电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM)

Lecture 5 1956 Cathode material for LIBs: Li-Mn-O and NCM Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04
Cathode material for LIBs: Li-Mn-O and NCM Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04 Lecture 5

Content /986 ·Introduction 00 Chemistry Molecular structure and Li diffusion Advantages and disadvantages 2
Content • Introduction • Chemistry • Molecular structure and Li diffusion • Advantages and disadvantages 2
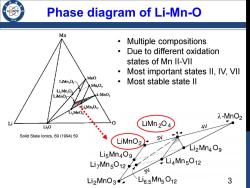
Phase diagram of Li-Mn-O /986 Mn Multiple compositions Due to different oxidation states of Mn Il-VII Most important states Il,IV,VIl MnO LiMngO Most stable state ll MnO LizMn,O LiMnO2☑ λ-MnO2 LiMn,On2 λ-MnO2 Li,O LiMn204 4V Solid State lonics,69(1994)59 LiMnO2 3V Li2Mn4O9 LizMns1 LiMngO12 LisMn409 3V Li2MnO3∠天Li6.5Mn5O12 3
Phase diagram of Li-Mn-O • Multiple compositions • Due to different oxidation states of Mn II-VII • Most important states II, IV, VII • Most stable state II Solid State Ionics, 69 (1994) 59 3

Types of Li-Mn-O /986 ·LiMn2O4 。Spinel structure LiMnO2 Layered structure,like LiCoO, 4
Types of Li-Mn-O • LiMn2O4 • Spinel structure • LiMnO2 • Layered structure, like LiCoO2 4
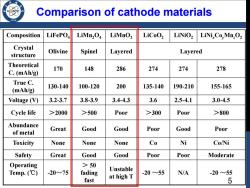
Comparison of cathode materials Composition LiFePOa LiMn2O LiMnO2 LiCoO2 LiNiOz LiNiCo,Mn,O2 Crystal Olivine Spinel Layered structure Layered Theoretical C.(mAh/g) 170 148 286 274 274 278 True C. 130-140 100-120 200 135-140 190-210 155-165 (mAh/g) Voltage(V) 3.2-3.7 3.8-3.9 3.4-4.3 3.6 2.5-4.1 3.0-4.5 Cycle life >2000 >500 Poor >300 Poor >800 Abundance Great Good Good Poor Good Poor of metal Toxicity None None None Co Ni Co/Ni Safety Great Good Good Poor Poor Moderate Operating >50 Temp.(℃) -20~75 fading Unstable -20~55 N/A -20~55 fast at high T 5
Comparison of cathode materials Composition LiFePO4 LiMn2O4 LiMnO2 LiCoO2 LiNiO2 LiNixCoyMnzO2 Crystal structure Olivine Spinel Layered Layered Theoretical C. (mAh/g) 170 148 286 274 274 278 True C. (mAh/g) 130-140 100-120 200 135-140 190-210 155-165 Voltage (V) 3.2-3.7 3.8-3.9 3.4-4.3 3.6 2.5-4.1 3.0-4.5 Cycle life >2000 >500 Poor >300 Poor >800 Abundance of metal Great Good Good Poor Good Poor Toxicity None None None Co Ni Co/Ni Safety Great Good Good Poor Poor Moderate Operating Temp. (℃) -20~75 > 50 fading fast Unstable at high T -20 ~55 N/A -20 ~55 5

