福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 1(UC Davis)试题

Food Science&Technology 100A D ung#1 October 22.2003 Name: Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above.Then SIGN the exam copy,to indicate that You have respected the UC Davis Honor Code in the taking of this exam. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000,and mark the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000. WRITE your student identification number in the appropriate area of your Scantron #2000 on Part 1 and follow the instructions'to CODE your ID number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 36 multiple choice questions.There are a total of 11 pages to the exam. Use a #2 pencil to mark your Scantron answers.You are responsibl for the accuracy and completen Do not put any marks (other than filling in Graded exams will be returned in class as soon as possible Multiple Choice 90 100
Food Science & Technology 100A Professor S.R. Dungan Midterm Examination #1 October 22, 2003 Name: Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above. Then SIGN the exam copy, to indicate that You have respected the UC Davis Honor Code in the taking of this exam. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000, and mark the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000. WRITE your student identification number in the appropriate area of your Scantron #2000 on Part 1 and follow the instructions to CODE your ID number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 36 multiple choice questions. There are a total of 11 pages to the exam. Use a #2 pencil to mark your Scantron answers. You are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of your Scantron. Do not put any marks (other than filling in the answer bubbles) on the left side(s) of the Scantron sheet. Graded exams will be returned in class as soon as possible. Multiple Choice 90 Short answers 10 Total 100

FST100A2003 Midterm1 1.Which of the following correctly describes a triglyceride molecule? a.It consists of three acyl chains connected to a glycerol backbone b.It has three chiral centers c.It has three fatty acid chains attached to a glycose subunit d.It has two fatty acid groups and an isoprene group e.All of the above correctly describe a triglyceride molecule 2.Which of the following are true of sugar alcohols? a.They are often called"uronic acids" b.They are good humectants c.They are produced by reduction of sugars d.They have0 calories e.Answer b and c 3.Which of the following pairs are diastereomers? a.B-D-glucopyranose and B-D-glucofuranose b.The straight chain forms of D-glucose and D-fructose c.a-D-glucopyranose and B-D-galactopyranose d.The straight chain form of D-glucose and D-glucitol e.a-D-glucopyranose and B-D-lactose 4.Why are monosaccharides and disaccharides added to foods? a.To increase the food's sweetness b.To increase the food's bitterness c.Because they are very hydrophobic d.Because they prevent enzymatic browning e.All of the above are reasons 5.Which of the following is a lipid? a.limonene b.phosphatidylcholine c.molasses d.triacylglycerols e.answers a,b and d 1
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 1 1. Which of the following correctly describes a triglyceride molecule? a. It consists of three acyl chains connected to a glycerol backbone b. It has three chiral centers c. It has three fatty acid chains attached to a glycose subunit d. It has two fatty acid groups and an isoprene group e. All of the above correctly describe a triglyceride molecule 2. Which of the following are true of sugar alcohols? a. They are often called "uronic acids" b. They are good humectants c. They are produced by reduction of sugars d. They have 0 calories e. Answer b and c 3. Which of the following pairs are diastereomers? a. β-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucofuranose b. The straight chain forms of D-glucose and D-fructose c. α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-galactopyranose d. The straight chain form of D-glucose and D-glucitol e. α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-lactose 4. Why are monosaccharides and disaccharides added to foods? a. To increase the food's sweetness b. To increase the food's bitterness c. Because they are very hydrophobic d. Because they prevent enzymatic browning e. All of the above are reasons 5. Which of the following is a lipid? a. limonene b. phosphatidylcholine c. molasses d. triacylglycerols e. answers a, b and d

FST100A2003 Midterm1 The following four questions refer to the molecule below A CH2OH -0 H 6.This molecule is OH OH a.maltose OH b.mannose H OH OH c.fructose d.sucrose e.None of the above 7.Which of the following does not describe the subunit marked A? a.It is a furanose b.It is a glycose subunit c.It is an a-D-glucopyranose subunit d.It is a hexose subunit e.It is a monosaccharide subunit 8.The bond joining subunits A and B is a.formed by Amadori rearrangment b.a glycosidic linkage c.formed during acetal formation from a hemiacetal d.Answer b and c are true e.Answers a,b and c are true 9.Molecule B has six labelled carbons.Which of these carbons are not chiral centers? a.Carbon 1 only b.Carbons 2,3,4 and 5 only c.Carbons 1 and 6 only d.Carbons 2 and 5 only e.There are no chiral centers in this molecule
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 2 The following four questions refer to the molecule below: 6. This molecule is a. maltose b. mannose c. fructose d. sucrose e. None of the above 7. Which of the following does not describe the subunit marked A? a. It is a furanose b. It is a glycose subunit c. It is an α-D-glucopyranose subunit d. It is a hexose subunit e. It is a monosaccharide subunit 8. The bond joining subunits A and B is a. formed by Amadori rearrangment b. a glycosidic linkage c. formed during acetal formation from a hemiacetal d. Answer b and c are true e. Answers a, b and c are true 9. Molecule B has six labelled carbons. Which of these carbons are not chiral centers? a. Carbon 1 only b. Carbons 2, 3, 4 and 5 only c. Carbons 1 and 6 only d. Carbons 2 and 5 only e. There are no chiral centers in this molecule A B O O OH H OH H H O H H H OH H OH H OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 4 3 1 5 6 2

