同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)12 Moment Distribution Method(弯矩分配法)

2016/4/6 Chapter 12 Moment Distribution Method(弯矩分配法) 输问冷大学 国土本2程学院 Background Methods for statically indeterminate structures:(超静定结构的计算方法) ·Force method(力法) ·Displacement method(位移法) ·Moment distribution method(弯矩分配法) 司问冷大学 闺土本红相季院 1
2016/4/6 1 1 Chapter 12 Moment Distribution Method(弯矩分配法) Background Methods for statically indeterminate structures:(超静定结构的计算方法) • Force method (力法) • Displacement method (位移法) • Moment distribution method(弯矩分配法)

2016/4/6 16 Candy distribution Game! 4 6 6 5 6 xWhat is the basic idea? 输问济大学 国土本2程季悦 Key points of distribution method 1.It does not need a complete set of equations. Force method A,=∑δyX,+AP Displacement method R-25Z,+R=0 2.It is a step-by-step iterative(送代)method. 3.Each step acts to refine the result from the previous step. 4.The process converges (to the correct solution with enough steps. 5.The process can be terminated(终止)when the desired accuracy(精度)has been achieved 包同冷大学 闺土本红程学院 2
2016/4/6 2 3*y=16 y=? Candy distribution What is the basic idea? 16 0 8 8 4 4 8 4 6 6 5 5 6 Game! 3. Each step acts to refine the result from the previous step. 4. The process converges (收敛) to the correct solution with enough steps. 5. The process can be terminated (终止) when the desired accuracy (精度) has been achieved. Key points of distribution method 2. It is a step-by-step iterative (迭代) method. 1. It does not need a complete set of equations. Force method Displacement method P 0 1 i n j Ri rijZ j R P 1 i n j i ijX j
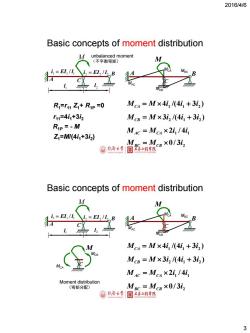
2016/4/6 Basic concepts of moment distribution M unbalanced moment (不平衡弯矩) i2=E2/12 B R=r11Z+RiP=0 Mc4=M×4i1/(4i1+3i2) r11=411+3i2 McB=M×3i2/(4i1+3i2) Rip =-M MAc=Mc4×2i1/4i1 Z1=M川4i1+3i2) MaC=McB×0/3i2 输问济大学 士齐1程幸悦 Basic concepts of moment distribution M i,=E1,/l A M Mc4=M×4i/(4i,+3i2) McB McB=M×3i2/(4i+3i2) McA n M4c=Mc4×2i,/4i1 Moment distribution (弯矩分配) MBc=McB×0/3i2 包同冷大学 国产本红相学院 3
2016/4/6 3 A B C M MCA MCB MBC MAC M A B 1 l 2 l 1 1 1 i EI / l 2 2 2 i EI / l C 4 /(4 3 ) 1 1 2 M M i i i CA 3 /(4 3 ) 2 1 2 M M i i i CB 1 4 1 M M 2i / i AC CA 3 2 M M 0/ i BC CB Basic concepts of moment distribution R1=r11 Z1+ R1P =0 r11=4i1+3i2 Z1=M/(4i1+3i2 ) R1P = - M unbalanced moment (不平衡弯矩) A B C M MCA MCB MBC MAC M A B 1 l 2 l 1 1 1 i EI / l 2 2 2 i EI / l C 4 /(4 3 ) 1 1 2 M M i i i CA 3 /(4 3 ) 2 1 2 M M i i i CB M M C CA MCB 1 4 1 M M 2i / i AC CA 3 2 M M 0/ i BC CB Moment distribution (弯矩分配) Basic concepts of moment distribution
