《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II - Elongation and Termination

Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation Il: Elongation and Termination Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission r d for reproduction or dis
Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II: Elongation and Termination

18.1 Direction of Polypeptide Synthesis and mRNA Translation ·Messenger RNAs are read in the5'→3' direction This is the same direction in which they are synthesized ·Proteins are made in the amino→carboxyl direction This means that the amino terminal amino acid is added first 18-2
18-2 18.1 Direction of Polypeptide Synthesis and mRNA Translation • Messenger RNAs are read in the 5’→3’ direction • This is the same direction in which they are synthesized • Proteins are made in the amino→carboxyl direction • This means that the amino terminal amino acid is added first

Strategy to Determine Direction of Translation Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. (a) HJleucine just added Finish abeling 5N8 。8 period N 00000 0000。●0 1↑2↑3↑4↑5↑6 Trypsin,isolate peptides, plot label vs.peptide position (N-term.) Peptide number (C-term.) 18-3
18-3 Strategy to Determine Direction of Translation

18.2 The Genetic Code The term genetic code refers to the set of 3-base code words (codons)in mRNA that represent the 20 amino acids in proteins Basic questions were answered about translation in the process of "breaking"the genetic code 18-4
18-4 18.2 The Genetic Code • The term genetic code refers to the set of 3-base code words (codons) in mRNA that represent the 20 amino acids in proteins • Basic questions were answered about translation in the process of “breaking” the genetic code

Nonoverlapping Codons Each base is part of at most one codon in nonoverlapping codons In an overlapping code,one base may be part of two or even three codones 18-5
18-5 Nonoverlapping Codons • Each base is part of at most one codon in nonoverlapping codons • In an overlapping code, one base may be part of two or even three codones

No Gaps in the Code If the code contained untranslated gaps or “commas”,mutations adding or subtracting a base from the message might change a few codons ·Vould still expect ribosome to be back“on track"after the next such comma Mutations might frequently be lethal Many cases of mutations should occur just before a comma and have little,if any,effect 18-6
18-6 No Gaps in the Code • If the code contained untranslated gaps or “commas”, mutations adding or subtracting a base from the message might change a few codons • Would still expect ribosome to be back “on track” after the next such comma • Mutations might frequently be lethal – Many cases of mutations should occur just before a comma and have little, if any, effect

Frameshift Mutations Frameshift mutations 。Translation starts AUGCAGCCAACG Insert an extra base AUXGCAGCCAACG -Extra base changes not only the codon in which is appears,but every codon from that point on -The reading frame has shifted one base to the left Code with commas Each codon is flanked by one or more untranslated bases -Commas would serve to set off each codon so that ribosomes recognize it 。Translation starts AUGZCAGZCCAZACGZ Insert an extra base AUXGZCAGZCCAZACGZ -First codon wrong,all others separated by Z,translated normally 18-7
18-7 Frameshift Mutations Frameshift mutations • Translation starts AUGCAGCCAACG • Insert an extra base AUXGCAGCCAACG – Extra base changes not only the codon in which is appears, but every codon from that point on – The reading frame has shifted one base to the left Code with commas • Each codon is flanked by one or more untranslated bases – Commas would serve to set off each codon so that ribosomes recognize it • Translation starts AUGZCAGZCCAZACGZ • Insert an extra base AUXGZCAGZCCAZACGZ – First codon wrong, all others separated by Z, translated normally
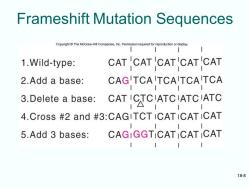
Frameshift Mutation Sequences Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. 1.Wild-type: CATCAT CAT'CATCAT 2.Add a base: CAG TCA TCATCA TCA 3.Delete a base: CAT ICTCIATCIATCIATC 4.Cross #2 and #3:CAGITCT ICATICAT ICAT 5.Add 3 bases: CAGIGGTICAT ICAT ICAT 18-8
18-8 Frameshift Mutation Sequences

The Triplet Code The genetic code is a set of three-base code words,or codons -In mRNA,codons instruct the ribosome to incorporate specific amino acids into a polypeptide Code is nonoverlapping -Each base is part of only one codon Devoid of gaps or commas -Each base in the coding region of an mRNA is part of a codon 18-9
18-9 The Triplet Code • The genetic code is a set of three-base code words, or codons – In mRNA, codons instruct the ribosome to incorporate specific amino acids into a polypeptide • Code is nonoverlapping – Each base is part of only one codon • Devoid of gaps or commas – Each base in the coding region of an mRNA is part of a codon

Coding Properties of Synthetic mRNAs CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. (a) UCUCUCUCUCUc Ser Leu Ser Leu (b) DUCUUCUUCUUC or UUCUUCUUcUuc 0 DUCUUCUUCUUc PhePhe Phe Phe Ser Ser Ser LeuLeuLeu UAUCUAUCUAUC (c) Tyr Leu Ser lle 18-10
18-10 Coding Properties of Synthetic mRNAs
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I - initiation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Messenger RNA Processing II - Capping and Polyadenylation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I - Splicing.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 08 Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription、Chapter 09 DNA-protein interactions in Prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 07 Operons - Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 06 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 05 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 04 Molecular Cloning Methods.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 A Brief History、Chapter 02 The Molecular Nature of Genes Molecular Biology、Chapter 03 An Introduction to Gene Function.ppt
- 《分子生物学》课程各章作业习题(含答案).docx
- 《分子生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,共二十一章).docx
- 海南大学:《生物统计学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章).pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程授课教授.pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程教学大纲 Biology of Microorganisms.pdf
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲教师:谭志琼).doc
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 DNA Replication I - Basic Mechanism and Enzymology.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 DNA Replication Ⅱ - Detailed Mechanism.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Homologous Recombination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Transposition(转座).ppt
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲 Cell Biology(生科生技专业,负责人:计巧灵).doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案1-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-3.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-3.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案4-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案4-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案5-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案5-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案6-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案6-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案7-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案7-2.doc
