南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Pushdown Automata

NANJING UNIVERSITY Pushdown Automata Definition Moves of the PDA Languages of the PDA Deterministic PDA's .1
Definition Moves of the PDA Languages of the PDA Deterministic PDA’s Pushdown Automata 1

效绵鼎 Pushdown Automata The PDA is an automaton equivalent to the CFG in language-defining power. ■ Only the nondeterministic PDA defines all the CFL's. ■ But the deterministic version models parsers. Most programming languages have deterministic PDA's. 2
Pushdown Automata ◼ The PDA is an automaton equivalent to the CFG in language-defining power. ◼ Only the nondeterministic PDA defines all the CFL’s. ◼ But the deterministic version models parsers. Most programming languages have deterministic PDA’s. 2

效绵鼎 Intuition:PDa Think of an E-NFA with the additional power that it can manipulate a stack. Its moves are determined by: The current state(of its“NFA”), 2. The current input symbol (or E),and 3. The current symbol on top of its stack. 3
Intuition: PDA ◼ Think of an ε-NFA with the additional power that it can manipulate a stack. ◼ Its moves are determined by: 1. The current state (of its “NFA”), 2. The current input symbol (or ε), and 3. The current symbol on top of its stack. 3
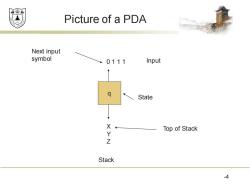
赖绵县 Picture of a PDa Next input symbol 0111 Input State X Top of Stack Y Z Stack 4
Picture of a PDA 4 q 0 1 1 1 X Y Z State Stack Top of Stack Input Next input symbol

效绵鼎 Intuition:PDA-(2) Being nondeterministic,the PDA can have a choice of next moves. In each choice,the PDA can: 1.Change state,and also 2.Replace the top symbol on the stack by a sequence of zero or more symbols. u Zero symbols=“pop.” Many symbols=sequence of“pushes.” .5
Intuition: PDA – (2) ◼ Being nondeterministic, the PDA can have a choice of next moves. ◼ In each choice, the PDA can: 1. Change state, and also 2. Replace the top symbol on the stack by a sequence of zero or more symbols. u Zero symbols = “ pop.” u Many symbols = sequence of “pushes.” 5
效绵鼎 PDA Formalism A PDA is described by: 1.A finite set of states (Q,typically). 2.An input alphabet(Σ,typically) 3. A stack alphabet(「,typically). 4. A transition function(δ,typically) 5. A start state (qo,in Q,typically) 6. A start symbol(Zo,in「,typically). 7.A set of final states (FQ,typically) 6
PDA Formalism ◼ A PDA is described by: 1. A finite set of states (Q, typically). 2. An input alphabet (Σ, typically). 3. A stack alphabet (Γ, typically). 4. A transition function (δ, typically). 5. A start state (q0 , in Q, typically). 6. A start symbol (Z0 , in Γ, typically). 7. A set of final states (F ⊆ Q, typically). 6

效绵鼎 Conventions ■ a,b,..are input symbols. 0 But sometimes we allow e as a possible value. ■.,X,Y,Z are stack symbols. ...w,X,y,z are strings of input symbols. a,B,...are strings of stack symbols. 7
Conventions ◼ a, b, … are input symbols. But sometimes we allow ε as a possible value. ◼ …, X, Y, Z are stack symbols. ◼ …, w, x, y, z are strings of input symbols. ◼ , ,… are strings of stack symbols. 7
效绵鼎 The Transition Function Takes three arguments: 1.A state,in Q. 2.An input,which is either a symbol in or E. 3. A stack symbol in「. 6(q,a,Z)is a set of zero or more actions of the form (p,a). o p is a state;a is a string of stack symbols. ◆8
The Transition Function ◼ Takes three arguments: 1. A state, in Q. 2. An input, which is either a symbol in Σ or ε. 3. A stack symbol in Γ. ◼ δ(q, a, Z) is a set of zero or more actions of the form (p, ). p is a state; is a string of stack symbols. 8

效绵鼎 Actions of the pda If 8(q,a,Z)contains (p,a)among its actions,then one thing the PDA can do in state q,with a at the front of the input,and Z on top of the stack is: 1. Change the state to p. 2. Remove a from the front of the input(but a may be e) 3. Replace Z on the top of the stack by a. 9
Actions of the PDA ◼ If δ(q, a, Z) contains (p, ) among its actions, then one thing the PDA can do in state q, with a at the front of the input, and Z on top of the stack is: 1. Change the state to p. 2. Remove a from the front of the input (but a may be ε). 3. Replace Z on the top of the stack by . 9

效绵鼎 Example:PDA Design a PDA to accept {on1n |n1). The states: q=start state.We are in state q if we have seen only 0's so far. o p=we've seen at least one 1 and may now proceed only if the inputs are 1's. o f=final state;accept. .10
Example: PDA ◼ Design a PDA to accept {0n1 n | n > 1}. ◼ The states: q = start state. We are in state q if we have seen only 0’s so far. p = we’ve seen at least one 1 and may now proceed only if the inputs are 1’s. f = final state; accept. 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Regular Expression.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Context Free Grammar.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Finite Automata.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Byzantine Generals Problem.ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Use-after-free.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Taint Analysis.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Program Analysis - Data Flow Analysis.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Control Flow - Representation, Extraction and Applications.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Return-Orinted Programming(ROP Attack).ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Format String Attacks.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Control Flow Integrity.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Redundant dynamic Canary.ppt
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Defense against Control Flow Hijack Defense - StackGuard, DEP, and ASLR.pdf
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Buffer Overflow Attack.pdf
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Software Security Overview.pptx
- 南京大学:《软件安全 Software Security》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Introduction to the course.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 入侵检测系统.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 抗恶意软件.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 网络边防.pdf
- 海南大学:《网络安全技术》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 无线网安全性.pdf
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Properties of CFL(The Pumping Lemma for CFL’s).pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Turing Machine.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Transition System.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Petri Net.pptx
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Timed Automata.ppt
- 南京大学:《形式语言与自动机 Formal Languages and Automata》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Decidability, Complexity(P, NP, NPC and related).pptx
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data Retrieval and Mining(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data Retrieval and Mining(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)大数据机器学习 Big Data Machine Learning.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)大数据机器学习 Big Data Machine Learning.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Learning to Hash for Big Data - A Tutorial.pdf
- 《大数据 Big Data》课程教学资源(参考文献)Parallel and Distributed Stochastic Learning - Towards Scalable Learning for Big Data Intelligence(南京大学:李武军).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Coherence functions for multicategory margin-based classification methods.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Latent Wishart processes for relational kernel learning.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Latent Wishart processes for relational kernel learning(讲稿).pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)agiCoFi - Tag informed collaborative filtering.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Localized content-based image retrieval through evidence region identification.pdf
- 《人工智能、机器学习与大数据》课程教学资源(参考文献)Relation regularized matrix factorization.pdf