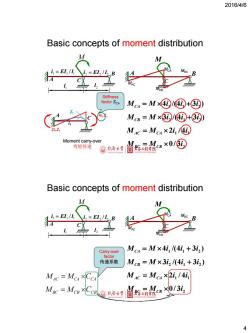
2016/4/6 Basic concepts of moment distribution Stiffness factor ScA Mc4=M×④/④+③@) 4i2 Ms=M×⑤/④+3①) MAc=Mc4×2i,/① Moment carry-over 弯矩传递 M Mcs×0/② 织程流 Basic concepts of moment distribution M =E11 2=E12/2B 公A Carry-over Mc4=M×4i/(4i1+3i2) factor 传递系数 MB=M×3i2/(4i+3i2) Mac McxCea MAc=McA×2i,/4i Mc=MCB XCCB③月卡 4cs0/3列 4
2016/4/6 4 A B C M MCA MCB MBC MAC M A B 1 l 2 l 1 1 1 i EI / l 2 2 2 i EI / l C 4 /(4 3 ) 1 1 2 M M i i i CA 3 /(4 3 ) 2 1 2 M M i i i CB 1 4 1 M M 2i / i AC CA 3 2 M M 0/ i BC CB Basic concepts of moment distribution A C Moment carry-over 弯矩传递 4i1Z1 2i1Z1 Z1 i1 Stiffness factor SCA A B C M MCA MCB MBC MAC M A B 1 l 2 l 1 1 1 i EI / l 2 2 2 i EI / l C 4 /(4 3 ) 1 1 2 M M i i i CA 3 /(4 3 ) 2 1 2 M M i i i CB 1 4 1 M M 2i / i AC CA 3 2 M M 0/ i BC CB Basic concepts of moment distribution M M C AC CA CA M M C BC CB CB Carry-over factor 传递系数
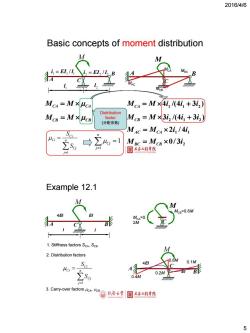
2016/4/6 Basic concepts of moment distribution M i=EI2/1 B Mc MXHc Mc4=M×41,/4i1+3i2) Distribution MCB MXHCB factor McB=M×3i2/(4i,+3i2) (分配系数) MAc=Mc4×2i,/4i1 Mac=McB×0/3i2 Example 12.1 M McB=0.8M 4E MCA 2M 1.Stiffness factors ScA.ScB 2.Distribution factors Sa 0.1M Sg 0.2M 0.4M j 3.Carry-over factors McA.AcB 圆间冷大学 目土本江相幸院 5
2016/4/6 5 A B C M MCA MCB MBC MAC M A B 1 l 2 l 1 1 1 i EI / l 2 2 2 i EI / l C 4 /(4 3 ) 1 1 2 M M i i i CA 3 /(4 3 ) 2 1 2 M M i i i CB 1 4 1 M M 2i / i AC CA 3 2 M M 0/ i BC CB Basic concepts of moment distribution MCA M CA MCB M CB Distribution factor (分配系数) 1 Ci Ci n Cj j S S 1 1 n Cj j Example 12.1 0.8M 0.2M M C MCA=0. 2M MCB=0.8M 0.1M 0.4M A B C M 4EI EI M A C B l l 4EI EI 1 Ci Ci n Cj j S S 1. Stiffness factors SCA, SCB 2. Distribution factors 3. Carry-over factors CA, CB

2016/4/6 Example 12.2 Take E/and /as constants. 16 n 输月冷大学 目土本2程学税 16 Candy distribution:review Gamel 0 8 8 4 6 5 5 6 包同冷大学 目土本2程幸悦 6
2016/4/6 6 Example 12.2 A B C 16 D Take EI and l as constants. 3*y=16 y=? Candy distribution: review 16 0 8 8 4 4 8 4 6 6 5 5 6 Game!
