同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Introduction to Pathology

4907 悠© WATH IS PATHOLOGY? HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?
+ WATH IS PATHOLOGY? + HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? + DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY + WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?

WATH IS PATHOLOGY? Pathology is the study(logos)of disease(pathos) PATHOLOGY is from GREEK “Patho”-Suffering Every body has “Loges”--Study a secret. + How the organs and tissues of a ILO VENTIMIGLIA healthy body PATHOLOGY (the basis of normal anatomy and physiology) C R E A T O ---change to those of a sick person IN THEATRES APRIL 18TH Pathology is the study of suffering?
WATH IS PATHOLOGY? + Pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos) + PATHOLOGY is from GREEK “Patho” --- Suffering “Loges” --- Study + How the organs and tissues of a healthy body (the basis of normal anatomy and physiology) ---change to those of a sick person Pathology is the study of suffering?

Pathology is the study ) (logos)of disease (pathos) To study the structural,biochemical and functional changes in cells,tissues and organs that underlie disease To use molecular,microbiologic, immunologic and morphologic techniques To explain the clinical manifestations of PATHOLOGY the disease +1 To provide basis for clinical care and therapy Is the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine Scientific foundation for all of medicine
Pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos) + To study the structural, biochemical and functional changes in cells, tissues and organs that underlie disease + To use molecular, microbiologic, immunologic and morphologic techniques + To explain the clinical manifestations of the disease + To provide basis for clinical care and therapy Is the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine Scientific foundation for all of medicine
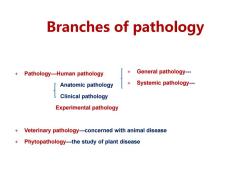
Branches of pathology Pathology---Human pathology General pathology--- Anatomic pathology Systemic pathology--- Clinical pathology Experimental pathology Veterinary pathology---concerned with animal disease Phytopathology---the study of plant disease
+ Pathology---Human pathology Anatomic pathology Clinical pathology Experimental pathology + Veterinary pathology---concerned with animal disease + Phytopathology---the study of plant disease + General pathology--- + Systemic pathology--- Branches of pathology

4907 © NGJI v WATH IS PATHOLOGY? HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?
+ WATH IS PATHOLOGY? + HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? + DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY + WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?

How to study Pathology? The four aspects of a disease process that form the core of pathology--- The cause---Etiology The mechanisms of its development---Pathogenesis The structural alterations induced in the cells and organs of the body---Morphologic changes The functional consequences of the morphologic changes ---Clinical significance
How to study Pathology? The four aspects of a disease process that form the core of pathology--- + The cause --- Etiology + The mechanisms of its development --- Pathogenesis + The structural alterations induced in the cells and organs of the body --- Morphologic changes + The functional consequences of the morphologic changes --- Clinical significance