4 1956 Layered LiMnO2 6
Layered LiMnO2 6

Layered LiMnO2 /986 Synthesis of layered LiMnO,as an electrode for rechargeable lithium batteries A.Robert Armstrong Peter G.Bruce School of Chemistry,University of St Andrews,North Haugh, St Andrews,Fife KY16 9ST,UK Peter G.Bruce Nature volume381,pages499-500(06 June 1996) Here we report the synthesis and electrochemical performance of a new material,layered LiMnO2,which is structurally analogous to LiCoO2.The charge capacity of LiMnO2(~270 mAhg-1)compares well with that of both LiCoO,and LiMn2O4,and preliminary results indicate good stability over repeated charge-discharge cycles. 7
Layered LiMnO2 Nature volume381, pages499–500 (06 June 1996) Here we report the synthesis and electrochemical performance of a new material, layered LiMnO2, which is structurally analogous to LiCoO2. The charge capacity of LiMnO2 (∼270 mAhg–1) compares well with that of both LiCoO2 and LiMn2O4, and preliminary results indicate good stability over repeated charge–discharge cycles. Peter G. Bruce 7
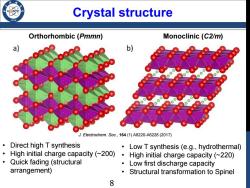
Crystal structure Orthorhombic (Pmmn) Monoclinic (C2/m) a b) J.Electrochem.Soc.,164(1)A6220-A6228(2017) Direct high T synthesis Low T synthesis (e.g.,hydrothermal) High initial charge capacity (~200) High initial charge capacity(~220) Quick fading (structural Low first discharge capacity arrangement) Structural transformation to Spinel 8
Crystal structure Orthorhombic (Pmmn) Monoclinic (C2/m) • Direct high T synthesis • High initial charge capacity (~200) • Quick fading (structural arrangement) • Low T synthesis (e.g., hydrothermal) • High initial charge capacity (~220) • Low first discharge capacity • Structural transformation to Spinel J. Electrochem. Soc., 164 (1) A6220-A6228 (2017) 8

Theoretical capacity /98 At the cathode: LiMnO2(Mn3+)←→MnO2(Mn4+)+Lit+e Molecular weight of: Li:6.94 g/mol,Mn:54.94 g/mol,O:16 g/mol So,molecular weight of LiMnO2: 6.94+54.94+16×2=93.88g/mol So,the theoretical capacity is: 96500÷93.88÷3.6=285.53mAh/g 9
Theoretical capacity At the cathode: LiMnO2 (Mn3+) ↔ MnO2 (Mn4+)+ Li+ + e─ Molecular weight of: Li: 6.94 g/mol, Mn: 54.94 g/mol, O: 16 g/mol So, molecular weight of LiMnO2: 6.94 + 54.94 + 16 × 2 = 93.88 g/mol So, the theoretical capacity is: 96500÷93.88÷3.6 = 285.53 mA·h/g 9

Drawbacks of LiMnO2 Structural instability:transform from layered to spinel structure upon Li extraction > Vitins and West (J Electrochem.Soc.,Vol.144,No.8, 1997): Mn with high movability-rearrangement of structure; Very low reversible capacity >Jahn-Teller (J-T)distortion: The geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations.(Wikipedia) ·Mn3+isJ-T active 10
Drawbacks of LiMnO2 Vitins and West (J Electrochem. Soc., Vol. 144, No. 8, 1997): • Mn with high movability → rearrangement of structure; • Very low reversible capacity Jahn-Teller (J-T) distortion: • The geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. (Wikipedia) • Mn3+ is J-T active Structural instability: transform from layered to spinel structure upon Li extraction 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Unit Commitment in Power System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Power System Economic Dispatch.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction of the course(黄琦).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 电力系统稳定性分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 电力系统不对称故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 电力系统不对称运行分析方法.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 电力系统三相短路故障分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
- 《电力电子技术 Power Electronics》:电能质量指标及其算法的研究.pdf
- 深圳市标准化指导性技术文件:分布式光伏发电系统并网接入技术规范(SZDB/Z 227 - 2017)Technical specification for distributed photovoltaic generation system Grid-connected.pdf
- 智能电网:改善低压农网电压质量的分布式光伏——储能系统优化配置方法.pdf
- 国投甘肃小三峡发电有限公司:浅析水电厂AVC控制策略.pdf
- 中国电机工程学会:核能发电专业发展报告(PPT宣讲稿,2019年11月).pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第一章 绪论 1.1 传热学的研究内容及其在科学技术和工程中的应用 1.2 热能传递的三种基本方式.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.1 导热基本定律-傅里叶定律.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二讲 第一章 绪论 1.3 传热过程和传热系数 1.4 传热学的发展简史和研究方法.pdf