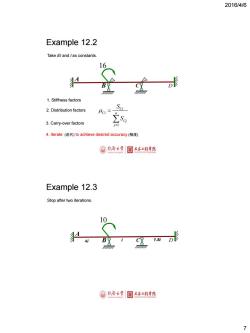
2016/4/6 Example 12.2 Take E/and /as constants. 16 1.Stiffness factors 2.Distribution factors 3.Carry-over factors i=1 4.Iterate(迭代)to achieve desired accuracy(精度) 月冷大学 国土本2程季悦 Example 12.3 Stop after two iterations. 10 41 1.5i D形 国月冷大学 目土本2程幸院 >
2016/4/6 7 Example 12.2 A B C 16 D Take EI and l as constants. 1 Ci Ci n Cj j S S 1. Stiffness factors 2. Distribution factors 3. Carry-over factors 4. Iterate (迭代) to achieve desired accuracy (精度) Example 12.3 A B C 10 4i i 1.5i D Stop after two iterations

2016/4/6 Unbalanced moment due to in-span loading (跨间荷载导致的不平衡弯矩) The negative value of total fixed end moments at the joint is to be distributed. P2 MR+M女9a品 Mc4=M×44+Ma McB=M×4B+MEB MAc MX Hc xCc+Mic MBc M X HcB XCcB+MBc CB 输问冷大学 国土本2相学悦 Factors for different boundary conditions: (不同边界条件下的系数取值) Stiffness factors SAj SAB=4i SAn=3i A B i B Distribution factors MAj ΣS i=1 A Carry-over factors CAj AB=1/2 AB =0 AB A 包向傍大学 目土本工程学院 8
2016/4/6 8 F MCA M CA MCA F MCB M CB MCB R1P C F MCB F MCA ( ) 1 F F M R P MCA MCB Z1 1 A B 1i 2 C i 1 4i 2 3i 1 2i A B 1 l 2 l 1 1 1 i EI / l 2 2 2 C i EI / l FP1 FP2 F MAC M CA CCA MAC F MBC M CB CCB MBC Unbalanced moment due to in-span loading (跨间荷载导致的不平衡弯矩) R1P C M The negative value of total fixed end moments at the joint is to be distributed. Factors for different boundary conditions: (不同边界条件下的系数取值) A B S i AB 4 i A B S i AB 3 i A B S i AB i Distribution factors Aj Carry-over factors CAj n j Aj Ai Ai S S 1 A B CAB 1/ 2 i A B CAB 0 i A B CAB 1 i Stiffness factors SAj

2016/4/6 Example 12.4 E/=constant,/=6 m,1=5 m. 2.5F 1.5F 1.5F i,=EI/5 Solution: 4B4=0.625,4Bc=0.375。 4cB=0.5,4cD=0.5.4oc=0.706,4oE=0.294。 @月冷大学国产本红指核 B D 0-50.62503750.505050.5070G0294-E¥,F -1.5 2.5 -2.5 -0.469 -0.938-0.562 0.8831.7650.735-0.735 0.281 -0.301-0.301 -0.15 -0.151 0.029 0.0940.0570.0280.0540.1070.044-0.044 -1.94 0.656 -0.65G0.040.041.721.721-3.279 -0.5950.595 41/2 Fp 1.94 1.721 0.656 M(xF) C D i1≥E3 Qi,=E750.595, 3.279 国月冷大学 目土本红相学院 9
2016/4/6 9 Example 12.4 EI=constant,l1=6 m,l2=5 m. A B 1 l 2 l i1 EI / 3 i2 EI / 5 C 2FP FP D E 2 l 1 l 2 i 1 i l1 / 2 5 P 1. F 5 P 2. F 5 P 2. F 5 P 1. F BA 0.625, BC 0.375。 CB 0.5, CD 0.5。 DC 0.706, DE 0.294。 Solution: A B 0.5 C D 0.6250.375 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.7060.294 1 E 0.469 0.883 0.735 0.281 0.938 0.562 1.765 0.735 0.301 0.301 0.151 0.151 0.029 0.094 0.057 0.028 0.054 0.107 0.044 0.044 0.656 0.041 0.041 0.656 1.94 1.7211.721 3.279 0.595 0.595 A B 1 l 2 l i1 EI / 3 i2 EI / 5 C 2FP FP D E 2 l 1 l 2 i 1 i l1 / 2 3.279 1.721 0.595 1.94 0.656 ( ) M FP 1.5 1.5 2.5 2.5 ( ) FP
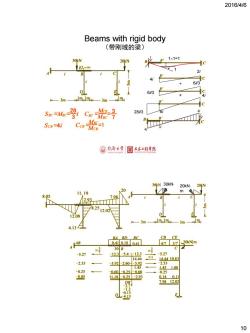
2016/4/6 Beams with rigid body (带刚域的梁) 30kN 1×1=1 20kN El1=∞ 6i/3 63 Swc -Ma MCB_3 283 ScB=4i MBC=1 CCB-MCB @月冷大学 主本1程季院 30kN 30kN. 20kN- 20kN 20 11.18 m 8.05 7.98 2.93 8.25 12.02 12.08 3m 3m 4.13 BA BD BC CB CE 天 0.410.18041 4737 _20kN]m 30B C -5.27 -12.3 -5.41-12.3 -5.27 14.44 ×1 14.4410.83 -2.53 -592 -2.60-5.92 -2.53 1.45 145 108 -0.25 0.60 -0250.6① -0.25 -80 11.18-8.25 -2.93 014 0.11 DB 29812.02 0.13 4.13 10
2016/4/6 10 Beams with rigid body (带刚域的梁) + = 11=1 1 4i 2i 6i/3 6i/3 6i 4i 28i/3 30kN m 20kN m
