电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite)

Lecture 6 196 Anode material for LIBs: Graphite Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04
Anode material for LIBs: Graphite Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04 Lecture 6

Content /986 Overview of anode materials Introduction of graphite 。 Chemistry of graphite Molecular structure and Li insertion Synthesis and modification methods One literature example 2
2 Content • Overview of anode materials • Introduction of graphite • Chemistry of graphite • Molecular structure and Li insertion • Synthesis and modification methods • One literature example

Overview /986 。 General requirement React with Li+at a low potential vs.Li/Lit With a high Lit storage capacity Category:storage mechanism Insertion/deinsertion:graphite,TiO2,etc. Alloy/dealloy:Sn,Tin,etc. Replacement reaction:Fe2O3,Co3O4,etc. 3
3 Overview • General requirement React with Li+ at a low potential vs. Li/Li+ With a high Li+ storage capacity • Category: storage mechanism • Insertion/deinsertion: graphite, TiO2 , etc. • Alloy/dealloy: Sn, Tin, etc. • Replacement reaction: Fe2O3 , Co3O4 , etc

Graphite /98 Crystalline allotrope of carbon,most stable form Characteristics:1.thermally and chemically stable 2.thermally and electrically conductive 3.lubricating Origin:graphite mines in Heilongjiang,Shandong Preparation:purification of graphite mine: >1)chemical:NaOH reaction neutralize using HCI >2)physical:annealing at high T without oxygen https://b2b.hc360.com/viewPics/s https://b2b.hc360.com/viewPics/s http://www.99114.com/pi upplyself_pics/80332485791.html upplyself_pics/80332485791.html cture/598650.html 4
http://www.99114.com/pi cture/598650.html https://b2b.hc360.com/viewPics/s upplyself_pics/80332485791.html https://b2b.hc360.com/viewPics/s upplyself_pics/80332485791.html 4 Graphite • Crystalline allotrope of carbon, most stable form • Characteristics: 1. thermally and chemically stable 2. thermally and electrically conductive 3. lubricating • Origin:graphite mines in Heilongjiang, Shandong • Preparation:purification of graphite mine: 1) chemical:NaOH reaction → neutralize using HCl 2) physical:annealing at high T without oxygen
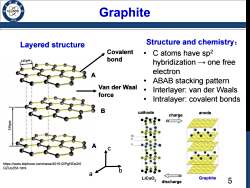
Graphite Layered structure Structure and chemistry: Covalent C atoms have sp2 42pm bond hybridization-one free electron ABAB stacking pattern Van der Waal 。 Interlayer:van der Waals force Intralayer:covalent bonds B cathode charge anode https://www.leiphone.com/news/201512/Pgf3Ds2r0 QZUoZ6X.html a LiCoO2 Graphite discharge 5
5 • C atoms have sp2 hybridization → one free electron • ABAB stacking pattern • Interlayer: van der Waals • Intralayer: covalent bonds A B A https://www.leiphone.com/news/201512/Pgf3Ds2r0 QZUoZ6X.html Layered structure Covalent bond Van der Waal force Structure and chemistry: charge discharge cathode LiCoO2 Graphite anode Graphite a b c

Graphite anode /98 The electrochemical reaction: C+1/6Lit+1/6e←→1/6LiC6 Reversible process (insertion/deinsertion) >Lit ions insert into(charge)and deinsert from (discharge) the interlayer space of graphite >Only the ions stored in the interlayer space can reversibly take part in the charge/discharge process 6
6 Graphite anode • The electrochemical reaction: C + 1/6Li+ + 1/6e- ↔ 1/6LiC6 • Reversible process (insertion/deinsertion) Li+ ions insert into (charge) and deinsert from (discharge) the interlayer space of graphite Only the ions stored in the interlayer space can reversibly take part in the charge/discharge process

Theoretical capacity of graphite /98 The electrochemical reaction: C+1/6Lit+1/6e←→1/6LiC6 >Molecular weight of C is 12 g/mol >So,the theoretical capacity is: 96500÷12÷3.6×1/6=372.3mAh/g 7
7 Theoretical capacity of graphite • The electrochemical reaction: C + 1/6Li+ + 1/6e- ↔ 1/6LiC6 Molecular weight of C is 12 g/mol So, the theoretical capacity is: 96500÷12÷3.6×1/6 = 372.3 mA·h/g

Properties of graphite 196 Advantages Disadvantage Low cost Working voltage too low + Electrochemically Poor rate stable performance ·Lit+6C+eLiC6 Solution: Rational structure design 06 x in LigCo 8
8 Properties of graphite Low cost Electrochemically stable Advantages Disadvantage Working voltage too low Poor rate performance Solution: Rational structure design
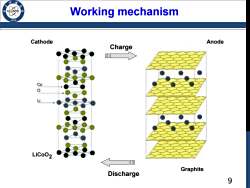
Working mechanism /986 Cathode Anode Charge LiCoO2 00 Graphite Discharge 9
9 Charge Discharge Cathode Anode Graphite LiCoO2 Working mechanism

A case study nature ARTICLES energy PUBLISHED:4 JULY 2016|ARTICLE NUMBER:16097 DOI:10.1038/NENERGY.2016.97 Magnetically aligned graphite electrodes for high-rate performance Li-ion batteries Juliette Billaud1,Florian Bouville2,Tommaso Magrini2,Claire Villevieille1*and Andre R.Studart2* As lithium-ion batteries become ubiquitous,the energy storage market is striving for better performance,longer lifetime and better safety of the devices.This race for performance is often focused on the search for new materials,whereas less effort has been dedicated to the electrode engineering.Enhancing the power density by increasing the amount of active material remains impractical since it impinges the transport of ions across the electrode during the charging and discharging processes.Here,we show that the electrochemical performance of a battery containing a thick (about 200 um),highly loaded (about 10 mg cm-2) graphite electrode can be remarkably enhanced by fabricating anodes with an out-of-plane aligned architecture using a low external magnetic field.The lower tortuosity resulting from such a simple and scalable magnetic alignment approach leads to a specific charge up to three times higher than that of non-architectured electrodes at a rate of 1C. 10
10 A case study
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Unit Commitment in Power System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Power System Economic Dispatch.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction of the course(黄琦).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 电力系统稳定性分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 电力系统不对称故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 电力系统不对称运行分析方法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
- 《电力电子技术 Power Electronics》:电能质量指标及其算法的研究.pdf
- 深圳市标准化指导性技术文件:分布式光伏发电系统并网接入技术规范(SZDB/Z 227 - 2017)Technical specification for distributed photovoltaic generation system Grid-connected.pdf
- 智能电网:改善低压农网电压质量的分布式光伏——储能系统优化配置方法.pdf
- 国投甘肃小三峡发电有限公司:浅析水电厂AVC控制策略.pdf
- 中国电机工程学会:核能发电专业发展报告(PPT宣讲稿,2019年11月).pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第一章 绪论 1.1 传热学的研究内容及其在科学技术和工程中的应用 1.2 热能传递的三种基本方式.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.1 导热基本定律-傅里叶定律.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二讲 第一章 绪论 1.3 传热过程和传热系数 1.4 传热学的发展简史和研究方法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.2 导热问题的数学描写 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过平壁的导热.pdf