Etiology (or cause) Carl Posner Rudolf Virchow Two major classes of etiologic factors--- Acquired Infection,Nutritional, Chemical,and physical Genetic Genetic mutation All forms of organ injury start with molecular or 1821-1902 structural alteration in cells, "All disease is disease of a concept first put forth cells";"All cells come from during the 19th century by pre-existing cells". Dr.Rudolf Virchow. ----Cell Pathology
Etiology (or cause) Two major classes of etiologic factors--- Acquired Infection, Nutritional, Chemical, and physical & Genetic Genetic mutation All forms of organ injury start with molecular or structural alteration in cells, a concept first put forth during the 19th century by Dr. Rudolf Virchow. 1821-1902 “All disease is disease of cells”; “All cells come from pre-existing cells”. ----Cell Pathology
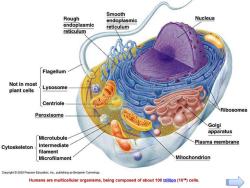
Smooth Rough endoplasmic Nucleus endoplasmic reticulum reticulum Flagellum Not in most plant cells Lysosome Centriole Ribosomes Peroxisome Golgi apparatus Microtubule Plasma membrane Cytoskeleton Intermediate filament Microfilament Mitochondrion Copyright2003 Pearson Education,Ine..publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Humans are multicellular organisms,being composed of about 100 trillion(1014)cells
Humans are multicellular organisms, being composed of about 100 trillion (1014) cells
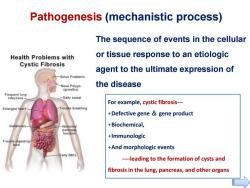
Pathogenesis (mechanistic process) The sequence of events in the cellular Health Problems with or tissue response to an etiologic Cystic Fibrosis agent to the ultimate expression of Sinus Problems Nose Polyps the disease (growths) Infections Salty sweat For example,cystic fibrosis--- Enlarged heart Trouble breathing +Defective gene gene product +Biochemical, pancreas functio +Immunologic Trouble dgesting +And morphologic events atty BM's ----leading to the formation of cysts and fibrosis in the lung,pancreas,and other organs
Pathogenesis (mechanistic process) The sequence of events in the cellular or tissue response to an etiologic agent to the ultimate expression of the disease For example, cystic fibrosis--- +Defective gene & gene product +Biochemical, +Immunologic +And morphologic events ----leading to the formation of cysts and fibrosis in the lung, pancreas, and other organs
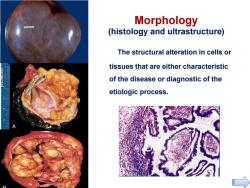
Morphology (histology and ultrastructure) The structural alteration in cells or tissues that are either characteristic of the disease or diagnostic of the etiologic process
Morphology (histology and ultrastructure) The structural alteration in cells or tissues that are either characteristic of the disease or diagnostic of the etiologic process
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题B卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题A卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)GIpathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Female reproductivepathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cardiac pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Thrombosis I-II, Hemodynamics, Atherosclerosis.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Neoplasia.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Inflammation.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cell Injury.pdf
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼肿瘤 Ocular trauma.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)青光眼 Glaucoma.pptx
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)角膜病总论 Corneal disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视觉系统 Visual Organ.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视网膜疾病 Retinal Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视光学基础 Basic Optics.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)葡萄膜炎 Disease of the Uvea.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼组织学 Histology of the Eye.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼科导论 Introduction(负责人:徐国彤).ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)眼科学教学大纲(英文,Ophthalmology).doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)眼科学教学大纲(中文,负责人:徐国彤).doc
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Adaptation of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Irreversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 02 组织再生与修复 Tissue regeneration and repair.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 14 女性生殖系统和乳房疾病 THE DISEASE OF FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM AND BREAST.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 16 神经系统疾病 Diseases of the Nervous System.pdf
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 绪论、第一篇 细菌学总论 第一章 细菌的形态学(负责人:侯芳玉).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 细菌的生理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 消毒与灭菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 细菌的遗传与变异.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.1-6.3).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.4)、第七章 细菌感染的检查方法与防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第一节 葡萄球菌属 第二节 链球菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第三节 肺炎链球菌 第四节 奈瑟菌属、第九章 肠杆菌科 第一节 埃希菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 肠杆菌科 第二节 志贺菌属 第三节 沙门菌属 第四节 其他菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 弧菌属 第一节 霍乱弧菌 第二节 副溶血性弧菌、第十一章 厌氧性细菌(1/2).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 厌氧性细菌(2/2)、第12 章放线菌属与诺卡菌属、第13章 棒状杆菌、第14章分枝杆菌属 第1节 结核分枝杆菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第14章分枝杆菌属 第2节 麻风分枝杆菌、第15章 动物源性细菌 第一节 布鲁斯菌属 第二节 耶尔森菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第15章 动物源性细菌 第三节 芽胞杆菌属、第16章 其他细菌 第一节 弯曲菌属 第二节 螺杆菌属 第三节 假单胞菌属 第四节 嗜血杆菌属 第五节 军团菌属 第6节 鲍特菌属、第17章 支原体 第一节 概述 第二节 主要致病性支原体.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第18章 立克次体、第19章 衣原体、第二十章 螺旋体 第一节 密螺旋体属 第二节 疏螺旋体属.ppt
