《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes
Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Courtesy Nicola P.Pavletich,Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center,Science(15 July 1994)cover.Copyright AAAS
Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes

12.1 Categories of Activators(激活因子) Activators (gene-specific TF)can stimulate or inhibit transcription by RNA polymerase ll Structure is composed of at least 2 functional domains(功能域) - DNA-binding domain(DNA结合域) -Transcription-activation domain(转录激活域) - Many also have a dimerization domain(二聚 作用域) 12-2
12-2 12.1 Categories of Activators (激活因子) ✓ Activators (gene-specific TF) can stimulate or inhibit transcription by RNA polymerase II ✓ Structure is composed of at least 2 functional domains (功能域) – DNA-binding domain (DNA结合域) – Transcription-activation domain (转录激活域) – Many also have a dimerization domain (二聚 作用域)

DNA-Binding Domains √Protein domain(蛋白质结构域)isan independently folded region of a protein DNA-binding domains have DNA-binding motif (DNA结合基序) -Part of the domain having characteristic shape specialized for specific DNA binding -Most DNA-binding motifs fall into 3 classes 1.Zinc-Containing Modules(含锌组件) 2.Homeodomains(同源域) 3.bZIP and bHLH Motifs(Bzip和bHLH基序) 12-3
12-3 DNA-Binding Domains ✓ Protein domain (蛋白质结构域) is an independently folded region of a protein ✓ DNA-binding domains have DNA-binding motif (DNA结合基序) – Part of the domain having characteristic shape specialized for specific DNA binding – Most DNA-binding motifs fall into 3 classes 1. Zinc-Containing Modules (含锌组件) 2. Homeodomains (同源域) 3. bZIP and bHLH Motifs (Bzip和bHLH基序)

Zinc-Containing Modules There are at least 3 kinds of zinc-containing modules that act as DNA-binding motifs All use one or more zinc ions to create a shape to fit an a-helix of the motif into the DNA major groove -Zinc fingers(锌指):TFlA,Sp1 -Zinc modules(锌组件):nuclear receptor -Modules containing 2 zinc and 6 cysteines (含两个锌离子和六个半胱氨酸组件):GAL4 12-4
12-4 Zinc-Containing Modules ✓ There are at least 3 kinds of zinc-containing modules that act as DNA-binding motifs ✓ All use one or more zinc ions to create a shape to fit an a-helix of the motif into the DNA major groove – Zinc fingers (锌指): TFII A,Sp1 – Zinc modules (锌组件):nuclear receptor – Modules containing 2 zinc and 6 cysteines (含两个锌离子和六个半胱氨酸组件):GAL4

Homeodomains These domains contain about 60 amino acids Resemble the helix-turn-helix proteins in structure and function Found in a variety of activators Originally identified in homeobox proteins (同源盒蛋白)regulating fruit fly development 12-5
12-5 Homeodomains ✓These domains contain about 60 amino acids ✓Resemble the helix-turn-helix proteins in structure and function ✓Found in a variety of activators ✓Originally identified in homeobox proteins (同源盒蛋白) regulating fruit fly development
bZIP and bHLH Motifs A number of transcription factors have a highly basic DNA-binding motif linked to protein dimerization motifs -Leucine zippers -Helix-loop-helix Examples include: -CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein -MyoD protein 12-6
12-6 bZIP and bHLH Motifs ✓ A number of transcription factors have a highly basic DNA-binding motif linked to protein dimerization motifs – Leucine zippers – Helix-loop-helix ✓Examples include: – CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein – MyoD protein

Transcription-Activating Domains Most activators have one of these domains, Some have more than one These domains fall into three classes: - Acidic domains(酸性域)such as yeast GAL4 with 11 acidic amino acids out of 49 amino acids in the domain Glutamine-rich domains(谷酰胺富含域) include Sp1 having 2 that are 25%glutamine Proline-rich domains(脯氨酸富含域)such as CTF which has a domain of 84 amino acids, 19 proline 12-7
12-7 Transcription-Activating Domains ✓ Most activators have one of these domains, Some have more than one ✓ These domains fall into three classes: – Acidic domains (酸性域) such as yeast GAL4 with 11 acidic amino acids out of 49 amino acids in the domain – Glutamine-rich domains (谷酰胺富含域) include Sp1 having 2 that are 25% glutamine – Proline-rich domains (脯氨酸富含域) such as CTF which has a domain of 84 amino acids, 19 proline

