同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 16 神经系统疾病 Diseases of the Nervous System

CHAPTER 16 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM JIANG,WENXIA Department of Pathology Tongji University School of Medicine
CHAPTER 16 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM JIANG, WENXIA Department of Pathology Tongji University School of Medicine

厂 Disorders of the Nervous Systems *General disorders 。Infections 。Neoplasms 。Vascular diseases 。Trauma Congenital malformations 。Metabolic disorders Specific disorders 。Diseases of myelin Degenerative diseases
Disorders of the Nervous Systems General disorders Infections Neoplasms Vascular diseases Trauma Congenital malformations Metabolic disorders Specific disorders Diseases of myelin Degenerative diseases

The General Characteristics of the Nervous System Disorders 1 Location of lesions is closely relation to dysfunction 2 The same disorders in the different regions will lead to different syndromes and effects 3 Cells of the nervous systems react straitlaced to different pathogenic factors->the same lesions will be present in different disorders
The General Characteristics of the Nervous System Disorders ① Location of lesions is closely relation to dysfunction ② The same disorders in the different regions will lead to different syndromes and effects ③ Cells of the nervous systems react straitlaced to different pathogenic factors → the same lesions will be present in different disorders

4 The effects of some certain anatomic features are two sides of coin e.g.,skull (the rigid confines): protects the brain from trauma and noxious elements in the external environment >renders the brain vulnerable to expansile intracranial lesions,raise intracranial pressure-compromise the function of the organ,cerebral hernia
④ The effects of some certain anatomic features are two sides of coin e.g., skull (the rigid confines): protects the brain from trauma and noxious elements in the external environment renders the brain vulnerable to expansile intracranial lesions, raise intracranial pressure → compromise the function of the organ, cerebral hernia

5 Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier and Virchow-Robin space not only act as a natural line of defense,but also prevent the inflammation to penetrate to the parenchyma 6 There is no resident lymphoid tissues,the lymphocytes are all conveyed by the blood circulation
⑤ Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier and Virchow-Robin space not only act as a natural line of defense, but also prevent the inflammation to penetrate to the parenchyma ⑥ There is no resident lymphoid tissues, the lymphocytes are all conveyed by the blood circulation

Section I The Cells and It's Basic Changes of Nervous System I.Neuron The neuron is a pyramidal cell with a rounded nucleus and prominent nucleolus. The granularity of the cytoplasm is imparted by rough endoplasmic reticulum(Nissl substance)
Section I The Cells and It’s Basic Changes of Nervous System I. Neuron The neuron is a pyramidal cell with a rounded nucleus and prominent nucleolus. The granularity of the cytoplasm is imparted by rough endoplasmic reticulum (Nissl substance)
Basic Changes of Neuron: (I)Acute injury Neuron necrosis (red neuron,ghost cell) Neuronophagia (Il )Simple neuronal atrophy e.g.Neuronal transsynaptic degeneration (Ill)Central chromatolysis(Disapearance of central Nissl body )and Waller degeneration (IV)Forming of inclusions e.g.Negri body (V)Abnormalities of the structural proteins e.g.neurofibrillary tangle-Alzheimer disease Lewy body formation-Parkinson disease
Basic Changes of Neuron: ( I ) Acute injury Neuron necrosis (red neuron, ghost cell) Neuronophagia ( II ) Simple neuronal atrophy e.g.Neuronal transsynaptic degeneration (III) Central chromatolysis (Disapearance of central Nissl body ) and Waller degeneration (IV) Forming of inclusions e.g. Negri body (V) Abnormalities of the structural proteins e.g. neurofibrillary tangle — Alzheimer disease Lewy body formation — Parkinson disease

