《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 05 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity

Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 5 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity Peter Dazeley/Stone/Getty
Chapter 5 Molecular Tools for Studying Genes and Gene Activity
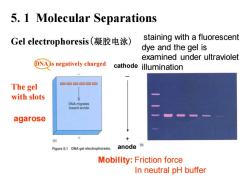
5.1 Molecular Separations Gel electrophoresis(凝胶电泳) staining with a fluorescent dye and the gel is examined under ultraviolet DNA is negatively charged cathode illumination The gel with slots DNA migrates toward anode agarose Figure 5.1 DNA gel electrophoresis. anode向 Mobility:Friction force In neutral pH buffer
Mobility: Friction force In neutral pH buffer 5.1 Molecular Separations Gel electrophoresis(凝胶电泳) The gel with slots DNA is negatively charged anode cathode staining with a fluorescent dye and the gel is examined under ultraviolet illumination agarose _ + anode
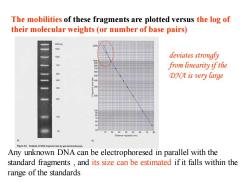
The mobilities of these fragments are plotted versus the log of their molecular weights (or number of base pairs) 2000p 1500 deviates strongly from linearity if the DNA is very large (mm Any unknown DNA can be electrophoresed in parallel with the standard fragments,and its size can be estimated if it falls within the range of the standards
logarithmic The mobilities of these fragments are plotted versus the log of their molecular weights (or number of base pairs) Any unknown DNA can be electrophoresed in parallel with the standard fragments , and its size can be estimated if it falls within the range of the standards deviates strongly from linearity if the DNA is very large

For the DNAs in the size ranges ~Mb(million base pairs,megabases) pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (脉冲凝胶电泳,PFGE) Instead of a constant current through the gel this method uses pulses of current with relatively long pulses in the forward direction and shorter pulses in the opposite,or Figure 5.3 Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of yeast chromosomes. even sideways, direction·
For the DNAs in the size ranges ~Mb(million base pairs, megabases) pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (脉冲凝胶电泳,PFGE) Instead of a constant current through the gel, this method uses pulses of current, with relatively long pulses in the forward direction and shorter pulses in the opposite,or even sideways, direction.

polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE,聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳) Sodium dodecy1 sulfate(SDS,十二烷基磺酸钠) M,(kD) Denaturing the subunits so they no longer 250 bind to one another. 160 105 The SDS has two added advantages: It coats all the polypeptides with negative charges so they all electrophorese toward 35 the anode(正极). It masks the natural charges of the subunits,so they electrophorese according to 15 0 their molecular masses and not by their native charges. Figure 5.4 SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Pre-stained protein markers
Pre-stained protein markers polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE,聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳) Sodium dodecyl sulfate(SDS,十二烷基磺酸钠) Denaturing the subunits so they no longer bind to one another. The SDS has two added advantages: ✓It coats all the polypeptides with negative charges,so they all electrophorese toward the anode(正极). ✓ It masks the natural charges of the subunits, so they electrophorese according to their molecular masses and not by their native charges
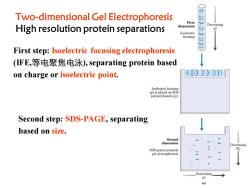
Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis First Decreasing High resolution protein separations dimension Isoelectric focusing First step:Isoelectric focusing electrophoresis (FE,等电聚焦电泳),separating protein based on charge or isoelectric point. gel is placed on SDS polyacrylamide gel. Second step:SDS-PAGE,separating based on size. Seeond dimension SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Decreasing
Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis High resolution protein separations Second step: SDS-PAGE, separating based on size. First step: Isoelectric focusing electrophoresis (IFE,等电聚焦电泳), separating protein based on charge or isoelectric point
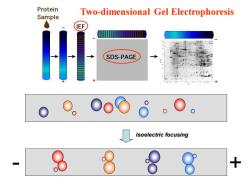
Protein Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis Sample IEF SDS-PAGE Isoelectric focusing 8 8 +
- + Isoelectric focusing Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis

Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display -Cy3 Mixed 5 (Source:Courtesy of Amersham Pharmacia Biotech.)

SUMMARY High-resolution separation of polypeptides can be achieved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis,which uses isoelectric focusing in the first dimension and SDS-PAGE in the second
SUMMARY High-resolution separation of polypeptides can be achieved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, which uses isoelectric focusing in the first dimension and SDS-PAGE in the second
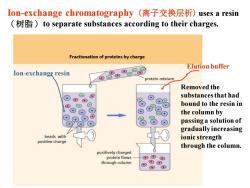
Ion-exchange chromatography(离子交换层析)uses a resin (to separate substances according to their charges. Fractionation of proteins by charge Elution buffer lon-exchang默resin protein mixture Removed the substances that had bound to the resin in (+ the column by passing a solution of gradually increasing beads with K ionic strength positive charge through the column. positively charged protein flows ④⊕④ through column ⊕⊕
Ion-exchange chromatography (离子交换层析) uses a resin (树脂)to separate substances according to their charges. Ion-exchange resin Elution buffer Removed the substances that had bound to the resin in the column by passing a solution of gradually increasing ionic strength through the column
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 04 Molecular Cloning Methods.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 A Brief History、Chapter 02 The Molecular Nature of Genes Molecular Biology、Chapter 03 An Introduction to Gene Function.ppt
- 《分子生物学》课程各章作业习题(含答案).docx
- 《分子生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,共二十一章).docx
- 海南大学:《生物统计学》课程授课教案(讲义,共十章).pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程授课教授.pdf
- 海南大学:《微生物生物学》课程教学大纲 Biology of Microorganisms.pdf
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲教师:谭志琼).doc
- 海南大学:《农业微生物学》课程教学大纲 Agricultural Microbiology.doc
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第14章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第13章 微生物类群.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第12章 微生物的进化、系统发育和分类鉴定.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第11章 微生物生态.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 微生物与基因工程.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第08章 微生物遗传.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第07章 病毒.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 微生物的生长繁殖及其控制.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第05章 微生物的代谢.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第04章 微生物的营养.ppt
- 海南大学:《微生物学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第03章 微生物的结构与功能.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 06 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 07 Operons - Fine Control of Prokaryotic Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 08 Major Shifts in Prokaryotic Transcription、Chapter 09 DNA-protein interactions in Prokaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases and Their Promoters.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 General Transcription Factors in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Transcription Activators in Eukaryotes.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and Its Effects on Transcription.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Messenger RNA Processing I - Splicing.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Messenger RNA Processing II - Capping and Polyadenylation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Other RNA Processing Events.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I - initiation.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 The Mechanism of Translation II - Elongation and Termination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 DNA Replication I - Basic Mechanism and Enzymology.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 DNA Replication Ⅱ - Detailed Mechanism.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Homologous Recombination.ppt
- 《分子生物学 Molecular Biology》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Transposition(转座).ppt
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲 Cell Biology(生科生技专业,负责人:计巧灵).doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案1-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-1.doc
- 新疆大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教案2-2.doc
