上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antipyretic-analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs(nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,NSAIDs)

® 上游充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 漏 Antipyretic-analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,NSAIDs) UALAO TONG UNIVEDSK MAAA
Antipyretic-analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,NSAIDs)

上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) NSAIDs have three major actions,all of which are due mainly to the inhibition of arachidonic acid cyclo-oxygenase in inflammatory cells (the COX-2 isoenzyme), and the resultant decrease in prostanoid synthesis. AJIAO TONG U
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) NSAIDs have three major actions, all of which are due mainly to the inhibition of arachidonic acid cyclo-oxygenase in inflammatory cells (the COX-2 isoenzyme), and the resultant decrease in prostanoid synthesis

上降充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Common Pharmacological Effects to be covered below Analgesic (CNS and peripheral effect)may involve non-PG related effects Antipyretic (CNS effect) Anti-inflammatory (except acetaminophen)due mainly to PG inhibition. Some shown to inhibit activation,aggregation,adhesion of neutrophils release of lysosomal enzymes Some are Uricosuric
Common Pharmacological Effects to be covered below • Analgesic (CNS and peripheral effect) may involve non-PG related effects • Antipyretic (CNS effect) • Anti-inflammatory (except acetaminophen) due mainly to PG inhibition. Some shown to inhibit activation, aggregation, adhesion of neutrophils & release of lysosomal enzymes • Some are Uricosuric

上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 COX: COX-1:constitutive enzyme:is involved in tissue homeostasis. COX-2:inducible enzyme:is responsible for the production of the prostanoid mediators of inflammation. VG JIAO TONG UNIVERSI 1三三5
• COX: • COX-1: constitutive enzyme: is involved in tissue homeostasis. • COX-2: inducible enzyme: is responsible for the production of the prostanoid mediators of inflammation
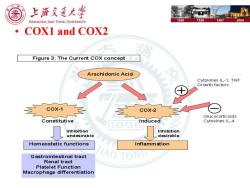
上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 COX1 and COX2 Figure 3:The Current COX concept Arachidonic Acid Cytokines IL-1,TNF Growth factors C0X-1 C0X-2 Glucocorticoids Constitutive Induced Cytokines IL-4 1三 Inhibition Inhibition undesirable desirable Homeostatic functions Inflammation Gastrointestinal tract IAO Renal tract Platelet Function Macrophage differentiation
• COX1 and COX2
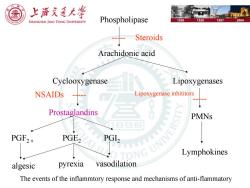
上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Phospholipase 1896 1920 1987 2006 Steroids Arachidonic acid Cyclooxygenase Lipoxygenases NSAIDs Lipoxygenase inhititors Prostaglandins PMNs PGF2a PGE2 PGL, ON Lymphokines algesic pyrexia vasodilation The events of the inflammtory response and mechanisms of anti-flammatory
Phospholipase Arachidonic acid Cyclooxygenase Lipoxygenases ----- Steroids NSAIDs ----- Prostaglandins PGF2α PGE2 PGI2 algesic pyrexia vasodilation PMNs Lymphokines ----- Lipoxygenase inhititors The events of the inflammtory response and mechanisms of anti-flammatory

上降充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Pharmacological Effects Diverse group of chemicals,but all inhibit cyclooxygenase. Resultant inhibition of PG synthesis is largely responsible for their therapeutic effects. But,inhibition of PG synthase in gastric mucosa>GIT damage(dyspepsia, gastritis)
Pharmacological Effects • Diverse group of chemicals, but all inhibit cyclooxygenase. • Resultant inhibition of PG synthesis is largely responsible for their therapeutic effects. • But, inhibition of PG synthase in gastric mucosa GIT damage (dyspepsia, gastritis)

