《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 04 Molecular Cloning Methods
CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 4 Molecular Cloning Methods
Chapter 4 Molecular Cloning Methods

Why do biologists must clone genes? The molecular structure and function of the human growth hormone(hGH)gene [base sequence?promoter? Hypopituitary(垂体功能衰减的)d小warfism(侏儒症)?] You have to purify enough of the gene to study-probably about a milligram.A milligram is an overwhelming amount when you imagine purifying it from whole human DNA.And you would not know how to separate the gene from all the rest of the DNA. Gene cloning neatly solves these problems.In this chapter we will see how to clone genes in bacteria and in eukaryotes( 核细胞)
Why do biologists must clone genes? The molecular structure and function of the human growth hormone(hGH)gene [base sequence? promoter? Hypopituitary (垂体功能衰减的) dwarfism (侏儒症)?] You have to purify enough of the gene to study-probably about a milligram. A milligram is an overwhelming amount when you imagine purifying it from whole human DNA.And you would not know how to separate the gene from all the rest of the DNA. Gene cloning neatly solves these problems. In this chapter we will see how to clone genes in bacteria and in eukaryotes(真 核细胞).
4.1 Gene Cloning(Molecular Cloning) Clone:a group of identical cells or organisms/molecular Gene cloning:The process of inserting a piece of DNA molecular (foreign gene into a DNA carrier (vector)and making multiple copies of the DNA of interest in a host cell,such as bacteria Purposes of molecular cloning 1.Isolation of a gene from a pool of genetic materials 2.Amplification of a gene 3.Manipulation of a piece of DNA for further experiments Vector(DNA carrier):Plasmids(质粒)/Bateriophage(噬菌体 YAC(yeast artificial chromosome,人工酵母染色体)/BAC(Bacteria artificial chromosome,人工细菌染色体)/Cosmids(粘粒)Virus Restriction Endonucleases,ligase
4.1 Gene Cloning(Molecular Cloning) Clone:a group of identical cells or organisms/molecular Gene cloning: The process of inserting a piece of DNA molecular (foreign gene ) into a DNA carrier (vector) and making multiple copies of the DNA of interest in a host cell, such as bacteria Purposes of molecular cloning 1. Isolation of a gene from a pool of genetic materials 2. Amplification of a gene 3. Manipulation of a piece of DNA for further experiments Vector (DNA carrier): Plasmids(质粒)/Bateriophage(噬菌体 /YAC(yeast artificial chromosome, 人工酵母染色体)/ BAC(Bacteria artificial chromosome, 人工细菌染色体)/ Cosmids(粘粒)/Virus Restriction Endonucleases, ligase

The usual procedure of a gene cloning experiment 1 Source DNA/RNA and vector To clone the gene that induce cervical(子宫颈的)cancer Biopsies(活检组织) DNA extract the tissue DNA/RNA ector DNA 2 DNA construct separate the target gene Restriction Endonucleases Ligase DNA comstruct Recombinant 3 Transformation Introduce DNA into host cell lsolate cells with cloned gene separate individual cells 转化 ho以cel colonies clone the gene by cloning its host
The usual procedure of a gene cloning experiment To clone the gene that induce cervical(子宫颈的) cancer Biopsies(活检组织) extract the tissue DNA/RNA 1 Source DNA/RNA and vector 2 DNA construct separate the target gene 3 Transformation 转化 Recombinant separate individual cells ( colonies ) clone the gene by cloning its host Restriction Endonucleases Ligase

