电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO)

Lecture 3 196 Lithium-ion Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04
Lithium-ion Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04 Lecture 3

Content /986 Lithium-metal batteries ·Safety problem Lithium-ion batteries Components,working mechanism ● Cathode materials:LiFePO4,Li-Mn-O 2
2 Content • Lithium-metal batteries • Safety problem • Lithium-ion batteries • Components, working mechanism • Cathode materials: LiFePO4 , Li-Mn-O

2019 Nobel Prize Chemistry THE NOBEL PRIZE Goodenough:discovery of LiCoO,and IN CHEMISTRY 2019 LiFePO,which become the cathode materials in the commercial LIBs now. Whittingham:discovery of layered TiS2 to reversibly intercalate lithium ions,and the concept of rechargeable Li battery. Yoshino:built the first rechargeable LIB John B. M.Stanley Akira by using LiCoO2 cathode and a graphite Goodenough Whittingham Yoshino anode. "for the development of lithium-ion batteries" THE ROYAL SWEDISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES 3
3 2019 Nobel Prize Chemistry Goodenough: discovery of LiCoO2 and LiFePO4 , which become the cathode materials in the commercial LIBs now. Whittingham: discovery of layered TiS2 to reversibly intercalate lithium ions, and the concept of rechargeable Li battery. Yoshino: built the first rechargeable LIB by using LiCoO2 cathode and a graphite anode

196 4
4

Types of Li batteries 196 Li Batteries Rechargeable batteries Primary batteries Li metal Liion Li/FeS2 Li/MnO2 Li/SOCl2 5
5 Li Batteries Li/FeS2 Li/MnO2 Li/SOCl Li metal Li ion 2 Types of Li batteries Rechargeable batteries Primary batteries

例 196 Li metal batteries 6
6 Li metal batteries
Advantage of Li /986 -Atomic weight: 18 H 6.94 g/mol He Heliom 16016- 13 14 15 16 17 403 Lightest alkali metal 9 10 Li (0.54g1/cm3) B C N 0 Ne u Cartcn Ncen 64941 012 1011 12511 14657 15 1R日 20.10 11 2 Silvery,metallic solid 14 15 16 18 Na Si Ar Theoretical capacity: Ah地m sfcca Salfar 24305 2692 3974 35453 3游94B 19 20 22 23 3.86 Ah/g 31 32 33 34 35 36 Ca Sc Ga Ge AS Se Br Kr Fetastiam Ttaniom ,线边n国国 Arserk Seknian 4007日 44956 50 72631 74922 78971 79904 37 38 39 40 41 E。=-3.04VsHE 49 50 51 52 53 Rb Sr Zr n Rab nt达ntra Rhodiam Cadnitm Sb Te Xe ttfmom 900 25% 9907 101.67 1028% 10642 1078e 112.410 1171 1217 1276 12690 1224 55 57-71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 92 83 84 85 86 Cs Ba Hf W Re r Pt Au Hg c信u用 Oimlem risies fna间 M元 盟 Bi At Rn 129 13732 178.49 18u20 190.23 192217 15 1696 200592 2043☒ 2072 2e980 289 2099 2218 87 89-103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 Ra Rf Db Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn Uut Lv Uus Uuo tt与线m htr 2220 226025 261 26 B9 57 58 60 61 62 63 65 66 67 68 69 70 La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd D Ho Er Tm Yb Lu a司fHn Terbiam Holnim Tbein T月a3un 和图等而 1905 140.116 140.90 1442日 144913 15036 151964 15725 1925 160 164930 16129 16934 1725g 1749%67 89 93 95 96 98 100 101 102 103 AC. Th a Np Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Tortn a忙aem nengio Crin Beriellum Prlum 4otl柱与 2028 26 229 244064 243661 24070 2070 281 2511 lkal Metal Akalat山 Batie Metal emimeta国 7
7 - Atomic weight: 6.94 g/mol - Lightest alkali metal (0.54 g/cm3 ) - Silvery, metallic solid - Theoretical capacity: 3.86 Ah/g - Eo = -3.04 VSHE Advantage of Li

Calculation of theoretical capacity Li←→Lit+e- The full lithium intercalation/deintercalation in 1 mol of electrode material leads to the transfer of 96500 C of charge (96500 C/mol is the Faraday constant) >From the unit of mA.h/g,we know that the theoretical discharge capacity of each gram of electrode material: 1mAh=1×(10-3)Amp×360s=3.6C >Using Lithium as an example:The molecular weight of lithium is 6.94 g/mol,so its theoretical capacity is: 96500÷6.94÷3.6=3862.5m4h/g 09 8
8 Calculation of theoretical capacity The full lithium intercalation/deintercalation in 1 mol of electrode material leads to the transfer of 96500 C of charge (96500 C/mol is the Faraday constant) From the unit of mA·h/g, we know that the theoretical discharge capacity of each gram of electrode material: 1 mA·h=1×(10-3 ) Amp×360 s=3.6 C Using Lithium as an example: The molecular weight of lithium is 6.94 g/mol, so its theoretical capacity is: 96500÷6.94÷3.6 = 3862.5 mA·h/g Li ↔ Li+ + e─

Li metal batteries /96 Polymeric Li host Cathode Anode Separator allowing reversible intake/release of Lit What happens at the surface of Li metal?? (next slide...) Li intercalation Li metal compounds https://pubs.rsc.org/services/images/RSCpubs.ePlatform.Service.FreeContent.ImageService.svc/ ImageService/Articleimage/2014/EE/c3ee40795k/c3ee40795k-f1_hi-res.gif 9
9 Li metal batteries https://pubs.rsc.org/services/images/RSCpubs.ePlatform.Service.FreeContent.ImageService.svc/ ImageService/Articleimage/2014/EE/c3ee40795k/c3ee40795k-f1_hi-res.gif Polymeric Li host Separator allowing reversible intake/release of Li+ What happens at the surface of Li metal?? (next slide…)
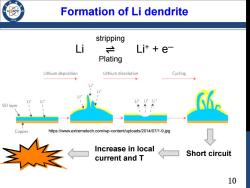
Formation of Li dendrite 196 stripping Li 户 Lit e Plating Lithium deposition Lithium dissolution Cycling L Li计Li计L计 SEI layer Copper https://www.extremetech.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/1-9.jpg Increase in local Short circuit current and T 10
10 Formation of Li dendrite Li ⇌ Li+ + e─ https://www.extremetech.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/1-9.jpg stripping Plating Short circuit Increase in local current and T
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Unit Commitment in Power System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Power System Economic Dispatch.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction of the course(黄琦).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 电力系统稳定性分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 电力系统不对称故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 电力系统不对称运行分析方法.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 电力系统三相短路故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 电力系统功率平衡与控制.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 复杂电力系统潮流计算.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
- 《电力电子技术 Power Electronics》:电能质量指标及其算法的研究.pdf
- 深圳市标准化指导性技术文件:分布式光伏发电系统并网接入技术规范(SZDB/Z 227 - 2017)Technical specification for distributed photovoltaic generation system Grid-connected.pdf
- 智能电网:改善低压农网电压质量的分布式光伏——储能系统优化配置方法.pdf
- 国投甘肃小三峡发电有限公司:浅析水电厂AVC控制策略.pdf
- 中国电机工程学会:核能发电专业发展报告(PPT宣讲稿,2019年11月).pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第一章 绪论 1.1 传热学的研究内容及其在科学技术和工程中的应用 1.2 热能传递的三种基本方式.pdf
