电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Power System Reactive Power and Voltage Control

Lecture #6 Power System Reactive power and voltage control Dr.Qi Huang School of Energy Science and Engineering,UESTC
Lecture #6 Power System Reactive power and voltage control Dr. Qi Huang School of Energy Science and Engineering, UESTC

Contents Introduction Concept of Reactive power in power system Control and management of reactive and voltage Difference between active power frequency regulation Importance of voltage control Measures for voltage control Rules of reactive compensation and voltage control Excitation control of generator 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Contents Introduction Concept of Reactive power in power system Control and management of reactive and voltage Difference between active power & frequency regulation Importance of voltage control Measures for voltage control Rules of reactive compensation and voltage control Excitation control of generator

Concept of reactive power Power in an electric circuit is the rate of flow of energy past a given point of the circuit.In alternating current circuits,energy storage elements such as inductance and capacitance may result in periodic reversals of the direction of energy flow. 口 The portion of power that,averaged over a complete cycle of the AC waveform,results in net transfer of energy in one direction is known as real power. The portion of power due to stored energy,which returns to the source in each cycle,is known as reactive power. 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Concept of reactive power Power in an electric circuit is the rate of flow of energy past a given point of the circuit. In alternating current circuits, energy storage elements such as inductance and capacitance may result in periodic reversals of the direction of energy flow. The portion of power that, averaged over a complete cycle of the AC waveform, results in net transfer of energy in one direction is known as real power. The portion of power due to stored energy, which returns to the source in each cycle, is known as reactive power
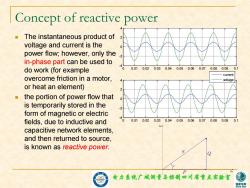
Concept of reactive power The instantaneous product of voltage and current is the 0 power flow;however,only the in-phase part can be used to do work(for example 0.010.020.030.040.050.060.070.080.09 0.1 current overcome friction in a motor, voltage or heat an element) the portion of power flow that is temporarily stored in the 2 form of magnetic or electric fields,due to inductive and 0 0.010.02 0.030.040.050.060.070.080.09 0.1 Im capacitive network elements, and then returned to source, is known as reactive power. 电力集镜广城测量与控制四川省重点实脸室 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Concept of reactive power The instantaneous product of voltage and current is the power flow; however, only the in-phase part can be used to do work (for example overcome friction in a motor, or heat an element) the portion of power flow that is temporarily stored in the form of magnetic or electric fields, due to inductive and capacitive network elements, and then returned to source, is known as reactive power. 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1 -4 -2 0 2 4 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1 -4 -2 0 2 4 current voltage

Concept of reactive power The active power is used to keep the normal operation of appliances,converting electrical energy into other forms(mechanical,light or heat) Reactive power is used to exchange energy (electric field and magnetic field).It does not do work,but just help exchange the energy.Any appliances that have coils would consume reactive power. Reactive power is not useless!Motor needs to build up a magnetic field,driving mechanical movements; Transformer needs to build up magnetic field, helping induction of voltage. 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Concept of reactive power The active power is used to keep the normal operation of appliances, converting electrical energy into other forms (mechanical, light or heat) Reactive power is used to exchange energy (electric field and magnetic field). It does not do work, but just help exchange the energy. Any appliances that have coils would consume reactive power. Reactive power is not useless! Motor needs to build up a magnetic field, driving mechanical movements; Transformer needs to build up magnetic field, helping induction of voltage
Concept of reactive power 食蜜 Figure 2-29.Reactive Power Inclined Plane Analogy 家电
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Concept of reactive power

Concept of reactive power Under normal operation condition,appliances not only absorb active power,but also reactive power.If the reactive power is not enough,then electromagnetic field cannot be built,causing the decrease of voltage,hence affecting the operation of appliances. Reactive power may affect the power system in following aspects: 0 (1)reduce the active power output of generator (2)reduce the power delivery capability of transmission and transformers (3)increase the voltage loss and power loss on transmission line (4)cause voltage drop and operation under low power factor condition,under which the nominal capacity cannot be fully used 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 国家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Concept of reactive power Under normal operation condition, appliances not only absorb active power, but also reactive power. If the reactive power is not enough, then electromagnetic field cannot be built, causing the decrease of voltage, hence affecting the operation of appliances. Reactive power may affect the power system in following aspects: (1)reduce the active power output of generator (2)reduce the power delivery capability of transmission and transformers (3)increase the voltage loss and power loss on transmission line (4)cause voltage drop and operation under low power factor condition, under which the nominal capacity cannot be fully used
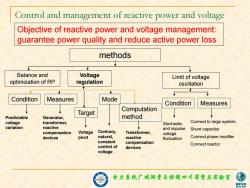
Control and management of reactive power and voltage Objective of reactive power and voltage management: guarantee power quality and reduce active power loss methods Balance and Voltage Limit of voltage optimization of RP regulation oscillation Condition Measures Mode Condition Measures Target Computation Predictable Generator, method voltage transformer, Stochastic Connect to large system; variation reactive ↓ and impulse Shunt capacitor compensation Voltage Contrary, Transformer, voltage devices pivot natural, reactive fluctuation Connect phase modifier constant compensation control of Connect reactor devices voltage 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Control and management of reactive power and voltage Objective of reactive power and voltage management: guarantee power quality and reduce active power loss methods Limit of voltage oscillation Voltage regulation Predictable voltage variation Generator, transformer, reactive compensation devices Voltage pivot Contrary, natural, constant control of voltage Stochastic and impulse voltage fluctuation Transformer, reactive compensation devices Connect to large system; Shunt capacitor Connect phase modifier Connect reactor Balance and optimization of RP Condition Measures Target Mode Computation method Condition Measures

