《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I - Splicing

Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies.Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I:Splicing Dr.David Spector/Peter Arnold,Inc
Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I: Splicing

14.1 Genes in Pieces Consider the sequence of the human B-globin (β-球蛋白)gene as a sentence: This is bhgty the human B-globin qwtzptlrbn gene. Two italicized regions make no sense -( Contain sequences unrelated to the globin coding sequences surrounding them Called intervening sequences(插入序列,IVSs) - Usually called introns(内含子) Parts of the gene making sense -Coding regions - Eons(外显子) Some lower eukaryotic genes have no introns 14-2
14-2 14.1 Genes in Pieces ✓ Consider the sequence of the human b-globin (b-球蛋白) gene as a sentence: This is bhgty the human b-globin qwtzptlrbn gene. ✓ Two italicized regions make no sense – Contain sequences unrelated to the globin coding sequences surrounding them – Called intervening sequences (插入序列, IVSs) – Usually called introns (内含子) ✓ Parts of the gene making sense – Coding regions – Exons (外显子) ✓ Some lower eukaryotic genes have no introns

RNA Splicing Introns are present in genes but not in mature RNA Process of cutting introns out of immature RNAs and stitching together the exons to form final product is RNA splicing (RNA 接) 14-3
14-3 RNA Splicing ✓Introns are present in genes but not in mature RNA ✓Process of cutting introns out of immature RNAs and stitching together the exons to form final product is RNA splicing (RNA剪 接)
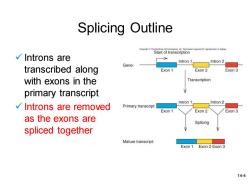
Splicing Outline CopyrightTe MeGraw-Hll Co Start of transcription √Introns are Intron 1 Intron 2 transcribed along Gene: Exon 1 Exon 2 Exon 3 with exons in the Transcription primary transcript Intron 1 Intron 2 √Introns are removed Primary transcript: Exon 1 Exon 2 Exon 3 as the exons are Splicing spliced together Mature transcript: Exon 1 Exon 2 Exon 3 14-4
14-4 Splicing Outline ✓ Introns are transcribed along with exons in the primary transcript ✓ Introns are removed as the exons are spliced together

Stages of RNA Splicing Messenger RNA synthesis in eukaryotes occurs in stages √First stage: Synthesis of primary transcript product -This is an mRNA precursor containing introns copied from the gene if present - Precursor is part of a pool of large nuclear RNAs- heterogeneous nuclear RNA(核不均一RNA,hnRNAs) √Second stage: -mRNA maturation - Removal of introns in a process called splicing 14-5
14-5 Stages of RNA Splicing ✓ Messenger RNA synthesis in eukaryotes occurs in stages ✓ First stage: – Synthesis of primary transcript product – This is an mRNA precursor containing introns copied from the gene if present – Precursor is part of a pool of large nuclear RNAs – heterogeneous nuclear RNA (核不均一RNA, hnRNAs) ✓ Second stage: – mRNA maturation – Removal of introns in a process called splicing

Splicing Signals(剪接信号) Splicing signals in nuclear mRNA precursors are remarkably uniform -First 2 bases of introns are GU Last 2 are AG -Exon/GU-intron-AG/exon 5'-and 3'-splice sites have consensus sequences extending beyond GU and AG motifs 一 5'-AG/GUAAGU-intron-YNCURAC-YnNAG/exon Y:pyrimidine;Yn:about 9 pyrimidine;R:purine; Whole consensus sequences are important to proper splicing Abnormal splicing can occur when the consensus sequences are mutated 14-6
14-6 Splicing Signals (剪接信号) ✓ Splicing signals in nuclear mRNA precursors are remarkably uniform – First 2 bases of introns are GU – Last 2 are AG – Exon/ GU-intron- AG/ exon ✓ 5’- and 3’-splice sites have consensus sequences extending beyond GU and AG motifs – 5’- AG/ GUAAGU-intron- YNCURAC-YnNAG/ exon Y: pyrimidine; Yn: about 9 pyrimidine; R: purine; ✓ Whole consensus sequences are important to proper splicing ✓ Abnormal splicing can occur when the consensus sequences are mutated

