated later that this is not true in most cases
Occupational Theory of Drug action In occupational theory of drug action, fraction of receptor binding was assumed to be equal to the fraction of max effect. However, it was demonstrated later that this is not true in most cases
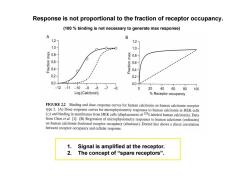
Response is not proportional to the fraction of receptor occupancy. (100%binding is not necessary to generate max response) A B 1.2- 1.2- 1.0- 1.0- 0.8- xew 0.8- 06 0.6- 0.4- 0.4 0.2- 0.2 0.0+ 0.0 -12-11-10-9 -8 -7 -6 20 40 60 80 100 Log [Calcitonin] Receptor occupancy FIGURE 2.2 Binding and dose-response curves for human calcitonin on human calcitonin receptor type 2.(A)Dose-response curves for microphysiometry responses to human calcitonin in HEK cells ()and binding in membranes from HEK cells(displacement of 125I-labeled human calcitonin).Data from Chen et al.[1].(B)Regression of microphysiometry responses to human calcitonin (ordinates) on human calcitonin fractional receptor occupancy (abscissae).Dotted line shows a direct correlation between receptor occupancy and cellular response. 1.Signal is amplified at the receptor. 2. The concept of“spare receptors
Response is not proportional to the fraction of receptor occupancy. 1. Signal is amplified at the receptor. 2. The concept of “spare receptors”. (100 % binding is not necessary to generate max response)
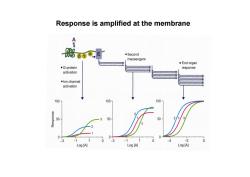
Response is amplified at the membrane d- ·Second messengers ◆End organ ●G-protein response activation ●lon channel activation 100- 100- 100 2 50 3 50- 50 2 2 0 0+ -1 1 0 -3 -1 0 -2 0 Log [A] Log [A] Log [A]
Response is amplified at the membrane

Agonist and Antagonist Occupation Activation governed governed by by affinity efficacy Dr K+1 B A AR AR* ◆RESPONSE (agonist) K1 Drug K+1 B BR ◆NO RESPONSE (antagonist) Fig.2.1 The distinction between drug binding and receptor activation.The rate constantsk,k,B and a,which apply to the binding and activation reactions,respectively are referred to in the text(p.17).Ligand A is an agonist,since it leads to activation of the receptor,whereas ligand B is an antagonist
Agonist and Antagonist
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 3:Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 2:Pharmacokinetics(2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 1:Introduction to Pharmacology、Chapter 2:Pharmacokinetics(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(八).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(七).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(六).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(五).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(四).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(三).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(二).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)药理学教学教案(一).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antipyretic-analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)antiAS drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Agents used in blood.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONIST DRUGS.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Adrenergic agonists Adrenoceptor-activating drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心绞痛药 antianginal drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心律失常药 Anti-Arrhythmic Drug.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)充血性心力衰竭治疗药物 Drugs for Congestive Heart Failure.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗肿瘤药物 Anti-neoplastic drugs.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 4:Pharmacology of Peripheral Nervous System - Overview.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 6 Adrenoceptor drugs(agonists and antagonists).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 5:Cholinergic Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 8:Antihypertensive Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心绞痛药物 ANTIANGINAL DRUGS.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心律失常药物 Anti-Arrhythmic Drug.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for Congestive Heart Failure.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)血液中使用的药剂 Agents used in blood.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lipidemic modulating drugs Antiatherosclerotic agents.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Diuretics Excretion of Water and Electrolytes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Hypnotics & anxiolytics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)General anesthetics(全身麻醉药)Anti-epileptics(抗癫痫药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for psychiatric disorders.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Opioid Analgesics & drug abuse.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease & Alzheimer's disease.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Histamine &H-R blocking drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antipyretic-analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs(nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,NSAIDs).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 24:Autacoid Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 26:Drugs for Digestive Disorders.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 28:Antidiabetic Drugs.pdf