Difference between voltage reactive power regulation and frequency active power regulation Active power source:only generator ->uniqueness Reactive power sources:generator, reactive power compensation devices (capacitor,reactor,phase modifier, static VAR)->diversity ■Active power source consumes primary energy, while reactive power source does not 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省童点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Difference between voltage & reactive power regulation and frequency & active power regulation Active power source: only generator ->uniqueness Reactive power sources: generator, reactive power compensation devices (capacitor, reactor, phase modifier, static VAR)->diversity Active power source consumes primary energy, while reactive power source does not

Difference between voltage reactive power regulation and frequency active power regulation Frequency of whole system is the same. Frequency regulation is only in power plant,can only be realized by regulating the output of prime mover. Voltage level at different point in power network is different.Voltage regulation can be done dispersedly.There are various type of voltage regulation measures.Voltage regulation: hierarchical regulation and local balance In power network, reactive power consumption is much larger than active power. 电力拿镜广城洲量写控制四川省重点实验蜜 家电网
电力系统广域测量与控制四川省重点实验室 Difference between voltage & reactive power regulation and frequency & active power regulation Frequency of whole system is the same. Frequency regulation is only in power plant, can only be realized by regulating the output of prime mover. Voltage level at different point in power network is different. Voltage regulation can be done dispersedly. There are various type of voltage regulation measures. Voltage regulation: hierarchical regulation and local balance In power network, reactive power consumption is much larger than active power
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Power Generation Control and Frequency Regulation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Unit Commitment in Power System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Power System Economic Dispatch.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Introduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introduction of the course(黄琦).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 电力系统稳定性分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 电力系统不对称故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 电力系统不对称运行分析方法.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 电力系统三相短路故障分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 电力系统功率平衡与控制.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 复杂电力系统潮流计算.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 简单电力系统潮流分析.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 电力系统元件等效电路和参数.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 电力系统概述(李莉).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(讲稿)电力线路等效电路及参数.pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(电子教案,共八章).pdf
- 银川能源学院(银川大学):《电力系统分析》课程教学资源(说课稿,李莉).pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《锅炉原理》课程教学资源(教学大纲)陈佰满-葛亚-2019级能源与动力工程1-2班.pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《计算流体力学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)杨小平,陈捷超-2018能源1,2班,建能1班.pdf
- 东莞理工学院:《节能原理与技术》课程教学资源(教学大纲)何清,陈佰满-2019级能源与动力工程1、2班,建筑环境与能源应用1班.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Power System Wide-area Measurement and Control.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 power system state estimation.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 Power System Optimal Power Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Power System Security.pdf
- 《电力系统运行与控制 Power System Operation and Control》课程参考书籍文献:《Operation and Control in Power Systems》PDF电子书(Prof. P. S. R. MURTY).pdf
- “十四五”可再生能源发展规划(发布稿).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 01 Background of Batteries(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 02 Introduction of Lithium Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 03 Lithium-ion Batteries(LiCoO).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 04 Cathode material for LIBs(LiFePO4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 05 Cathode material for LIBs(Li-Mn-O and NCM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 06 Anode material for LIBs(Graphite).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 07 Anode material for LIBs(Lithium).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section I Background and Fuel Cell(陈俊松).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section II Nuclear energy(Fundamentals of Fusion Enery).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section III Fundamentals of Solar Cell.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第一部分)Section IV THERMODYNAMICS.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 10 Anode material for LIB(TiO2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 11 Safety of Li-ion Batteries.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《物理与化学电源基础 Fundamental of Physical and Chemical Power Sources》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,第二部分)Lecture 12 Solid-state Electrolyte in Li-ion Batteries(SSE of LIB).pdf