14.2 Mechanism of Splicing of Nuclear mRNA Precursors Intermediate in nuclear mRNA precursor splicing is branched-looks like a lariat(套索) √2-step model -2'-OH group of adenosine nucleotide in middle of intron attacks phosphodiester bond between 1st exon and G beginning of intron Forms loop of the lariat Separates first exon from intron -3'-OH left at end of 1st exon attacks phosphodiester bond linking intron to 2nd exon Forms the exon-exon phosphodiester bond Releases intron in lariat form at same time 14-7
14-7 14.2 Mechanism of Splicing of Nuclear mRNA Precursors ✓ Intermediate in nuclear mRNA precursor splicing is branched – looks like a lariat (套索) ✓ 2-step model – 2’-OH group of adenosine nucleotide in middle of intron attacks phosphodiester bond between 1 st exon and G beginning of intron • Forms loop of the lariat • Separates first exon from intron – 3’-OH left at end of 1st exon attacks phosphodiester bond linking intron to 2nd exon • Forms the exon-exon phosphodiester bond • Releases intron in lariat form at same time
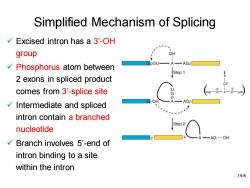
Simplified Mechanism of Splicing Excised intron has a 3'-OH group Phosphorus atom between Step 1 2 exons in spliced product comes from 3'-splice site AGD Intermediate and spliced intron contain a branched Step 2 nucleotide -AG-OH Branch involves 5'-end of intron binding to a site within the intron 14-8
14-8 Simplified Mechanism of Splicing ✓ Excised intron has a 3’-OH group ✓ Phosphorus atom between 2 exons in spliced product comes from 3’-splice site ✓ Intermediate and spliced intron contain a branched nucleotide ✓ Branch involves 5’-end of intron binding to a site within the intron

Signal at the Branch Along with consensus sequences at 5'-and 3'-ends of nuclear introns,branchpoint consensus sequences also occur Yeast sequence invariant:UACUAAC Higher eukaryote consensus sequence is more variable Branched nucleotide is final A in the sequence Wild-type Spliced Mutant #1 Not spliced Mutant#2 Aberrantly splicec Mutant #3 Aberrantly spliced 14-9
14-9 Signal at the Branch ✓ Along with consensus sequences at 5’- and 3’-ends of nuclear introns, branchpoint consensus sequences also occur ✓ Yeast sequence invariant: UACUAAC ✓ Higher eukaryote consensus sequence is more variable ✓ Branched nucleotide is final A in the sequence

Spliceosomes(剪接体) Splicing takes place on a particle called a spliceosome Spliceosomes contain the pre-mRNA -Along with snRNPs (small nuclear ribonuclearprotein,核内小核糖核蛋白体)and protein splicing factors -These recognize key splicing signals and orchestrate(组织)the splicing process 14-10
14-10 Spliceosomes (剪接体) ✓Splicing takes place on a particle called a spliceosome ✓Spliceosomes contain the pre-mRNA – Along with snRNPs (small nuclear ribonuclearprotein, 核内小核糖核蛋白体) and protein splicing factors – These recognize key splicing signals and orchestrate (组织) the splicing process
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 08 Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription、Chapter 09 DNA-protein interactions in Prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 07 Operons - Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 06 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 05 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 04 Molecular Cloning Methods.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 A Brief History、Chapter 02 The Molecular Nature of Genes Molecular Biology、Chapter 03 An Introduction to Gene Function.ppt
- 《分子生物学》课程各章作业习题(含答案).docx
- 《分子生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,共二十一章).docx
- 海南大学:《生物统计学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章).pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程授课教授.pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程教学大纲 Biology of Microorganisms.pdf
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲教师:谭志琼).doc
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程教学大纲 Agricultural Microbiology.doc
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第14章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第13章 微生物类群.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第12章 微生物的进化、系统发育和分类鉴定.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Messenger RNA Processing II - Capping and Polyadenylation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I - initiation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II - Elongation and Termination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 DNA Replication I - Basic Mechanism and Enzymology.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 DNA Replication Ⅱ - Detailed Mechanism.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Homologous Recombination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Transposition(转座).ppt
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲 Cell Biology(生科生技专业,负责人:计巧灵).doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案1-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-3.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案3-3.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案4-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案4-2.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案5-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案5-2.doc