Red Neuron
red neuron Red Neuron
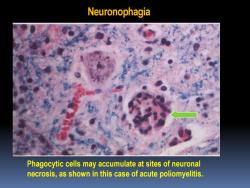
Neuronophagia Phagocytic cells may accumulate at sites of neuronal necrosis,as shown in this case of acute poliomyelitis
Neuronophagia Phagocytic cells may accumulate at sites of neuronal necrosis, as shown in this case of acute poliomyelitis
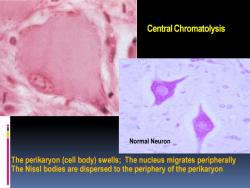
Central Chromatolysis Normal Neuron The perikaryon(cell body)swells;The nucleus migrates peripherally The Nissl bodies are dispersed to the periphery of the perikaryon
Central Chromatolysis The perikaryon (cell body) swells; The nucleus migrates peripherally The Nissl bodies are dispersed to the periphery of the perikaryon Normal Neuron
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 14 女性生殖系统和乳房疾病 THE DISEASE OF FEMALE GENITAL SYSTEM AND BREAST.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 02 组织再生与修复 Tissue regeneration and repair.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Irreversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Chapter 01 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue(Adaptation of Cell and Tissue).pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Introduction to Pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题B卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)试题A卷.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)GIpathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Female reproductivepathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cardiac pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Thrombosis I-II, Hemodynamics, Atherosclerosis.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Neoplasia.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Inflammation.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cell Injury.pdf
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼肿瘤 Ocular trauma.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)青光眼 Glaucoma.pptx
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)角膜病总论 Corneal disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视觉系统 Visual Organ.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视网膜疾病 Retinal Disease.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 绪论、第一篇 细菌学总论 第一章 细菌的形态学(负责人:侯芳玉).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 细菌的生理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 消毒与灭菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 细菌的遗传与变异.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.1-6.3).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 细菌的感染与致病机制(6.4)、第七章 细菌感染的检查方法与防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第一节 葡萄球菌属 第二节 链球菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 球菌 第三节 肺炎链球菌 第四节 奈瑟菌属、第九章 肠杆菌科 第一节 埃希菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 肠杆菌科 第二节 志贺菌属 第三节 沙门菌属 第四节 其他菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 弧菌属 第一节 霍乱弧菌 第二节 副溶血性弧菌、第十一章 厌氧性细菌(1/2).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 厌氧性细菌(2/2)、第12 章放线菌属与诺卡菌属、第13章 棒状杆菌、第14章分枝杆菌属 第1节 结核分枝杆菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第14章分枝杆菌属 第2节 麻风分枝杆菌、第15章 动物源性细菌 第一节 布鲁斯菌属 第二节 耶尔森菌属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第15章 动物源性细菌 第三节 芽胞杆菌属、第16章 其他细菌 第一节 弯曲菌属 第二节 螺杆菌属 第三节 假单胞菌属 第四节 嗜血杆菌属 第五节 军团菌属 第6节 鲍特菌属、第17章 支原体 第一节 概述 第二节 主要致病性支原体.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第18章 立克次体、第19章 衣原体、第二十章 螺旋体 第一节 密螺旋体属 第二节 疏螺旋体属.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二十章 螺旋体 第三节 钩端螺旋体属、第三篇 真菌学 第21章 真菌概述 第一节 生物学性状 第二节 致病性与免疫性 第三节 微生物学检查法 第四节 真菌感染的防治原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第22章 主要病原性真菌.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)病毒的遗传与变异、病毒的分类、第24章 病毒的感染与免疫 第一节 病毒的致病作用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第24章 病毒的感染与免疫 第二节 抗病毒免疫、第25章 病毒感染的检查方法与防治原则 第一节 病毒的诊断 第二节 抗病毒治疗 第三节 抗病毒感染的预防、第26章 呼吸道病毒 第一节 流感病毒.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第26章 呼吸道病毒 第二节 副粘病毒 第三节其他呼吸道病毒.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学微生物学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第27章 肠道病毒、第二十八章 急性胃肠炎病毒、第29章 肝炎病毒 第一节 甲型肝炎病毒 第二节 乙型肝炎病毒.ppt
