南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Properties of CFL(The Pumping Lemma for CFL’s)

NANJING UNIVERSITY The Pumping Lemma for CFL's Statement Applications .1
Statement Applications The Pumping Lemma for CFL’s 1

效绵鼎 Intuition Recall the pumping lemma for regular languages. It told us that if there was a string long enough to cause a cycle in the DFA for the language,then we could "pump"the cycle and discover an infinite sequence of strings that had to be in the language. 2
Intuition ◼ Recall the pumping lemma for regular languages. ◼ It told us that if there was a string long enough to cause a cycle in the DFA for the language, then we could “ pump” the cycle and discover an infinite sequence of strings that had to be in the language. 2

效绵鼎 Intuition-(2) For CFL's the situation is a little more complicated. ■ We can always find two pieces of any sufficiently long string to“pump”in tandem. o That is:if we repeat each of the two pieces the same number of times,we get another string in the language. 3
Intuition – (2) ◼ For CFL’s the situation is a little more complicated. ◼ We can always find two pieces of any sufficiently long string to “ pump” in tandem. That is: if we repeat each of the two pieces the same number of times, we get another string in the language. 3

效绵鼎 Statement of the CFL Pumping Lemma For every context-free language L There is an integer n,such that For every string z in L of length >n There exists z uvwxy such that: 1. wwx≤n. 2 vx>0. 3.For all i>0,uv'wx'y is in L 4
Statement of the CFL Pumping Lemma For every context-free language L There is an integer n, such that For every string z in L of length > n There exists z = uvwxy such that: 1. |vwx| 0. 3. For all i > 0, uviwxiy is in L. 4

效绵鼎 Proof of the Pumping Lemma Start with a CNF grammar for L-{e). Let the grammar have m variables. Pick n=2m. Let z,of length >n,be in L. We claim(“Lemma 1”)that a parse tree with yield z must have a path of length m+2 or more. .5
Proof of the Pumping Lemma ◼ Start with a CNF grammar for L – {ε}. ◼ Let the grammar have m variables. ◼ Pick n = 2m. ◼ Let z, of length > n, be in L. ◼ We claim (“Lemma 1 ”) that a parse tree with yield z must have a path of length m+2 or more. 5
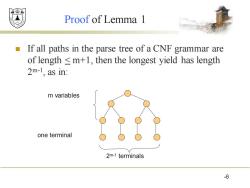
效绵鼎 Proof of Lemma 1 If all paths in the parse tree of a CNF grammar are of length m+1,then the longest yield has length 2m-1,as in: m variables one terminal 2m-1 terminals 6
Proof of Lemma 1 ◼ If all paths in the parse tree of a CNF grammar are of length < m+1, then the longest yield has length 2 m-1 , as in: 6 m variables one terminal 2 m-1 terminals

效绵县 Back to the Proof of the Pumping Lemma Now we know that the parse tree for z has a path with at least m+1 variables. Consider some longest path. There are only m different variables,so among the lowest m+1 we can find two nodes with the same label,say A. The parse tree thus looks like: 7
Back to the Proof of the Pumping Lemma ◼ Now we know that the parse tree for z has a path with at least m+1 variables. ◼ Consider some longest path. ◼ There are only m different variables, so among the lowest m+1 we can find two nodes with the same label, say A. ◼ The parse tree thus looks like: 7
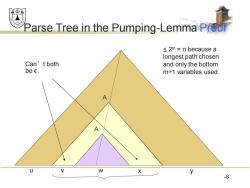
效绵易 Parse Tree in the Pumping-Lemma Preol ≤2m=n because a longest path chosen Can't both and only the bottom be c. m+1 variables used. A A V W X y 8
Parse Tree in the Pumping-Lemma Proof 8 < 2 m = n because a longest path chosen and only the bottom m+1 variables used. A A u v w x y Can’t both be ε
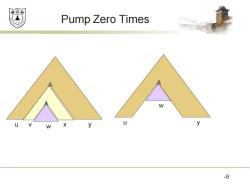
效绵鼎 Pump Zero Times A W U W X y y 9
Pump Zero Times 9 u y A v x A w u y A w

效绵鼎 Pump Twice W X y y W X .10
Pump Twice 10 u y A v x A w u y A w A v x A v x
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Pushdown Automata.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Regular Expression.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Context Free Grammar.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Finite Automata.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Byzantine Generals Problem.ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Use-after-free.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Taint Analysis.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Program Analysis - Data Flow Analysis.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Control Flow - Representation, Extraction and Applications.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Return-Orinted Programming(ROP Attack).ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Format String Attacks.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Control Flow Integrity.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Redundant dynamic Canary.ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Defense against Control Flow Hijack Defense - StackGuard, DEP, and ASLR.pdf
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Buffer Overflow Attack.pdf
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Software Security Overview.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Introduction to the course.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 入侵检测系统.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 抗恶意软件.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 网络边防.pdf
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Turing Machine.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Transition System.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Petri Net.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Timed Automata.ppt
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Decidability, Complexity(P, NP, NPC and related).pptx
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data Retrieval and Mining(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data Retrieval and Mining(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)大数据机器学习 Big Data Machine Learning.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)大数据机器学习 Big Data Machine Learning.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data - A Tutorial.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Parallel and Distributed Stochastic Learning - Towards Scalable Learning for Big Data Intelligence(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Coherence functions for multicategory margin-based classification methods.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Latent Wishart processes for relational kernel learning.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Latent Wishart processes for relational kernel learning(讲稿).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)agiCoFi - Tag informed collaborative filtering.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Localized content-based image retrieval through evidence region identification.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Relation regularized matrix factorization.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Relation regularized matrix factorization(讲稿).pdf