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)11 Slope Deflection Method(转角变位移法)(and Other Equilibrium Methods).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)10 Method of Consistent Deformations(协调变形法)(and Other Compatibility Methods).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)06 Influence Lines(影响线)and Maximum Load Effects..pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)09 More Basic Concepts of Structural Analysis.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)08 Elastic Deflections(弹性变形)of Beam and Frame Structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)07 Elastic Deflections(弹性变形)of Trusses and Frameworks..pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)05 Member Forces in Beams(梁)and Frames.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)04 Member Forces in Planar Trusses平面桥架()and Space Frameworks(空间构架).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)03 Reactions(反力).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)02 Kinematic(运动学)analysis of structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)01 Introduction.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 08 Generalized SDOF Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 07 Frequency Domain Method.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 06 Numerical Evaluation of Dynamic Response.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 05 Response to Arbitrary, Step , and Pulse Excitations.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 04 Response to harmonic and periodic excitations - Application.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 03 Response to Harmonic and Periodic Excitations.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 02.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构动力学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 01 Introduction of Structural Dynamics(负责人:陈隽).pdf
- 《力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)美国物理试题与解答(第1卷)力学.pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)13 Matrix Displacement Method(矩阵位移法).pdf
- 同济大学:《结构力学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿,打印版)16 Dynamic analysis of structures.pdf
- 吉林大学:《土质学与土力学》课程教学资源(讲义,共十一章,负责人:郑孝玉).docx
- 科学出版社:现代力学丛书《高等断裂力学》书籍PDF电子版 Advanced Fracture Mechanics(2009版,共14章,主编:王自强、陈少华).pdf
- 国家自然科学基金重大项目:《材料的损伤断裂机理和宏微观力学理论》书籍PDF电子版(共六章,清华大学出版社,主编:黄克智、肖纪美).pdf
- 《断裂力学》课程教学资源(书籍教材)断裂力学教程电子版(PDF电子书,共四章).pdf
- 清华大学出版社:《损伤力学》书籍PDF电子版(PDF电子书,无图版,共七章,主编:余寿文).pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)简介 - MEMORIAL RESOLUTION STEPHEN P. TIMOSHENKO(187-1972).pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)Helical structure of the waves propagating in a spinning Timoshenko beam.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)Timoshenko - Theory of elastic stability, 2e.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)Timoshenko - Theory of Plates and Shells, 2e.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)弹性稳定理论(第二版,中文版,共十一章).pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)铁摩辛柯《材料力学》教材书籍中文版PDF电子书(共十一章).pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)科学出版社:《板壳理论》电子书(铁摩辛柯、沃诺斯基,中文版,共十六章).pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)Stephen Prokofievitch Timoshenko, 1878-1972.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)Theory of Elasticity - TIMOSHENKO.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)Timoshenko-RSmemorial.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)板壳理论 - Timoshenko[美]S.铁摩辛柯S.沃诺斯基.pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)铁摩辛柯《工程中的振动问题》书籍PDF电子版(共五章).pdf
- 铁摩辛柯系列丛书(Timoshenko)铁摩辛柯《结构理论》原书第2版 Theory of Structures(S.P.铁木辛柯(S.P.Timoshenko)D.H.杨(D.H.Young)).pdf
