南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Petri Net

NANJING UNIVERSITY Petri Nets Lei Bu .1
Lei Bu Petri Nets 1
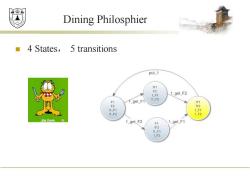
效鼎 Dining Philosphier 4 States,5 transitions put_1 IF1 1F1 1_get_F2 F1 1_get_F1 11F2 IF1 F2 1F2 11F1 1F1 11F2 1F2 M出果 1_get_F2 F1 1_get_F1 IF2 11_F1 1F2
Dining Philosphier ◼ 4 States, 5 transitions

效绵 9 States 14 Transitions 1利 2 put_back 1 put back 2.get_F1 02 1-geLF1 2.90tF2 19做F2 1F1 11 NF2 F2 2程 2_get_F2 198LF2 19tF2 1_get_F1 2.get_F2 1_got_F1 2_get_F1 2 get F1 F 1F1 宝 2 22
◼ 9 States 14 Transitions
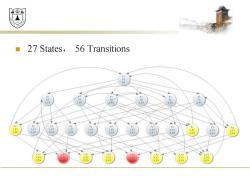
效绵 27 States,56 Transitions F2 F1 F1 F2 F3 F3 F2 1F1 1F2 F 2F3 3F3 F3 F3 F2 F2 F3 F3 F2 1F1 1F 1F2 1F2 1F2 2F 2F2 2F3 2F3 3F1 1F2 2F2 2F3 3F3 2F3 3F3 3F1 3F3 2F3 3F3 1 F1 2F2 1F2 2F2 1F2 2F3 F F3
◼ 27 States, 56 Transitions
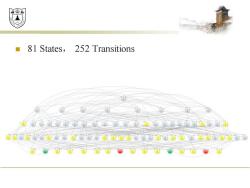
效鼎 81 States,252 Transitions 的前o白色 自dr电通©o百尚电通
◼ 81 States, 252 Transitions

效绵鼎 From automata to Petri Net automata are a theoretical and idealised model they reflect a Newtonian world-view: space time as an absolute frame of reference clockwork view of processes within this frame Carl Adam Petri has made an attempt to combine automata from theoretical CS,and pragmatic expertise from engineers:Petri Net state is distributed,transitions are localised local causality replaces global time subsystems interact by explicit communication
• automata are a theoretical and idealised model • they reflect a Newtonian world-view: • space & time as an absolute frame of reference • clockwork view of processes within this frame • Carl Adam Petri has made an attempt to combine automata from theoretical CS, and pragmatic expertise from engineers: Petri Net From automata to Petri Net • state is distributed, transitions are localised • local causality replaces global time • subsystems interact by explicit communication

效绵鼎 Petri nets-Motivation In contrast to state machines,state transitions in Petri nets are asynchronous.The ordering of transitions is partly uncoordinated;it is specified by a partial order. Therefore,Petri nets can be used to model concurrent distributed systems. Many flavors of Petri nets are in use,e.g. 0 Activity charts(UML) o Data flow graphs and marked graphs 7
Petri nets-Motivation ◼ In contrast to state machines, state transitions in Petri nets are asynchronous. The ordering of transitions is partly uncoordinated; it is specified by a partial order. ◼ Therefore, Petri nets can be used to model concurrent distributed systems. ◼ Many flavors of Petri nets are in use, e.g. Activity charts(UML) Data flow graphs and marked graphs 7

效绵 History 1962:C.A.Petri's dissertation(U.Darmstadt,W.Germany) ■ 1970:Project MAC Conf.on Concurrent Systems and Parallel Computation(MIT,USA) 1975:Conf.on Petri Nets and related Methods(MIT,USA) 1979:Course on General Net Theory of Processes and Systems (Hamburg,W.Germany) 1980:First European Workshop on Applications and Theory of Petri Nets (Strasbourg,France) 1985:First International Workshop on Timed Petri Nets(Torino,Italy)
History ◼ 1962: C.A. Petri’s dissertation (U. Darmstadt, W. Germany) ◼ 1970: Project MAC Conf. on Concurrent Systems and Parallel Computation (MIT, USA) ◼ 1975: Conf. on Petri Nets and related Methods (MIT, USA) ◼ 1979: Course on General Net Theory of Processes and Systems (Hamburg, W. Germany) ◼ 1980: First European Workshop on Applications and Theory of Petri Nets (Strasbourg, France) ◼ 1985: First International Workshop on Timed Petri Nets (Torino, Italy)

效绵县 Introduction Petri Nets:Graphical and Mathematical modeling tools 0 graphical tool ■ visual communication aid o mathematical tool state equations,algebraic equations,etc concurrent,asynchronous,distributed,parallel, nondeterministic and/or stochastic systems
Introduction ◼ Petri Nets: Graphical and Mathematical modeling tools graphical tool ◼ visual communication aid mathematical tool ◼ state equations, algebraic equations, etc ◼ concurrent, asynchronous, distributed, parallel, nondeterministic and/or stochastic systems

效绵 Informal Definition ■ The graphical presentation of a Petri net is a bipartite graph There are two kinds of nodes o Places:usually model resources or partial state of the system o Transitions:model state transition and synchronization Arcs are directed and always connect nodes of different types Tokens are resources in the places
Informal Definition ◼ The graphical presentation of a Petri net is a bipartite graph ◼ There are two kinds of nodes Places: usually model resources or partial state of the system Transitions: model state transition and synchronization ◼ Arcs are directed and always connect nodes of different types ◼ Tokens are resources in the places
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Transition System.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Turing Machine.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Properties of CFL(The Pumping Lemma for CFL’s).pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Pushdown Automata.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Regular Expression.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Context Free Grammar.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Finite Automata.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Byzantine Generals Problem.ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Use-after-free.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Taint Analysis.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Program Analysis - Data Flow Analysis.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Control Flow - Representation, Extraction and Applications.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Return-Orinted Programming(ROP Attack).ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Format String Attacks.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Control Flow Integrity.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Redundant dynamic Canary.ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Defense against Control Flow Hijack Defense - StackGuard, DEP, and ASLR.pdf
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Buffer Overflow Attack.pdf
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Software Security Overview.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Introduction to the course.pdf
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Timed Automata.ppt
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Decidability, Complexity(P, NP, NPC and related).pptx
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data Retrieval and Mining(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data Retrieval and Mining(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)大数据机器学习 Big Data Machine Learning.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)大数据机器学习 Big Data Machine Learning.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data - A Tutorial.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Parallel and Distributed Stochastic Learning - Towards Scalable Learning for Big Data Intelligence(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Coherence functions for multicategory margin-based classification methods.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Latent Wishart processes for relational kernel learning.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Latent Wishart processes for relational kernel learning(讲稿).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)agiCoFi - Tag informed collaborative filtering.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Localized content-based image retrieval through evidence region identification.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Relation regularized matrix factorization.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Relation regularized matrix factorization(讲稿).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Probabilistic relational PCA.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Gaussian process latent random field.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Multiple-instance learning via disambiguation.pdf
