同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 02 组织再生与修复 Tissue regeneration and repair

OVERVIEW OF TISSUE REPAIR Repair,sometimes called healing, refers to the restoration of tissue architecture and function after an injury. 1.Regeneration 2.Scar formation
OVERVIEW OF TISSUE REPAIR Repair, sometimes called healing, refers to the restoration of tissue architecture and function after an injury. 1. Regeneration 2. Scar formation
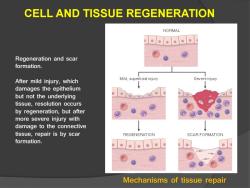
CELL AND TISSUE REGENERATION NORMAL Regeneration and scar formation. After mild injury,which Mild,superficial injury Severe injury damages the epithelium but not the underlying tissue,resolution occurs by regeneration,but after more severe injury with damage to the connective tissue,repair is by scar REGENERATION SCAR FORMATION formation. 。。●g Mechanisms of tissue repair
Regeneration and scar formation. After mild injury, which damages the epithelium but not the underlying tissue, resolution occurs by regeneration, but after more severe injury with damage to the connective tissue, repair is by scar formation. Mechanisms of tissue repair CELL AND TISSUE REGENERATION
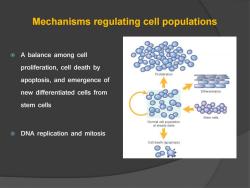
Mechanisms regulating cell populations A balance among cell proliferation,cell death by Prolifer ation apoptosis,and emergence of new differentiated cells from Differentiation stem cells 8 ← od Stem cells Normal cell population at steady state DNA replication and mitosis Cell death (apoptosis)
Mechanisms regulating cell populations A balance among cell proliferation, cell death by apoptosis, and emergence of new differentiated cells from stem cells DNA replication and mitosis

Proliferative Capacities of Tissues Labile (continuously dividing)tissues o Stable tissues O Permanent tissues
Proliferative Capacities of Tissues Labile (continuously dividing) tissues Stable tissues Permanent tissues

Labile (continuously dividing)tissues o Divide continuously o The majority of surface epithelia,such as the stratified squamous surfaces of the skin,oral cavity,vagina,and cervix;the cuboidal epithelia of the ducts draining exocrine organs;the columnar epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract, uterus,and fallopian tubes;and the transitional epithelium of the urinary tract May undergo hyperplasia as an adaptation to injury
Labile (continuously dividing) tissues Divide continuously The majority of surface epithelia, such as the stratified squamous surfaces of the skin, oral cavity, vagina, and cervix; the cuboidal epithelia of the ducts draining exocrine organs; the columnar epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract, uterus, and fallopian tubes; and the transitional epithelium of the urinary tract May undergo hyperplasia as an adaptation to injury

√Stable tissues Divide infrequently (usually in GO phase) o i.e.,hepatocytes,astrocytes,smooth muscle cells May be stimulated (GF)to enter the cell cycle,and undergo hyperplasia or hypertrophy as an adaptation
Stable tissues Divide infrequently (usually in G0 phase) i.e., hepatocytes, astrocytes, smooth muscle cells May be stimulated (GF) to enter the cell cycle, and undergo hyperplasia or hypertrophy as an adaptation
√Permanent tissues i.e.,neuron,skeletal and cardiac muscle cells May undergo hypertrophy (muscle only)
Permanent tissues i.e., neuron, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells May undergo hypertrophy (muscle only)

Role of the Extracellular Matrix in Tissue Repair o sequestering water o providing turgor to soft tissues,and minerals giving rigidity to bone o regulates the proliferation,movement,and differentiation of the cells living within it supplying a substrate for cell adhesion and migration o serving as a reservoir for growth factors
Role of the Extracellular Matrix in Tissue Repair sequestering water providing turgor to soft tissues, and minerals giving rigidity to bone regulates the proliferation, movement, and differentiation of the cells living within it supplying a substrate for cell adhesion and migration serving as a reservoir for growth factors

