同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 06 Numerical Evaluation of Dynamic Response

Structural Dynamics Lecture 6 Numerical Evaluation of Dynamic Response 自 同海大学 土本工相学院
Structural Dynamics Lecture 6 Numerical Evaluation of Dynamic Response
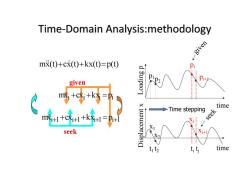
Time-Domain Analysis:methodology given m(t)+cx(t)+kx(t)=p(t) Pi given 'd 3u!peoT p} m++k= time Time stepping m++c++k=+ seek seek time
Time-Domain Analysis:methodology Time-Domain Analysis:methodology mx(t)cx(t)kx(t)p(t) L o a d i n g p time D i s p l a c e m e n t x time p1 x1 t1 p2 x2 t2 given seek i xi kxi pi mx c i 1 xi 1 kxi 1 pi 1 mx c pi ti xi given pi+1 tj xi+1 seek Time stepping
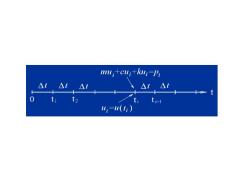
m4,+c4;+u,=P2 △ △t △ t计 u:-u(t1)

Duhamel's integral provides a general result for evaluating the response of a linear SDOF system to arbitrary force. When the force is simple,Duhamel's integral method is applicable. If the force is complicated function,evaluation of the integral requires numerical method and usually not efficient The exciting force exists only in digitized form,such as earthquake records. u()=p()(i-)d
• Duhamel’s integral provides a general result for evaluating the response of a linear SDOF system to arbitrary force. • When the force is simple, Duhamel’s integral method is applicable. • If the force is complicated function, evaluation of the integral requires numerical method and usually not efficient • The exciting force exists only in digitized form, such as earthquake records. 0 t u t p d h t

Accordingly,two basic approaches: Numerical evaluation of the Duhamel integral; Principle of Superposition->Linear system Direct integration of the equation of motion- step-by-step integration.Valid for both Linear and Non-linear systems->more commonly utilized. Response:at discrete time,usually with equal time internal
• Accordingly, two basic approaches: • Numerical evaluation of the Duhamel integral; Principle of Superposition → Linear system • Direct integration of the equation of motion – step-by-step integration. Valid for both Linear and Non-linear systems → more commonly utilized. • Response: at discrete time, usually with equal time internal

Convergence:As the time step decreases,the numerical solution should approach the exact solution; Stability:the numerical solution should be stable in the presence of numerical round-off errors, Accuracy:the numerical procedure should provide results that are close enough to the eact solution
• Convergence: As the time step decreases, the numerical solution should approach the exact solution; • Stability: the numerical solution should be stable in the presence of numerical round-off errors; • Accuracy: the numerical procedure should provide results that are close enough to the eact solution

Time-Domain Analysis .(1)Interpolation of Excitation Method .(2)Central Difference Method ·(3)Newmark's Method ·(4)Vilson-O Method .(5)State space method
Time-Domain Analysis • (1) Interpolation of Excitation Method • (2) Central Difference Method • (3) Newmark’s Method • (4) Wilson- Method • (5) State space method
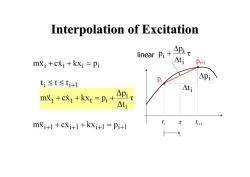
Interpolation of Excitation linear PiAPi mi+cxi+kxi Pi △ti p+1 Pi △pi ti≤t≤ti+l △ti m成t+cx+kxt=Pi+ piT △t mXi+1+cXi+1+kxi+1=Pi+l ti+l
Interpolation of Excitation Interpolation of Excitation i t τ Δt Δp pkxxcxm i i ittt i i 1 t t t i i i t p linear p i 1 xi 1 kxi 1 pi 1 mx c pi+1 i1 t i xi kxi pi mx c pi i t pi

Interpolation of Excitation m戊+cx,+kX,=p;+ pi元 △t\ constant linear ramp Solution of x(t)consists of 3 parts Step response due to pi A Ramp response due tot Free vibration response
Interpolation of Excitation Interpolation of Excitation i i i t p pkxxcxm constant linear ramp Solution of x(t) consists of 3 parts - Step response due to pi - Ramp response due to - Free vibration response i i t P