上降充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Common Adverse Effects Platelet Dysfunction Gastritis and peptic ulceration with bleeding (inhibition of PG+other effects) Acute Renal Failure in susceptible o Sodium+water retention and edema Increase in risk of cardiovascular events Hypersensitivity(not immunologic but due to PG inhibition) ·Headache,dizziness
Common Adverse Effects • Platelet Dysfunction • Gastritis and peptic ulceration with bleeding (inhibition of PG + other effects) • Acute Renal Failure in susceptible • Sodium+ water retention and edema • Increase in risk of cardiovascular events • Hypersensitivity (not immunologic but due to PG inhibition) • Headache ,dizziness

上降充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) An anti-inflammatory action: (1)The decrease in vasodilator prostaglandinds (PGE2,PGI,)means less vasodilatation and, indirectly,less edema (2)The inhibition of activity of adhesion molecule. (3)Accumulation of inflammatory cells is also reduced
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) • An anti-inflammatory action: (1) The decrease in vasodilator prostaglandinds (PGE2 , PGI2 ) means less vasodilatation and, indirectly, less edema. (2) The inhibition of activity of adhesion molecule. (3) Accumulation of inflammatory cells is also reduced

上降充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1896 1920 1987 2006 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) .An analgesic effect:decreased prostaglandin generation means less sensitisation of nociceptive nerve endings to inflammatory mediators such as bradykinin and 5-hydroxytryptamine Relief of headache is probably due to decreased prostaglandin-mediated vasodilatation
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) • An analgesic effect: decreased prostaglandin generation means less sensitisation of nociceptive nerve endings to inflammatory mediators such as bradykinin and 5-hydroxytryptamine. • Relief of headache is probably due to decreased prostaglandin-mediated vasodilatation
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Histamine &H-R blocking drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease & Alzheimer's disease.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Opioid Analgesics & drug abuse.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for psychiatric disorders.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)General anesthetics(全身麻醉药)Anti-epileptics(抗癫痫药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Hypnotics & anxiolytics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Diuretics Excretion of Water and Electrolytes.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Lipidemic modulating drugs Antiatherosclerotic agents.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)血液中使用的药剂 Agents used in blood.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Drugs for Congestive Heart Failure.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心律失常药物 Anti-Arrhythmic Drug.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)抗心绞痛药物 ANTIANGINAL DRUGS.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 8:Antihypertensive Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 5:Cholinergic Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 6 Adrenoceptor drugs(agonists and antagonists).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 4:Pharmacology of Peripheral Nervous System - Overview.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 3:Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics(2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 3:Receptor Theory and Pharmacodynamics(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 2:Pharmacokinetics(2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 1:Introduction to Pharmacology、Chapter 2:Pharmacokinetics(1).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 24:Autacoid Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 26:Drugs for Digestive Disorders.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 28:Antidiabetic Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 29:Thyroid Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)性激素类药及避孕药 Sex Hormones and Contraceptives.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Anti-bacterial drugs——general principles.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)β-lactams and other antibiotics acting upon cell wall.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Aminoglycosides(氨基糖苷 类)and polymyxins 多粘菌素)Macrolides(大环内酯类)and other antibiotics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Anti-fungal drugs 抗真菌药.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antimycobacterial drugs(抗结核分枝杆菌药)and antileprotic drugs(抗麻风病药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Anti-parasitic drugs(抗寄生虫药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Antiviral drugs(抗病毒药).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Cancer Chemotherapy 肿瘤化疗.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 4 Overview of Peripheral Nervous System.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学 Pharmacology》课程教学资源(讲义课件)Chapter 5 Cholinergic Drugs.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第八章 抗高血压药.doc
- 上海交通大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第十章 抗心力衰竭药、第十一章 抗心律失常药.docx
- 上海交通大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)中枢概论麻醉 Drugs that act in the central nervous system(殷明).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)镇静抗癫痫 Sedative-hypnotics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)抗精神失常药 Drugs for psychiatric disorders.ppt
