电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon)

Lecture 8 196 Anode Material for LIBs: Silicon Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04
Anode Material for LIBs: Silicon Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.04 Lecture 8

Content /986 Introduction of silicon 0 Chemistry of silicon Reaction mechanisms of silicon anode 。Problems Synthesis and modification methods One literature example 2
2 Content • Introduction of silicon • Chemistry of silicon • Reaction mechanisms of silicon anode • Problems • Synthesis and modification methods • One literature example
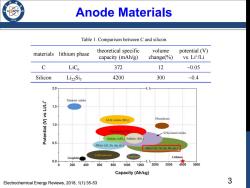
Anode Materials 936 Table 1.Comparison between C and silicon. materials lithium phase theoretical specific volume potential (V) capacity (mAh/g) change(%) vs.Lit/Li C LiCs 372 12 0.05 Silicon Li22Sis 4200 300 ~0.4 2.0 Titanium oxides 1.5 3d-M oxides(MO,) Phosphorus 1.0 Phosphides (MP. Si/Sn-based oxides Nitrides (MN,)Sulfides (MS,) 0.5 Alloys (AL,Zn.Ag.etc.) Alloys(Si.Ge,Sn,Sb,etc.) Carbonaceous Graphite Graphene Lithium 0.0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 2000 3000 4000 5000 Capacity(Ah/kg) Electrochemical Energy Reviews,2018,1(1):35-53 3
3 Anode Materials materials lithium phase theoretical specific capacity (mAh/g) volume change(%) potential (V) vs. Li+ /Li C LiC6 372 12 ~0.05 Silicon Li22Si5 4200 300 ~0.4 Table 1. Comparison between C and silicon. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2018, 1(1):35-53

Silicon Origin:widely distributed in dusts,sands,clay in the forms of silicon dioxide(silica)or silicates Characteristics:1.amorphous and crystalline silicon,2.diamond cubic crystal structure,3semiconductor (E=1.12 eV) Preparation:conversion of silica(SiO2) >Carbothermal reduction→SiO,+2C→Si+2CO2 SiC+SiO2→3Si+2C0 >Aluminothermal reduction-3 SiO,+4 Al->3 Si+2 Al2O3 quartz,agate,agate
4 Silicon • Origin:widely distributed in dusts, sands, clay in the forms of silicon dioxide (silica) or silicates • Characteristics: 1. amorphous and crystalline silicon, 2. diamond cubic crystal structure, 3.semiconductor (Eg=1.12 eV) • Preparation:conversion of silica (SiO2 ) Carbothermal reduction → SiO2 + 2 C → Si + 2 CO2 SiC + SiO2 → 3 Si + 2 CO Aluminothermal reduction → 3 SiO2 + 4 Al → 3 Si + 2 Al2O3 quartz, agate, agate

Silicon Anode /98 The electrochemical reaction: >Si+4.4Li LiSi(fully lithiated state,each silicon atom can host 4.4 lithium atoms) Reversible process (lithiation/delithiation) >Lit ions insert into silicon and form Li-Si alloy(charge) Si→Li2.oSi→Li3sSi→Li44Si >Then deinsert from silicon and Li-Si dealloy (discharge) Li4,4Si→Li3sSi→Li2.oSi→Si 5
5 Silicon Anode • The electrochemical reaction: Si + 4.4Li+ ↔ Li4.4Si (fully lithiated state, each silicon atom can host 4.4 lithium atoms) • Reversible process (lithiation/delithiation) Li+ ions insert into silicon and form Li-Si alloy(charge) Si → Li2.0Si → Li3.5Si → Li4.4Si Then deinsert from silicon and Li-Si dealloy (discharge) Li4.4Si → Li3.5Si → Li2.0Si → Si

Advantages 95 High theoretical specific capacity Li22Sis-4200 mAh/g Low discharge potential plateau 0.4 V versus Lit/Li-high working voltage,leading to high energy density in a full LIB Environmentally friendly ·Low toxicity High abundance (the 2nd most abundant element in the earth's crust) 6
6 Advantages • High theoretical specific capacity Li22Si5—— 4200 mAh/g • Low discharge potential plateau ≈ 0.4 V versus Li+ /Li —— high working voltage, leading to high energy density in a full LIB • Environmentally friendly • Low toxicity • High abundance (the 2 nd most abundant element in the earth’s crust)
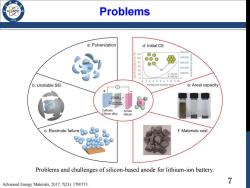
Problems /96 a:Pulverization d:Initial CE 500.000 20 oO w100 00O 400.000 80 o 300.000 60 200.000 40 E 20 a=25 nm 100.000 d=80 nm 0T斤 -0 012345678910 b:Unstable SEl Pomegranate diameter (um) e:Areal capacity Charge Li Discharge Si Cathode Anode Lithium alloy Silicon c:Electrode failure f:Materials cost Problems and challenges of silicon-based anode for lithium-ion battery. Advanced Energy Materials,2017,7(23):1700715. 7
7 Problems Problems and challenges of silicon-based anode for lithium-ion battery. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(23): 1700715

