电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries

Lecture 12 /986 Safety of Li-ion Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04
Safety of Li-ion Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04 Lecture 12

Content /986 ·Why safety? Origins of safety concerns Thermal runaway process:3 stages Materials with improved battery safety Materials to solve problems in 3 stages 2
Content • Why safety? • Origins of safety concerns • Thermal runaway process: 3 stages • Materials with improved battery safety • Materials to solve problems in 3 stages 2

Why battery safety? 1956 Samsung Note 7 incidents PA F5 @层车 3
Why battery safety? Samsung Note 7 incidents 3

How to catch fire? TORCH The Fire Triangle O2:to sustain the fire OXYGEN IGNITION Temperature/heat:Reaching the ignition point of the fuel FUEL Flammable substance:the thing to catch fire Where do these things come from in a Li-ion battery? 4
How to catch fire? The Fire Triangle O2: to sustain the fire Temperature/heat: Reaching the ignition point of the fuel Flammable substance: the thing to catch fire Where do these things come from in a Li-ion battery? 4

Origins of safety concerns SCIENCE ADVANCES REVIEW MATERIALS SCIENCE Materials for lithium-ion battery safety Kai Liu',Yayuan Liu',Dingchang Lin',Allen Pei,Yi Cui2* Samsung Note 7 after the battery The Fire Triangle in a caught fire Li-ion battery O2:To sustain the fire Temperature/heat: Gas release from side Reaching the ignition reactions during charge/discharge OXYGEN point of the fuel IGNITION Thermal runaway due to heat released from side reactions FUEL Fuel:The thing to catch fire The organic liquid electrolyte is combustible 5
Origins of safety concerns Fuel: The thing to catch fire The organic liquid electrolyte is combustible O2: To sustain the fire Gas release from side reactions during charge/discharge Temperature/heat: Reaching the ignition point of the fuel Thermal runaway due to heat released from side reactions The Fire Triangle in a Li-ion battery Samsung Note 7 after the battery caught fire 5
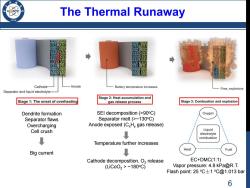
The Thermal Runaway /986 Cathode- Anode Battery temperature increases Fires,explosions Separator and liquid electrolyte Stage 2:Heat accumulation and Stage 1:The onset of overheating gas release process Stage 3:Combustion and explosion Dendrite formation SEI decomposition (>90C) Oxygen Separator flaws Separator melt(>~130C) Overcharging Anode exposed(C.H gas release) Cell crush Liquid ↓ electrolyte combustion Temperature further increases ↓ Heat Fuel Big current Cathode decomposition,O2 release EC+DMC(1:1) (LiC002>~180C) Vapor pressure:4.8 kPa@R.T. Flash point::25℃±1C@1.013bar 6
The Thermal Runaway Dendrite formation Separator flaws Overcharging Cell crush Big current SEI decomposition (>90oC) Separator melt (>~130oC) Anode exposed (CxHy gas release) Temperature further increases Cathode decomposition, O2 release (LiCoO2 > ~180oC) EC+DMC(1:1) Vapor pressure: 4.8 kPa@R.T. Flash point: 25 oC±1 oC@1.013 bar 6

The Thermal Runaway 1956 Accelerated rate calorimetry: to simulate the environment inside the battery Stage 1:onset 20 Thermal runaway of overheating 15 Stage 3:Combustion 10 SEI decomposition, and explosion separator melts,etc. 5 0 MMG -5 100 150 200 250 Stage 2:heat Temperature (C) Fig.2.Typical self-heating rate tests by ARC during thermal ramp test of LIB.The accumulation and anode is mesocarbon microbead graphite.The cathode is LiNio.sCoo.osAlo.osO2. gas release The electrolyte is 1.2 M LiPF in EC/PC/DMC.A Celgard 2325 trilayer separator was used.Adapted with permission from Electrochemical Society Inc. 7
The Thermal Runaway Accelerated rate calorimetry: to simulate the environment inside the battery Stage 1: onset of overheating Stage 3: Combustion and explosion Stage 2: heat accumulation and gas release 7
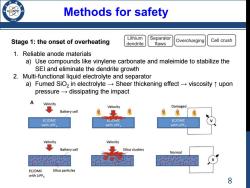
Methods for safety 795 Lithium Stage 1:the onset of overheating Separator Overcharging Cell crush dendrite flaws 1.Reliable anode materials a)Use compounds like vinylene carbonate and maleimide to stabilize the SEI and eliminate the dendrite growth 2.Multi-functional liquid electrolyte and separator a)Fumed SiO,in electrolyte-Sheer thickening effect-viscosity t upon pressure-dissipating the impact A Velocity Velocity Damaged Battery cell 象 EC/DMC EL/DMC EC/DMC with LiPF with LiPFs with LiPFe Velocity Velocity Battery cell Silica clusters Normal EC/DMC Silica particles with LiPFs 8
Methods for safety Stage 1: the onset of overheating 1. Reliable anode materials a) Use compounds like vinylene carbonate and maleimide to stabilize the SEI and eliminate the dendrite growth 2. Multi-functional liquid electrolyte and separator a) Fumed SiO2 in electrolyte → Sheer thickening effect → viscosity ↑ upon pressure → dissipating the impact 8