Extracellular matrix o Two basic forms of o Three basic components ECM 1.Collagens and elastins 1.Basement membranes 2.Proteoglycans and hyaluronan 2.Interstitial matrix 3.Adhesive glycoproteins
Extracellular matrix Three basic components 1. Collagens and elastins 2. Proteoglycans and hyaluronan 3. Adhesive glycoproteins Two basic forms of ECM 1. Basement membranes 2. Interstitial matrix
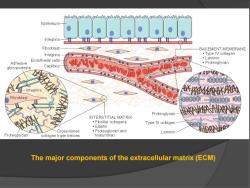
Epithelium Integrins Fibroblast BASEMENT MEMBRANE Integrins Type IV collagen Endothelial cells ◆Laminin Adhesive Proteoglycan glycoproteins Capillary 瓶欢 -Int egrins 孩封 Fibroblast Pr oteoglycan INTERSTITIAL MATRIX ·Fibrillar collagens Type IV collagen- ·Elastin -Cross-linked Proteoglycan and Laminin- Proteoglycan collagen triple helices hyaluronan The major components of the extracellular matrix(ECM)
The major components of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Irreversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Adaptation of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Introduction to Pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题B卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题A卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)GIpathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Female reproductivepathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cardiac pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Thrombosis I-II, Hemodynamics, Atherosclerosis.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Neoplasia.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Inflammation.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cell Injury.pdf
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼肿瘤 Ocular trauma.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)青光眼 Glaucoma.pptx
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)角膜病总论 Corneal disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视觉系统 Visual Organ.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视网膜疾病 Retinal Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视光学基础 Basic Optics.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)葡萄膜炎 Disease of the Uvea.ppt
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 14 女性生殖系统和乳房疾病 THE DISEASE OF FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM AND BREAST.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 16 神经系统疾病 Diseases of the Nervous System.pdf
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 绪论、第一篇 细菌学总论 第一章 细菌的形态学(负责人:侯芳玉).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 细菌的生理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 消毒与灭菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 细菌的遗传与变异.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.1-6.3).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.4)、第七章 细菌感染的检查方法与防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第一节 葡萄球菌属 第二节 链球菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第三节 肺炎链球菌 第四节 奈瑟菌属、第九章 肠杆菌科 第一节 埃希菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 肠杆菌科 第二节 志贺菌属 第三节 沙门菌属 第四节 其他菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 弧菌属 第一节 霍乱弧菌 第二节 副溶血性弧菌、第十一章 厌氧性细菌(1/2).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 厌氧性细菌(2/2)、第12 章放线菌属与诺卡菌属、第13章 棒状杆菌、第14章分枝杆菌属 第1节 结核分枝杆菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第14章分枝杆菌属 第2节 麻风分枝杆菌、第15章 动物源性细菌 第一节 布鲁斯菌属 第二节 耶尔森菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第15章 动物源性细菌 第三节 芽胞杆菌属、第16章 其他细菌 第一节 弯曲菌属 第二节 螺杆菌属 第三节 假单胞菌属 第四节 嗜血杆菌属 第五节 军团菌属 第6节 鲍特菌属、第17章 支原体 第一节 概述 第二节 主要致病性支原体.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第18章 立克次体、第19章 衣原体、第二十章 螺旋体 第一节 密螺旋体属 第二节 疏螺旋体属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二十章 螺旋体 第三节 钩端螺旋体属、第三篇 真菌学 第21章 真菌概述 第一节 生物学性状 第二节 致病性与免疫性 第三节 微生物学检查法 第四节 真菌感染的防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第22章 主要病原性真菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)病毒的遗传与变异、病毒的分类、第24章 病毒的感染与免疫 第一节 病毒的致病作用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第24章 病毒的感染与免疫 第二节 抗病毒免疫、第25章 病毒感染的检查方法与防治原则 第一节 病毒的诊断 第二节 抗病毒治疗 第三节 抗病毒感染的预防、第26章 呼吸道病毒 第一节 流感病毒.ppt