Problems Materials Pulverization Due to the large volume expansion,induces large stress,which can cause cracking and pulverization of Si,leading to loss of electrical contact and capacity fading. Unstable Solid Electrolyte Interphase The anode surface will be covered by an SEI film,the reductive decomposition of the organic electrolyte,it's electronically insulating but ionically conducting. Initial Coulombic Efficiency In the first cycle,active Li+is consumed due to the SEI film formation, resulting in irreversible capacity and extra cathode electrode consumption 8
8 Problems • Materials Pulverization Due to the large volume expansion, induces large stress, which can cause cracking and pulverization of Si, leading to loss of electrical contact and capacity fading. • Unstable Solid Electrolyte Interphase The anode surface will be covered by an SEI film, the reductive decomposition of the organic electrolyte, it’s electronically insulating but ionically conducting. • Initial Coulombic Efficiency In the first cycle, active Li+ is consumed due to the SEI film formation, resulting in irreversible capacity and extra cathode electrode consumption
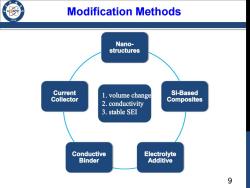
Modification Methods 1986 Nano- structures Current Si-Based Collector 1.volume change 2.conductivity Composites 3.stable SEI Conductive Electrolyte Binder Additive 9
9 Modification Methods
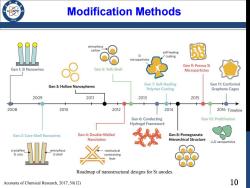
Modification Methods 936 amorphous carbon self-healing Si coating microparticles Gen 9:Porous Si Gen 1:Si Nanowires Gen 5:Yolk-Shell Microparticles Gen 3:Hollow Nanospheres Gen 7:Self-Healing Gen 11:Conformal Polymer Coating Graphene Cages 2009 2011 2013 2015 2008 2010 2012 2014 2016 Timeline Gen 6:Conducting Gen 10:Prelithiation Hydrogel Framework Gen 2:Core-Shell Nanowires Gen 4:Double-Walled Gen 8:Pomegranate Nanotubes Hierarchical Structure Li,Si nanoparticles crystalline amorphous mechanical Si core Si shell constraining layer Roadmap of nanostructural designs for Si anodes. Accounts of Chemical Research,2017,50(12) 10
10 Modification Methods Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50(12) Roadmap of nanostructural designs for Si anodes
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
- 《电力电子技术 Power Electronics》:电能质量指标及其算法的研究.pdf
- 深圳市标准化指导性技术文件:分布式光伏发电系统并网接入技术规范(SZDB/Z 227 - 2017)Technical specification for distributed photovoltaic generation system Grid-connected.pdf
- 智能电网:改善低压农网电压质量的分布式光伏——储能系统优化配置方法.pdf
- 国投甘肃小三峡发电有限公司:浅析水电厂AVC控制策略.pdf
- 中国电机工程学会:核能发电专业发展报告(PPT宣讲稿,2019年11月).pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第一章 绪论 1.1 传热学的研究内容及其在科学技术和工程中的应用 1.2 热能传递的三种基本方式.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.1 导热基本定律-傅里叶定律.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二讲 第一章 绪论 1.3 传热过程和传热系数 1.4 传热学的发展简史和研究方法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.2 导热问题的数学描写 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过平壁的导热.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第二章 稳态热传导 2.3 典型一维导热问题的分析解-通过圆筒壁的导热 2.4 通过肋片的导热.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.1 非稳态导热的基本概念.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.2 零维问题的分析法-集中参数法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.1 导热问题数值求解的基本思想 4.2 内节点离散方程的建立方法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第三章 非稳态热传导 3.3 典型一维非稳态导热的分析解.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.3 边界节点离散方程的建立及代数方程的求解.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第四章 热传导问题的数值解法 4.4 非稳态导热问题的数值解法.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第五章 对流传热的理论基础 5.1 对流传热概说 5.2 对流传热问题的数学描写.pdf
- 山西能源学院:《传热学》课程教学资源(电子教案)第五章 对流传热的理论基础 5.3 边界层型对流传热问题的数学描写.pdf