Recurrence Equations APLt m+k=p ur)(o.) sino,t ;on△t ↑ Free vibration Step force Ramp force l回-4 isino.+立coso,r+朵sino,r+若oA k 91(1-cos0,) 4+1=A4,+B,+CP,+Dp+l u'i+1=A'u,+B'u+C'p,+D'P+1 For constant time interval,ABCD need to be computed only once
Recurrence Equations Recurrence Equations i i i m p u ku p t 1 cos si os n c sin i n i i i n n n n i n i p k p k u u u t t Free vibration Step force Ramp force sin co 1 s sin 1 cos i i n i n n n n n i i n p p k k t u u u 1 1 1 1 ' ' ' ' ' i i i i i i i i i i u Au Bu Cp Dp u A u B u C p D p For constant time interval, ABCD need to be computed only once
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 05 Response to Arbitrary, Step , and Pulse Excitations.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 04 Response to harmonic and periodic excitations - Application.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 03 Response to Harmonic and Periodic Excitations.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 02.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 01 Introduction of Structural Dynamics(负责人:陈隽).pdf
- 《力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)美国物理试题与解答(第1卷)力学.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《力学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)教学大纲 Mechanics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)专题部分——机械振动基础.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十四章 虚位移原理 §14-1 约束、虚位移、虚功 §14-2 虚位移原理(虚功原理).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十三章 达朗贝尔原理.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十二章 动能定理 §12-6 普通定理的综合应用举例..pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十二章 动能定理 §12-1 力的功 §12-2 质点和质点系的功能 §12-3 动能定理.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十一章 动量矩定理 §11-3 刚体绕定轴的转动微分方程 §11-5 质点系相对质心的动量矩定理 §11-6 刚体的平面运动微分方程.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十一章 动量矩定理 §11-1 质点和质点系的动量矩 §11-2 动量矩定理 §11-4 刚体对轴的转动惯量.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 动量定理 §10-3 质心运动定理.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 质点动力学的基本方程、第十章 动量定理 §10-1 动量与冲量 §10-2 动量定理.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第八章 刚体的平面运动 §8-5 运动学综合应用举例.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第八章 刚体的平面运动 §8-4 用基点法求平面图形内各点的加速度.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第八章 刚体的平面运动 §8-1 刚体平面运动的概述和运动分解 §8-2 求平面图形内各点速度的基点法 §8-3 求平面图形内各点速度的瞬心法.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《理论力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 点的合成运动(复合运动)§7-4 牵连运动为转动时点的加速度合成定理·科氏加速度.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 07 Frequency Domain Method.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 08 Generalized SDOF Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)01 Introduction.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)02 Kinematic(运动学)analysis of structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)03 Reactions(反力).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)04 Member Forces in Planar Trusses平面桥架()and Space Frameworks(空间构架).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)05 Member Forces in Beams(梁)and Frames.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)07 Elastic Deflections(弹性变形)of Trusses and Frameworks..pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)08 Elastic Deflections(弹性变形)of Beam and Frame Structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)09 More Basic Concepts of Structural Analysis.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)06 Influence Lines(影响线)and Maximum Load Effects..pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)10 Method of Consistent Deformations(协调变形法)(and Other Compatibility Methods).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)11 Slope Deflection Method(转角变位移法)(and Other Equilibrium Methods).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)12 Moment Distribution Method(弯矩分配法).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)13 Matrix Displacement Method(矩阵位移法).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)16 Dynamic analysis of structures.pdf
- 吉林大学:《土质学与土力学》课程教学资源(讲义,共十一章,负责人:郑孝玉).docx
- 科学出版社:现代力学丛书《高等断裂力学》书籍PDF电子版 Advanced Fracture Mechanics(2009版,共14章,主编:王自强、陈少华).pdf
- 国家自然科学基金重大项目:《材料的损伤断裂机理和宏微观力学理论》书籍PDF电子版(共六章,清华大学出版社,主编:黄克智、肖纪美).pdf
- 《断裂力学》课程教学资源(书籍教材)断裂力学教程电子版(PDF电子书,共四章).pdf