Restriction Endonucleases(限制性核酸内切酶) -The Molecular Scissors The enzymes would cut DNA at specific sites->molecular knives ,or Molecular Scissors. Host enzymes that prevent the invasion of foreign DNAs such as viral DNA,by cutting them up. Restriction These enzymes cut within the foreign DNAs,rather than chewing them away from the ends. Endonucleases
Restriction Endonucleases(限制性核酸内切酶) -The Molecular Scissors Host enzymes that prevent the invasion of foreign DNAs such as viral DNA, by cutting them up. These enzymes cut within the foreign DNAs, rather than chewing them away from the ends. Restriction Endonucleases The enzymes would cut DNA at specific sites→molecular knives ,or Molecular Scissors
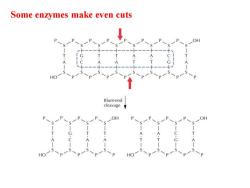
Some enzymes make even cuts HO Blunt-end cleavage OH
Some enzymes make even cuts
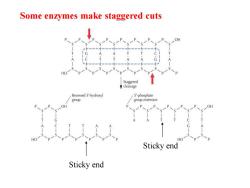
Some enzymes make staggered cuts OH HO Staggered cleavage Recessed 3'-hydroxyl 5'-phosphate group group extension HO Sticky end Sticky end
Sticky end Sticky end Some enzymes make staggered cuts
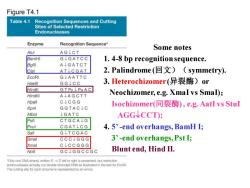
Figure T4.1 Table 4.1 Recognition Sequences and Cutting Sites of Selected Restriction Endonucleases Enzyme Recognition Sequence* AGICT Some notes Alul BamHI G↓GATCC 1.4-8 bp recognition sequence. Bglll ALGATCT Clal ATCGAT 2.Palindrome(▣文)(symmetry). EcoRl G↓AATTC Haelll GG↓CC 3.Heterochizomer(异裂酶)or Hindll GTPy↓PuAC Hindlll A↓AGCTT Neochizomer,e.g.Xmal vs SmaD; Hpall C↓CGG GGTAC↓C Isochizomer(同裂酶),e.g.AatI vs Stul Kpnl Mbol ↓GATC AGGVCCT); Pstl CTGCAJG Pvul CGAT↓CG 4.5'-end overhangs,BamH I; Sanl GJTCGAC Smal CCCJGGG 3'-end overhangs,Pst I; Xmal C↓CCGGG Notl GC↓GGCCGC Blunt end,Hind II. "Only one DNA strand,written 5'3'left to right is presented,but restriction endonucleases actually cut double-stranded DNA as illustrated in the text for EcoRl. The cutting site for each enzyme is represented by an arrow
Some notes 1. 4-8 bp recognition sequence. 2. Palindrome (回文)(symmetry). 3. Heterochizomer (异裂酶)or Neochizomer, e.g. XmaI vs SmaI); Isochizomer(同裂酶) , e.g. AatI vs StuI AGGCCT); 4. 5’ -end overhangs, BamH I; 3’ -end overhangs, Pst I; Blunt end, Hind II

Restriction fragments with complementary “sticky ends'”are ligated easily DNA I DNA II p/A-A-T-T-E3 a HO OH 5' (a1 pC-G3 3' ☐T-T-A-AP b ☐5 HO /A-G-C-T☐3 fe) ☐5 HO Complementary ends base-pair OH 5 A-A-T-T ☐3 Unpaired P +fragments -T-T-A-A ▣5' (b)and (c) HO 2 ATP DNA ligase A2 AMP +2 PP -A-A-T-T T-T-A-AC
Restriction fragments with complementary “sticky ends” are ligated easily
summary Restriction endonucleases recognize specific sequences in DNA molecules and make cuts in both strands. Because the cuts in the two strands are frequently staggered,restriction enzymes can create sticky ends that help link together two DNAs to form a recombinant DNA in vitro
✓Restriction endonucleases recognize specific sequences in DNA molecules and make cuts in both strands. ✓Because the cuts in the two strands are frequently staggered,restriction enzymes can create sticky ends that help link together two DNAs to form a recombinant DNA in vitro. summary
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 A Brief History、Chapter 02 The Molecular Nature of Genes Molecular Biology、Chapter 03 An Introduction to Gene Function.ppt
- 《分子生物学》课程各章作业习题(含答案).docx
- 《分子生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,共二十一章).docx
- 海南大学:《生物统计学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章).pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程授课教授.pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程教学大纲 Biology of Microorganisms.pdf
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲教师:谭志琼).doc
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程教学大纲 Agricultural Microbiology.doc
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第14章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第13章 微生物类群.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第12章 微生物的进化、系统发育和分类鉴定.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第11章 微生物生态.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 微生物与基因工程.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第08章 微生物遗传.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第07章 病毒.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 微生物的生长繁殖及其控制.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第05章 微生物的代谢.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第04章 微生物的营养.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第03章 微生物的结构与功能.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第02章 纯培养和显微技术.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 05 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 06 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 07 Operons - Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 08 Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription、Chapter 09 DNA-protein interactions in Prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I - Splicing.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Messenger RNA Processing II - Capping and Polyadenylation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I - initiation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II - Elongation and Termination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 DNA Replication I - Basic Mechanism and Enzymology.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 DNA Replication Ⅱ - Detailed Mechanism.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Homologous Recombination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Transposition(转座).ppt
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲 Cell Biology(生科生技专业,负责人:计巧灵).doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案1-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-1.doc