FST100A2003 Midterm1 10.Isomerization reactions are used a.to remove fructose from corn syrup b.to convert D-glucose to D-galactose c.to convert sucrose to invert sugar d.by bees to increase the fructose content of honey e.Answer a and d 11.Most abundant,natural sugars are a.ketoses b.hexoses c.furanoses d.L-sugars e.Most sugars are all of the above 12.Which of the following explains the very high purity of table sugar? a.Table sugar is primarily fructose,a pure sugar found in fruit b.Table sugar is made from sucrose,which crystallizes very easily c.Table sugar is made from sucrose,which is very hygroscopic d.Table sugar is made from L-sugars,which are naturally of high purity e.All of the above 13.Glucose is sometimes called a.grape sugar b.dextrose c.corn sugar d.Answer b and c e.Answer a,b and c 14.Hydrolysis reactions are used to a.form disaccharides from monosaccharides b.create invert sugar from sucrose c.convert glucose to mannose d.oxidize phenolics e.produce sugar alcohols 3
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 3 10. Isomerization reactions are used a. to remove fructose from corn syrup b. to convert D-glucose to D-galactose c. to convert sucrose to invert sugar d. by bees to increase the fructose content of honey e. Answer a and d 11. Most abundant, natural sugars are a. ketoses b. hexoses c. furanoses d. L-sugars e. Most sugars are all of the above 12. Which of the following explains the very high purity of table sugar? a. Table sugar is primarily fructose, a pure sugar found in fruit b. Table sugar is made from sucrose, which crystallizes very easily c. Table sugar is made from sucrose, which is very hygroscopic d. Table sugar is made from L-sugars, which are naturally of high purity e. All of the above 13. Glucose is sometimes called a. grape sugar b. dextrose c. corn sugar d. Answer b and c e. Answer a, b and c 14. Hydrolysis reactions are used to a. form disaccharides from monosaccharides b. create invert sugar from sucrose c. convert glucose to mannose d. oxidize phenolics e. produce sugar alcohols

