同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue)

Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue
Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue
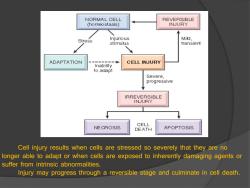
NORMAL CELL REVERSIBLE (homeostasis) INJURY Stress Injurious Mi以, stimulus transient ADAPTATION CELL INJURY Inability to adapt Severe, progressive IRREVERSIBLE INJURY CELL NE CROSIS DEATH APOPTOSIS Cell injury results when cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or when cells are exposed to inherently damaging agents or suffer from intrinsic abnormalities. Injury may progress through a reversible stage and culminate in cell death
Cell injury results when cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or when cells are exposed to inherently damaging agents or suffer from intrinsic abnormalities. Injury may progress through a reversible stage and culminate in cell death

CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia) o Chemical Agents o Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Factors oNutritional Imbalances o Physical Agents o Aging
CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia) Chemical Agents Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Factors Nutritional Imbalances Physical Agents Aging
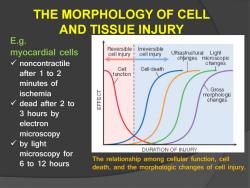
THE MORPHOLOGY OF CELL AND TISSUE INJURY E.g. myocardial cells Reversible i Irreversible cell injury cell injury Ultrastructural Light changes microscopic √noncontractile changes Cell Cell death after 1 to 2 function minutes of ischemia \Grass morphologic dead after 2 to changes 3 hours by electron microscopy by light DURATION OF INJURY microscopy for 6 to 12 hours The relationship among cellular function,cell death,and the morphologic changes of cell injury
THE MORPHOLOGY OF CELL AND TISSUE INJURY The relationship among cellular function, cell death, and the morphologic changes of cell injury. E.g. myocardial cells noncontractile after 1 to 2 minutes of ischemia dead after 2 to 3 hours by electron microscopy by light microscopy for 6 to 12 hours

>Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue Hydropic degeneration Fatty change Hyaline degeneration Myxoid degeneration Deposition of amyloid Intracellular accumulation of glycogen Deposition of pathological pigments
►Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue Hydropic degeneration Fatty change Hyaline degeneration Myxoid degeneration Deposition of amyloid Intracellular accumulation of glycogen Deposition of pathological pigments

Cellular swelling O Gross:when it affects many cells,it causes pallor,increase in size and weight of the affected organ,and loss of normal glistening translucence -“boiled meat”appearance O Microscope:The parenchyma cells are enlarged in various degrees and crowded together,and the cytoplasm is translucent and stains more lightly
Cellular swelling Gross: when it affects many cells, it causes pallor, increase in size and weight of the affected organ, and loss of normal glistening translucence – “boiled meat” appearance Microscope: The parenchyma cells are enlarged in various degrees and crowded together, and the cytoplasm is translucent and stains more lightly
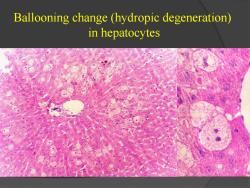
Ballooning change (hydropic degeneration) in hepatocytes
Ballooning change (hydropic degeneration) in hepatocytes

w√Fatty change Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells o In hypoxic injury and in various forms of toxic or metabolic injury Manifested by the appearance of small or large lipid vacuoles in the cytoplasm
Fatty change Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells In hypoxic injury and in various forms of toxic or metabolic injury Manifested by the appearance of small or large lipid vacuoles in the cytoplasm

1.Fatty liver --Causes of fatty liver Accumulation of triglycerides in the cytoplasm of liver cells occurs in the following conditions: (1)When there is increased mobilization of adipose tissue; (2)When the rate of conversion of fatty acids to triglycerides is increased; (3)When oxidation of triglycerides to acetyl-CoA and ketone bodies is decreased; (4)When synthesis of lipid acceptor proteins is deficient
1. Fatty liver --- Causes of fatty liver Accumulation of triglycerides in the cytoplasm of liver cells occurs in the following conditions: (1) When there is increased mobilization of adipose tissue; (2) When the rate of conversion of fatty acids to triglycerides is increased; (3) When oxidation of triglycerides to acetyl-CoA and ketone bodies is decreased; (4) When synthesis of lipid acceptor proteins is deficient
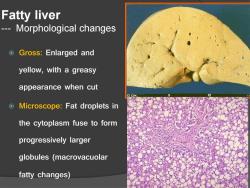
Fatty liver Morphological changes Gross:Enlarged and yellow,with a greasy appearance when cut Microscope:Fat droplets in the cytoplasm fuse to form progressively larger globules (macrovacuolar fatty changes)
Fatty liver --- Morphological changes Gross: Enlarged and yellow, with a greasy appearance when cut Microscope: Fat droplets in the cytoplasm fuse to form progressively larger globules (macrovacuolar fatty changes)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Adaptation of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Introduction to Pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题B卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题A卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)GIpathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Female reproductivepathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cardiac pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Thrombosis I-II, Hemodynamics, Atherosclerosis.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Neoplasia.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Inflammation.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cell Injury.pdf
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼肿瘤 Ocular trauma.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)青光眼 Glaucoma.pptx
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)角膜病总论 Corneal disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视觉系统 Visual Organ.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视网膜疾病 Retinal Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视光学基础 Basic Optics.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)葡萄膜炎 Disease of the Uvea.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼组织学 Histology of the Eye.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼科导论 Introduction(负责人:徐国彤).ppt
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Irreversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 02 组织再生与修复 Tissue regeneration and repair.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 14 女性生殖系统和乳房疾病 THE DISEASE OF FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM AND BREAST.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 16 神经系统疾病 Diseases of the Nervous System.pdf
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 绪论、第一篇 细菌学总论 第一章 细菌的形态学(负责人:侯芳玉).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 细菌的生理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 消毒与灭菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 细菌的遗传与变异.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.1-6.3).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.4)、第七章 细菌感染的检查方法与防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第一节 葡萄球菌属 第二节 链球菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第三节 肺炎链球菌 第四节 奈瑟菌属、第九章 肠杆菌科 第一节 埃希菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 肠杆菌科 第二节 志贺菌属 第三节 沙门菌属 第四节 其他菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 弧菌属 第一节 霍乱弧菌 第二节 副溶血性弧菌、第十一章 厌氧性细菌(1/2).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 厌氧性细菌(2/2)、第12 章放线菌属与诺卡菌属、第13章 棒状杆菌、第14章分枝杆菌属 第1节 结核分枝杆菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第14章分枝杆菌属 第2节 麻风分枝杆菌、第15章 动物源性细菌 第一节 布鲁斯菌属 第二节 耶尔森菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第15章 动物源性细菌 第三节 芽胞杆菌属、第16章 其他细菌 第一节 弯曲菌属 第二节 螺杆菌属 第三节 假单胞菌属 第四节 嗜血杆菌属 第五节 军团菌属 第6节 鲍特菌属、第17章 支原体 第一节 概述 第二节 主要致病性支原体.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第18章 立克次体、第19章 衣原体、第二十章 螺旋体 第一节 密螺旋体属 第二节 疏螺旋体属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二十章 螺旋体 第三节 钩端螺旋体属、第三篇 真菌学 第21章 真菌概述 第一节 生物学性状 第二节 致病性与免疫性 第三节 微生物学检查法 第四节 真菌感染的防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第22章 主要病原性真菌.ppt
