电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell

Physical power sources Section Ill Fundamentals of Solar Cell
Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell Physical power sources
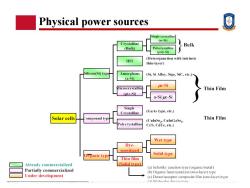
Physical power sources Single crystalline (se-Si) Crystalline Bulk (Bulk) Polycrystalline (poly-Si) (Heterojunction with intrinsic HIT thin-layer) Silicon(Si)type Amorphous (Si,Si Alloy,Sige,SiC,etc.) (a-Si) ue-Si licrocrystallin Thin Film (uc-Si) a-Siluc-Si Single Crystalline (GaAs type,ete.) Solar cells ompound typ Thin Film (CulnSe2 CulnGaSez Polycrystalline CdS,CdTe,ete.) Wet type Dye- sensitized Organic type Solid type Thin film Already commercialized (Solid type) (a)Schottky junction type (organic/metal) Partially commercialized (b)Organic heterojunction (two-layer)type Under development (c)Donor/acceptor composite film (one-layer)type (d)MAolecular davice tune
Physical power sources

Solar cell-monocrystal silicon Energy gap:1.12eV CE:19% Covalent bond Regular tetrahedron Diamond-structure
Solar cell- monocrystal silicon Energy gap: 1.12eV CE: 19% Covalent bond Regular tetrahedron Diamond-structure

Polycrystalline silicon solar cell CE:18% The manufacturing process of polycrystalline silicon solar cells is similar to that of single crystal silicon solar cells.Its photoelectric conversion efficiency is about 12%,which is slightly lower than that of single crystal silicon solar cells.Substantial development.With the improvement of technology,the conversion efficiency of polysilicon can now reach about 18%
Polycrystalline silicon solar cell CE: 18% The manufacturing process of polycrystalline silicon solar cells is similar to that of single crystal silicon solar cells. Its photoelectric conversion efficiency is about 12%, which is slightly lower than that of single crystal silicon solar cells. Substantial development. With the improvement of technology, the conversion efficiency of polysilicon can now reach about 18%

Amorphous silicon solar cells CE:10% (c) Amorphous silicon solar cell is a new type of thin film solar cell that appeared in 1976.It is completely different from the manufacturing method of single crystal silicon and polycrystalline silicon solar cells.The process is greatly simplified. The advantage is that it can generate electricity in low light conditions.However, the main problem of amorphous silicon solar cells is that the photoelectric conversion efficiency is low.At present,the international advanced level is about 10%,and it is not stable enough.As time goes by,its conversion efficiency decays
Amorphous silicon solar cells CE:10% Amorphous silicon solar cell is a new type of thin film solar cell that appeared in 1976. It is completely different from the manufacturing method of single crystal silicon and polycrystalline silicon solar cells. The process is greatly simplified. The advantage is that it can generate electricity in low light conditions. However, the main problem of amorphous silicon solar cells is that the photoelectric conversion efficiency is low. At present, the international advanced level is about 10%, and it is not stable enough. As time goes by, its conversion efficiency decays

Diversity of solar cell Classified by structure: Classified by purpose: Homojunction solar cell Space solar cell Heterojunction solar cell Ground solar battery Schottky junction solar cell Light sensor Composite junction solar cell Liquid junction solar cells Classified by work method: Flat solar battery Concentrating solar cell
Classified by structure: Homojunction solar cell Heterojunction solar cell Schottky junction solar cell Composite junction solar cell Liquid junction solar cells Diversity of solar cell Classified by purpose: Space solar cell Ground solar battery Light sensor Classified by work method: Flat solar battery Concentrating solar cell
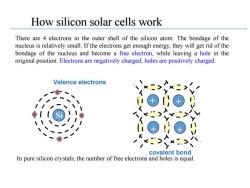
How silicon solar cells work There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of the silicon atom.The bondage of the nucleus is relatively small.If the electrons get enough energy,they will get rid of the bondage of the nucleus and become a free electron,while leaving a hole in the original position.Electrons are negatively charged;holes are positively charged. Valence electrons covalent bond In pure silicon crystals,the number of free electrons and holes is equal
How silicon solar cells work There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of the silicon atom. The bondage of the nucleus is relatively small. If the electrons get enough energy, they will get rid of the bondage of the nucleus and become a free electron, while leaving a hole in the original position. Electrons are negatively charged; holes are positively charged. In pure silicon crystals, the number of free electrons and holes is equal. Si + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 covalent bond Valence electrons
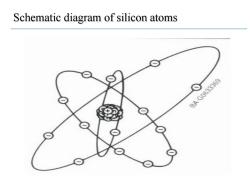
Schematic diagram of silicon atoms BAC0633369
Schematic diagram of silicon atoms
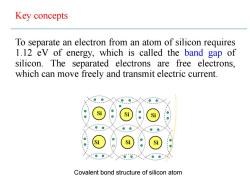
Key concepts To separate an electron from an atom of silicon requires 1.12 ev of energy,which is called the band gap of silicon.The separated electrons are free electrons. which can move freely and transmit electric current. Si Si Si Si Si Si Covalent bond structure of silicon atom
Key concepts To separate an electron from an atom of silicon requires 1.12 eV of energy, which is called the band gap of silicon. The separated electrons are free electrons, which can move freely and transmit electric current. Covalent bond structure of silicon atom
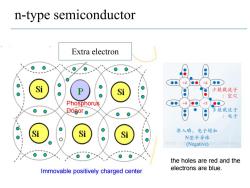
n-type semiconductor Extra electron +4 +4 Si Si 少数载流子 :空穴 Phosphorus DoBor o 多数载流子 :电子 Si Si Si 渗入磷,电子增加 N型半导体 http://b(Negative)net/cyousui the holes are red and the Immovable positively charged center electrons are blue
n-type semiconductor Extra electron Phosphorus Donor the holes are red and the electrons are blue. Immovable positively charged center
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Unit Commitment in Power System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Power System Economic Dispatch.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
- 《电力电子技术 Power Electronics》:电能质量指标及其算法的研究.pdf
- 深圳市标准化指导性技术文件:分布式光伏发电系统并网接入技术规范(SZDB/Z 227 - 2017)Technical specification for distributed photovoltaic generation system Grid-connected.pdf
- 智能电网:改善低压农网电压质量的分布式光伏——储能系统优化配置方法.pdf
- 国投甘肃小三峡发电有限公司:浅析水电厂AVC控制策略.pdf
- 中国电机工程学会:核能发电专业发展报告(PPT宣讲稿,2019年11月).pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第一章 绪论 1.1 传热学的研究内容及其在科学技术和工程中的应用 1.2 热能传递的三种基本方式.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.1 导热基本定律-傅里叶定律.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二讲 第一章 绪论 1.3 传热过程和传热系数 1.4 传热学的发展简史和研究方法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.2 导热问题的数学描写 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过平壁的导热.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过圆筒壁的导热 2.4 通过肋片的导热.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.1 非稳态导热的基本概念.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.2 零维问题的分析法-集中参数法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.1 导热问题数值求解的基本思想 4.2 内节点离散方程的建立方法.pdf