FST100A2003 Midterm1 15.Hexanoic acid is a fatty acid with a.6 carbons b.12 carbons c.one double bond d.two double bonds e.none of the above 16.Fructose is the only sugar found in a.sugar beets b.apples c.peaches d.tomatos e.All of the above would contain sugars besides fructose 17.Which of the following fatty acid groups are seldom found in food triglycerides? a.oleic acid b.18 carbon fatty acids c.monounsaturated fatty acids with cis double bonds d.answer a and c e.answers a,b and c are all found commonly in foods 18.Why are apples stored under modified atmosphere? a.to prevent conversion of sugar to sugar alcohols b.to prevent loss of essential amino acids due to Maillard browning c.to prevent oxygen from promoting enzymatic browning d.to prevent loss of erucic acid e.answers b and c 19.Which of the following is involved in caramelization? a.formation of quinones b.acetal formation c.Amadori rearrangement(isomerization)of an imine d.nucleophilic addition of an amine e.none of the above
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 4 15. Hexanoic acid is a fatty acid with a. 6 carbons b. 12 carbons c. one double bond d. two double bonds e. none of the above 16. Fructose is the only sugar found in a. sugar beets b. apples c. peaches d. tomatos e. All of the above would contain sugars besides fructose 17. Which of the following fatty acid groups are seldom found in food triglycerides? a. oleic acid b. 18 carbon fatty acids c. monounsaturated fatty acids with cis double bonds d. answer a and c e. answers a, b and c are all found commonly in foods 18. Why are apples stored under modified atmosphere? a. to prevent conversion of sugar to sugar alcohols b. to prevent loss of essential amino acids due to Maillard browning c. to prevent oxygen from promoting enzymatic browning d. to prevent loss of erucic acid e. answers b and c 19. Which of the following is involved in caramelization? a. formation of quinones b. acetal formation c. Amadori rearrangement (isomerization) of an imine d. nucleophilic addition of an amine e. none of the above
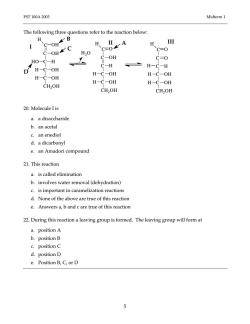
FST100A2003 Midterm1 The following three questions refer to the reaction below: H H、 H I C-OHC C=0 HO HO-C-H C-OH C-0 D H-C-OH C-H H-C-H H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 20.Molecule I is a.a disaccharide b.an acetal c.an enediol d.a dicarbonyl e.an Amadori compound 21.This reaction a.is called elimination b.involves water removal(dehydration) c.is important in caramelization reactions d.None of the above are true of this reaction e.Answers a,b and c are true of this reaction 22.During this reaction a leaving group is formed.The leaving group will form at a.position A b.positionB c.positionC d.position D e.Position B,C,or D 5
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 5 The following three questions refer to the reaction below: 20. Molecule I is a. a disaccharide b. an acetal c. an enediol d. a dicarbonyl e. an Amadori compound 21. This reaction a. is called elimination b. involves water removal (dehydration) c. is important in caramelization reactions d. None of the above are true of this reaction e. Answers a, b and c are true of this reaction 22. During this reaction a leaving group is formed. The leaving group will form at a. position A b. position B c. position C d. position D e. Position B, C, or D OH C C C C C OH OH OH HO H H H CH2OH H O C C C C C OH OH OH H H H CH2OH H C C C C C O OH OH H H H CH2OH H O H H2O A B C D I II III

FST100A2003 Midterm1 23.Sucrose is not the primary sugar in a.corn syrup b.maple syrup c.molasses d.confectioner's sugar e.Sucrose is the primary sugar in all of the above 24.Which of the following is necessary in order for Maillard browning to occur? a.amines b.very high temperatures c.phenolics d.sucrose e.sulfites 25.An oxidation test would not be used a.to measure the concentration of reducing ends b.to determine the presence of free carbonyl groups c.in determining the dextrose equivalence of a corn syrup d.to measure the concentration of sucrose e.An oxidation test would be used for all of the above 26.Which of the following would not undergo a caramelization reaction? a.Lactose b.Glucose c.Fructose d.Sucrose e.All of the above could react by caramelization 27.Which of the following sugars is the sweetest at room temperature? a.Lactose b.Fructose c.Sucrose d.Glucose e.Answers a-d are equally sweet
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 6 23. Sucrose is not the primary sugar in a. corn syrup b. maple syrup c. molasses d. confectioner's sugar e. Sucrose is the primary sugar in all of the above 24. Which of the following is necessary in order for Maillard browning to occur? a. amines b. very high temperatures c. phenolics d. sucrose e. sulfites 25. An oxidation test would not be used a. to measure the concentration of reducing ends b. to determine the presence of free carbonyl groups c. in determining the dextrose equivalence of a corn syrup d. to measure the concentration of sucrose e. An oxidation test would be used for all of the above 26. Which of the following would not undergo a caramelization reaction? a. Lactose b. Glucose c. Fructose d. Sucrose e. All of the above could react by caramelization 27. Which of the following sugars is the sweetest at room temperature? a. Lactose b. Fructose c. Sucrose d. Glucose e. Answers a-d are equally sweet

FST100A2003 Midterm1 The following two questions refer to the choices below: CH2OH CH2OH B -0H H OH H HO CH2OH OH OH CH2OH CH2OH OH 0、OH E O、H OH H OH OH y H OH OH H OH H H 28.Which of these molecules is B-D-galactose? a.choice A b.choice B c.choiceC d.choice D e.choiceE 29.During mutarotation,which pair of these molecules would interchange? a.choices AandC b.choices A and B c.choice B and D d.choice A and E e.choice C and E
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 7 The following two questions refer to the choices below: 28. Which of these molecules is β-D-galactose? a. choice A b. choice B c. choice C d. choice D e. choice E 29. During mutarotation, which pair of these molecules would interchange? a. choices A and C b. choices A and B c. choice B and D d. choice A and E e. choice C and E A O OH H H H H OH OH CH2OH H OH O OH H H H OH CH2OH H OH H OH O OH H H H OH CH2OH H OH H OH O H H HO OH H OH CH2OH CH2OH O OH H H H OH H OH CH2OH H OH E C B D