Methods for safety 9 Stage 1:the onset of overheating 2.Multi-functional liquid electrolyte and separator b)Trilayered separator:polymer-metal/SiO2-polymer Conducting layer parator 30 Separator 。=SiO,nanoparticle Lithiated SiO,nanoparticle Dendrite growth Dendrite growth Separator "Polymer-SiO,-polymer SiO,nanoparticles trilayer'”→SiO2 consumes Separator dendrite-improved safety 20m 600 Internal short circuit Dendrite detected (battery still safe) (possible explosion hazard) 400 Bare separator Sandwiched separator "Polymer-metal-polymer trilayer"dendrite 200 growth touches the middle metal layer 20 40 60 80100120 140 huge voltage drop-fail-safe triggered Time(hours) 9
Methods for safety Stage 1: the onset of overheating 2. Multi-functional liquid electrolyte and separator b) Trilayered separator: polymer-metal/SiO2-polymer “Polymer-metal-polymer trilayer” → dendrite growth touches the middle metal layer → huge voltage drop → fail-safe triggered “Polymer-SiO2-polymer trilayer” → SiO2 consumes dendrite → improved safety 9
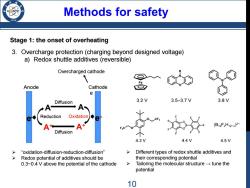
Methods for safety Stage 1:the onset of overheating 3.( Overcharge protection(charging beyond designed voltage) a)Redox shuttle additives (reversible) Overcharged cathode e Anode Cathode e Diffusion 3.2V 3.5-3.7V 3.8V ◆A A Reduction Oxidation◆e A+ A+ (B12FxH12-x)2- Diffusion 4.3V 4.4V 4.5V >"oxidation-diffusion-reduction-diffusion" Different types of redox shuttle additives and Redox potential of additives should be their corresponding potential 0.3~0.4 V above the potential of the cathode > Tailoring the molecular structure-tune the potential 10
Methods for safety Stage 1: the onset of overheating 3. Overcharge protection (charging beyond designed voltage) a) Redox shuttle additives (reversible) “oxidation-diffusion-reduction-diffusion” Redox potential of additives should be 0.3~0.4 V above the potential of the cathode Overcharged cathode Different types of redox shuttle additives and their corresponding potential Tailoring the molecular structure → tune the potential 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
- 《电力电子技术 Power Electronics》:电能质量指标及其算法的研究.pdf
- 深圳市标准化指导性技术文件:分布式光伏发电系统并网接入技术规范(SZDB/Z 227 - 2017)Technical specification for distributed photovoltaic generation system Grid-connected.pdf
- 智能电网:改善低压农网电压质量的分布式光伏——储能系统优化配置方法.pdf
- 国投甘肃小三峡发电有限公司:浅析水电厂AVC控制策略.pdf
- 中国电机工程学会:核能发电专业发展报告(PPT宣讲稿,2019年11月).pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第一章 绪论 1.1 传热学的研究内容及其在科学技术和工程中的应用 1.2 热能传递的三种基本方式.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.1 导热基本定律-傅里叶定律.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二讲 第一章 绪论 1.3 传热过程和传热系数 1.4 传热学的发展简史和研究方法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.2 导热问题的数学描写 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过平壁的导热.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过圆筒壁的导热 2.4 通过肋片的导热.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.1 非稳态导热的基本概念.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.2 零维问题的分析法-集中参数法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.1 导热问题数值求解的基本思想 4.2 内节点离散方程的建立方法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.3 典型一维非稳态导热的分析解.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.3 边界节点离散方程的建立及代数方程的求解.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.4 非稳态导热问题的数值解法.pdf