12.2 Structures of the DNA-Binding Motifs of Activators DNA-binding domains have well-defined structures √X-ray crystallographic(X射线晶体衍射)studies have shown how these structures interact with their DNA targets √Interaction domains forming dimers(二聚体), or tetramers(四聚体),have also been described Most classes of DNA-binding proteins can't bind DNA in monomer form 12-8
12-8 12.2 Structures of the DNA-Binding Motifs of Activators ✓ DNA-binding domains have well-defined structures ✓ X-ray crystallographic (X射线晶体衍射) studies have shown how these structures interact with their DNA targets ✓ Interaction domains forming dimers (二聚体), or tetramers (四聚体), have also been described ✓ Most classes of DNA-binding proteins can’t bind DNA in monomer form

Zinc Fingers Described by Klug in TFIIIA Nine repeats of a 30-residue element: -2 closely spaced cysteines(半胱氦 followed 12 amino acids later by 2 closely spaced histidines(组氨酸) -Rich in zinc,enough for 1 zinc ion per repeat -Each zinc ion is complexed by 2 cysteines and 2 histidines in each repeat to form the finger-shaped structure or domain -Specific recognition between the zinc finger and its DNA target occurs in the major groove 12-9
12-9 Zinc Fingers ✓Described by Klug in TFIIIA ✓Nine repeats of a 30-residue element: –2 closely spaced cysteines (半胱氨 酸) followed 12 amino acids later by 2 closely spaced histidines (组氨酸) –Rich in zinc, enough for 1 zinc ion per repeat –Each zinc ion is complexed by 2 cysteines and 2 histidines in each repeat to form the finger-shaped structure or domain –Specific recognition between the zinc finger and its DNA target occurs in the major groove Zn
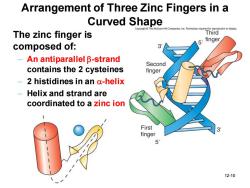
Arrangement of Three Zinc Fingers in a Curved Shape he McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required fo roduction or display The zinc finger is Third finger composed of: An antiparallel B-strand Second contains the 2 cysteines finger 2 histidines in an a-helix Helix and strand are coordinated to a zinc ion First finger 6 12-10
12-10 Arrangement of Three Zinc Fingers in a Curved Shape The zinc finger is composed of: – An antiparallel b-strand contains the 2 cysteines – 2 histidines in an a-helix – Helix and strand are coordinated to a zinc ion
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 08 Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription、Chapter 09 DNA-protein interactions in Prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 07 Operons - Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 06 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 05 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 04 Molecular Cloning Methods.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 A Brief History、Chapter 02 The Molecular Nature of Genes Molecular Biology、Chapter 03 An Introduction to Gene Function.ppt
- 《分子生物学》课程各章作业习题(含答案).docx
- 《分子生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,共二十一章).docx
- 海南大学:《生物统计学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章).pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程授课教授.pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程教学大纲 Biology of Microorganisms.pdf
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲教师:谭志琼).doc
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程教学大纲 Agricultural Microbiology.doc
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第14章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第13章 微生物类群.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第12章 微生物的进化、系统发育和分类鉴定.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第11章 微生物生态.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 微生物与基因工程.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I - Splicing.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Messenger RNA Processing II - Capping and Polyadenylation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I - initiation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II - Elongation and Termination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 DNA Replication I - Basic Mechanism and Enzymology.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 DNA Replication Ⅱ - Detailed Mechanism.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Homologous Recombination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Transposition(转座).ppt
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲 Cell Biology(生科生技专业,负责人:计巧灵).doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案1-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-3.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-3.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案4-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案4-2.doc
