《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 06 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes

Chapter 6 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes
Chapter 6 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes
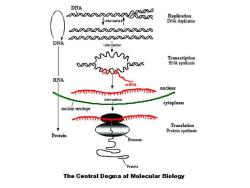
DNA aooogo Replication 叶 DNA duplicates NNV八X000a0 N八V八aa八NN DNA Transcription RNA synthesis RNA MRNA nucleus cytoplasm nuclear envelope T Translation Protein synthesis Protein Protein The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
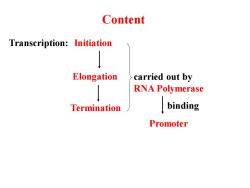
Content Transcription:Initiation Elongation carried out by RNA Polymerase Termination binding Promoter
Transcription: Initiation Elongation Termination binding carried out by RNA Polymerase Promoter Content
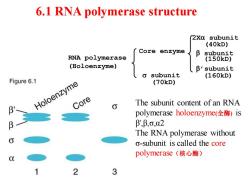
6.1 RNA polymerase structure 2Xa subunit (40kD) Core enzyme 】 B subunit RNA polymerase (150kD) (Holoenzyme) B'subunit subunit (160kD) Figure 6.1 (70kD) Holoenzyme Core The subunit content of an RNA polymerase holoenzyme(全酶)is β,β,o,02 The RNA polymerase without o-subunit is called the core polymerase(核心酶) 2 3
6.1 RNA polymerase structure RNA polymerase (Holoenzyme) Core enzyme 2Xa subunit b subunit b’subunit s subunit (150kD) (160kD) (40kD) (70kD) The subunit content of an RNA polymerase holoenzyme(全酶) is β',β,σ,α2 The RNA polymerase without σ-subunit is called the core polymerase(核心酶)
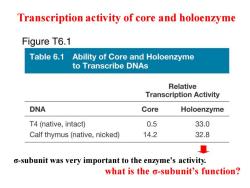
Transcription activity of core and holoenzyme Figure T6.1 Table 6.1 Ability of Core and Holoenzyme to Transcribe DNAs Relative Transcription Activity DNA Core Holoenzyme T4(native,intact) 0.5 33.0 Calf thymus(native,nicked) 14.2 32.8 o-subunit was very important to the enzyme's activity. what is the o-subunit's function?
Transcription activity of core and holoenzyme σ-subunit was very important to the enzyme's activity. what is the σ-subunit’s function?

Sigma(o)as a Specificity Factor Immediate early (0-2min) Delayed early (2-10min) 立即早期 延迟早期 3 Late(10-25min)) Holoenzyme 晚期 Immediate early (0-2min) Core enzyme o factor confers specificity to the polymerase. o directs polymerase to initiate at specific sites,called promoters. How can we confirm the o-subunit's function by experiment?
5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ Immediate early (0-2min) 立即早期 Delayed early (2-10min) 延迟早期 Late (10-25min) 晚期 Immediate early (0-2min) 5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ Holoenzyme Core enzyme 5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ s factor confers specificity to the polymerase. s directs polymerase to initiate at specific sites, called promoters. How can we confirm the σ-subunit’s function by experiment? Sigma (σ) as a Specificity Factor
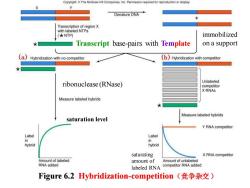
Copyright:The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. X Y Denature DNA Transcription of region X with labeled NTPs (大NTP) immobilized Transcript base-pairs with Template on a support (a) Hybridization with no competitor bHybridization with competitor Unlabeled ribonuclease(RNase) competitor X RNAS Measure labeled hybrids Measure labeled hybrids saturation level Y RNA competitor Label Label n hybrid hybrid saturating X RNA competitor Amount of labeled amount of Amount of unlabeled RNA added labeled RNA cmpetitor RNA added Figure6.2 Hybridization-.competition(竞争杂交)
Figure 6.2 Hybridization-competition(竞争杂交) Transcript base-pairs with Template immobilized on a support ribonuclease (RNase) saturation level saturating amount of labeled RNA
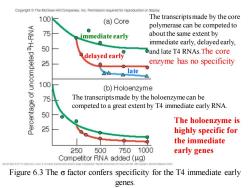
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. 100 The transcripts made by the core (a)Core polymerase can be competed to 75 immediate early about the same extent by immediate early,delayed early, 50 and late T4 RNAs.The core delayed early 25 enzyme has no specificity △△ late △ 100 (b)Holoenzyme 75 The transcripts made by the holoenzyme can be competed to a great extent by T4 immediate early RNA. 50 The holoenzyme is 25 highly specific for the immediate 250 500 7501000 early genes Competitor RNA added (ug) Figure 6.3 The o factor confers specificity for the T4 immediate early genes
Figure 6.3 The σ factor confers specificity for the T4 immediate early genes. The holoenzyme is highly specific for the immediate early genes The transcripts made by the core polymerase can be competed to about the same extent by immediate early, delayed early, and late T4 RNAs.The core enzyme has no specificity immediate early delayed early late The transcripts made by the holoenzyme can be competed to a great extent by T4 immediate early RNA

SUMMARY The key player in the transcription process is RNA polymerase.The E.coli enzyme is composed of a core,which contains the basic transcription machinery,and a o-factor,which directs the core to transcribe specific genes
SUMMARY The key player in the transcription process is RNA polymerase. The E.coli enzyme is composed of a core, which contains the basic transcription machinery, and a σ–factor, which directs the core to transcribe specific genes

Figure T6.1 Table 6.1 Ability of Core and Holoenzyme to Transcribe DNAs Relative Transcription Activity DNA Core Holoenzyme T4(native,intact) 0.5 33.0 Calf thymus(native,nicked) ★14.2 32.8 why was core RNA polymerase still capable of transcribing nicked DNA,but not intact DNA? Nicks and gaps in DNA provide ideal initiation sites for RNA polymerase (nonspecific when o was present,the holoenzyme could recognize the authentic RNA polymerase binding sites and begin transcription. Promoter
why was core RNA polymerase still capable of transcribing nicked DNA, but not intact DNA? Nicks and gaps in DNA provide ideal initiation sites for RNA polymerase (nonspecific ) when σ was present, the holoenzyme could recognize the authentic RNA polymerase binding sites and begin transcription. Promoter
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 05 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 04 Molecular Cloning Methods.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 A Brief History、Chapter 02 The Molecular Nature of Genes Molecular Biology、Chapter 03 An Introduction to Gene Function.ppt
- 《分子生物学》课程各章作业习题(含答案).docx
- 《分子生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,共二十一章).docx
- 海南大学:《生物统计学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章).pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程授课教授.pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程教学大纲 Biology of Microorganisms.pdf
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲教师:谭志琼).doc
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程教学大纲 Agricultural Microbiology.doc
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第14章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第13章 微生物类群.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第12章 微生物的进化、系统发育和分类鉴定.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第11章 微生物生态.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 微生物与基因工程.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第08章 微生物遗传.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第07章 病毒.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 微生物的生长繁殖及其控制.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第05章 微生物的代谢.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第04章 微生物的营养.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 07 Operons - Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 08 Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription、Chapter 09 DNA-protein interactions in Prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I - Splicing.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Messenger RNA Processing II - Capping and Polyadenylation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I - initiation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II - Elongation and Termination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 DNA Replication I - Basic Mechanism and Enzymology.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 DNA Replication Ⅱ - Detailed Mechanism.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Homologous Recombination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Transposition(转座).ppt
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲 Cell Biology(生科生技专业,负责人:计巧灵).doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案1-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-3.doc
