电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow

Lecture 9 Power System Optimal Power Flow Dr.QI Huang School of Energy Science and Engineering,UESTC
Lecture 9 Power System Optimal Power Flow Dr. QI Huang School of Energy Science and Engineering, UESTC

Contents Introduction Optimal power flow model Solution of optimal power flow by linear programming 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Contents Introduction Optimal power flow model Solution of optimal power flow by linear programming

Introduction Optimal power flow:a stable system operation status,while operation and security constraints s are satisfied,achieved by adjusting those controllable variables to realize the optimization of specific targets. First proposed by French scientist Carpentier in 60's More optimal than ED:more constraints are considered; more controllable variables (MW) ■ Generator Voltage Tap changer Synchronous condenser Switching capacitor ■ SVC Load shedding ■ DC power flow 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 国家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Introduction Optimal power flow: a stable system operation status, while operation and security constraints are satisfied, achieved by adjusting those controllable variables to realize the optimization of specific targets. First proposed by French scientist Carpentier in 60’s More optimal than ED: more constraints are considered; more controllable variables(MW) Generator Voltage Tap changer Synchronous condenser Switching capacitor SVC Load shedding DC power flow

Introduction Assumptions in optimal power flow The thermal(nuclear)plant commissioned is given(start up/shutdown is neglected) The output of every hydroplant is given(hydroplant ED) Power system structure remains unchanged Objective function of OPF: Min of operation cost:max of GenCO profit Min of active power loss:energy efficiency,improvement of voltage quality In order to guarantee the convex property of objective function,quadratic function is used (large than 3rd order may not guarantee convex) 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Introduction Assumptions in optimal power flow The thermal (nuclear) plant commissioned is given (start up/shutdown is neglected) The output of every hydroplant is given (hydroplant ED) Power system structure remains unchanged Objective function of OPF: Min of operation cost: max of GenCO profit Min of active power loss: energy efficiency, improvement of voltage quality In order to guarantee the convex property of objective function, quadratic function is used (large than 3rd order may not guarantee convex)
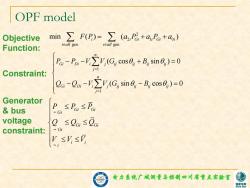
OPF model Objective min ∑F(P)=∑(a,P+a,P+a,) Function: ieall gen ieall gen. Po-Po-V V,(G cos0 +B sin)=0 Constraint: Q-0-25(G,sn8-R,os0,)=0 Generator bus P。≤PaSFa voltage Q≤Qo≤0a constraint: -Gi '≤r≤ 电力集院广城测量与控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 OPF model 2 2 1 0 gen. gen. min ( ) ( ) i i Gi i Gi i i all i all F P a P a P a 1 1 ( cos sin ) 0 ( sin cos ) 0 n Gi Di i j ij ij ij ij j n Gi Di i j ij ij ij ij j P P V V G B Q Q V V G B Gi Gi Gi Gi Gi Gi i i i P P P Q Q Q V V V Objective Function: Constraint: Generator & bus voltage constraint:

Solution of OPF Lambda-iterative: Gradient:slow convergence;cannot handle inequality constraints Newton method:fast convergence;may have problem with inequality constraints Linear Programming:mature algorithm;linearize the nonlinear objective function and constraints ■ Non-linear programming:handle non-linear objective function and constraint (equality or inequality) Interior point method:widely used;easy for handling inequality constraints 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Solution of OPF Lambda-iterative: Gradient: slow convergence; cannot handle inequality constraints Newton method: fast convergence; may have problem with inequality constraints Linear Programming: mature algorithm; linearize the nonlinear objective function and constraints Non-linear programming: handle non-linear objective function and constraint (equality or inequality) Interior point method: widely used; easy for handling inequality constraints
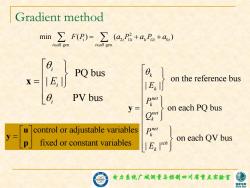
Gradient method min ∑F(E)=∑(a,P+a,P+a) ieall gen. ieall gen. PQ bus X= on the reference bus IEI PV bus P y= on each PQ bus control or adjustable variables V- P > p fixed or constant variables on each QV bus 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Gradient method 2 2 1 0 gen. gen. min ( ) ( ) i i Gi i Gi i i all i all F P a P a P a PQ bus | | PV bus i i i E x on the reference bus | | on each PQ bus on each QV bus | | k k net k net k net k sch k E P Q P E y control or adjustable variables fixed or constant variables u y p
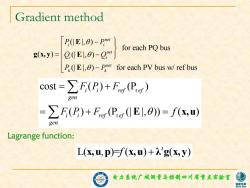
Gradient method P(El,0)-Pe for each PQ bus g(xy)=Q,E1,0)-g P.(1El0)-Pe for each PV bus w/ref bus cost=∑F(P)+Fgr(Per) gen =∑F(P)+Fer(Per(El,θ)=f(&,m) gen Lagrange function: L(x,u,p)(x,u)+g(x,y) 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Gradient method (| |, ) for each PQ bus ( ) (| |, ) (| |, ) for each PV bus w/ ref bus net i i net i i net k k P P Q Q P P E g x, y Ε E r r cost ( ) (P ) ( ) (P (| |, )) ( ) i i ref ef gen i i ref ef gen F P F F P F f E x,u Lagrange function: L( , )= ( ) ( ) t x,u p x,u f λ g x, y

Gradient method L(x,u,p)f(x,u)+g(x,y) L(x,u,p)=>F(P)+Fr(Prer(E,))+ gen P(E,0)-Pmet +[乃….n] Q,(E,0)-9"e P(El,)-Pme 电力康镜广城测量与控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Gradient method L( , )= ( ) ( ) t x,u p x,u f λ g x, y r 1 2 L( , )= ( ) (P (| |, )) (| |, ) (| |, ) (| |, ) i i ref ef gen net i i net i i m net k k F P F P P Q Q P P x,u p E E Ε E
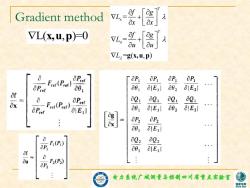
Gradient method VL 0g VL(x,u,p)-0 V 时 og Bu VL2-g(x,U,p) a 胎, OP OP aP Pret a01 lE,l a82 aE21 0x Pret 2 01 0Q1 01 aE:l 6JE,l a82 aE21 [ 码湖 OP2 alE,l a 0 a02 OP F(P) , alE:l of Qu 0P F2(P) 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Gradient method L( , )=0 x,u p x u = = = ( , ) T T f g L x x f g L u u L g x,u p
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Unit Commitment in Power System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Power System Economic Dispatch.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction of the course(黄琦).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 电力系统稳定性分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 电力系统不对称故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 电力系统不对称运行分析方法.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 电力系统三相短路故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 电力系统功率平衡与控制.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 复杂电力系统潮流计算.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 简单电力系统潮流分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 电力系统元件等效电路和参数.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 电力系统概述(李莉).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(讲稿)电力线路等效电路及参数.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(电子教案,共八章).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(说课稿,李莉).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 08 Anode Material for LIBs(Silicon).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 09 Anode material for LIBs(Tin).pdf
- 《电力系统自动化》:利用储能系统提升电网电能质量研究综述.pdf