FST100A2003 Midterm1 30.Which of the following describes honey? a.It contains primarily sucrose b.It contains slightly more fructose than glucose c.It contains about 20%sugars d.Answers b and c e.Answers a-d are all true 31.Which of the following sugars is the most hygroscopic? a.Milk sugar b.Fructose c.Refined suga d.Dextrose e.Brown sugar 32.How does glucopyranose form from the open chain structure? a.By nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon by the C5-OH group b.By keto-enol isomerization c.By nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon by the C6-OH group d.By nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon by the C2-OH group e.By oxidizing the carbonyl carbor 33.Which of the following describes lactose? a.It is a monosaccharide b.It contains two glucose subunits c.It contains a B[1,4]glycosidic linkage d.It is easily digested by the majority of adults worldwide e.It is found only in plants 34.If we hydrolyze a corn starch solution,which of the following would occur? a.The solution would be more susceptible to Maillard browning reactions b.The viscosity of the solution would increase c.DE value would decrease d.Most of the sugars in the solution would be oxidized e.None of the above would happen 86
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 8 30. Which of the following describes honey? a. It contains primarily sucrose b. It contains slightly more fructose than glucose c. It contains about 20% sugars d. Answers b and c e. Answers a-d are all true 31. Which of the following sugars is the most hygroscopic? a. Milk sugar b. Fructose c. Refined sugar d. Dextrose e. Brown sugar 32. How does glucopyranose form from the open chain structure? a. By nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon by the C5 -OH group b. By keto-enol isomerization c. By nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon by the C6 -OH group d. By nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon by the C2 -OH group e. By oxidizing the carbonyl carbon 33. Which of the following describes lactose? a. It is a monosaccharide b. It contains two glucose subunits c. It contains a β[1,4] glycosidic linkage d. It is easily digested by the majority of adults worldwide e. It is found only in plants 34. If we hydrolyze a corn starch solution, which of the following would occur? a. The solution would be more susceptible to Maillard browning reactions b. The viscosity of the solution would increase c. DE value would decrease d. Most of the sugars in the solution would be oxidized e. None of the above would happen

FST100A2003 Midterm 1 35Dgta2heermtomanennaoaomaaocadwhe Ihis measured angle a will not depend on a.the type of sugar(e.g.glucose versus fructose) b.the length of the sample chamber c.the concentration of the sugar solution d.the temperature e.All of the above will affect the measured angle a 36.Which of the following is an undesirable consequence of Maillard browning? a.Loss of essential amino acids b.An increase in DE value c.An undesirable brown color on the surface of fresh frui d.A"burnt sugar"smell e.None of the above are undesirable consequences of Maillard browning 9
FST 100A 2003 Midterm 1 9 35. During a polarimetry experiment, one measures an angle of rotation α associated with the light exiting the sample. This measured angle α will not depend on a. the type of sugar (e.g. glucose versus fructose) b. the length of the sample chamber c. the concentration of the sugar solution d. the temperature e. All of the above will affect the measured angle α 36. Which of the following is an undesirable consequence of Maillard browning? a. Loss of essential amino acids b. An increase in DE value c. An undesirable brown color on the surface of fresh fruit d. A "burnt sugar" smell e. None of the above are undesirable consequences of Maillard browning
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验五 美拉德褐变.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验四 蛋白质的溶解性.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验三 乳化实验.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 淀粉凝胶实验.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 水分活度的测定.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学大纲 Food Chemistry(负责人:倪莉).pdf
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)13 食品中有害物质的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)12 食品中限量元素的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)11 食品添加剂的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)10 蛋白质的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)09 多糖的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)08 糖类物质(碳水化合物)的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)07 脂类的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)06 酸度的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)05 灰分的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)04 水分的测定.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 食品的物理检测方法.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)01 绪论、02 食品样品的采集、制备与处理、保存.ppt
- 《食品分析》课程教学资源(相关标准)SNT1768-2006孔雀石绿和结晶及其紫代谢物快速测定方法.pdf
- 《食品分析》课程教学资源(相关标准)SNT1479-2004孔雀石绿残留检测方法.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 1(UC Davis)答案.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 2(UC Davis)试题.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 2(UC Davis)答案.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 3(UC Davis)答案.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 3(UC Davis)试题.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 4(UC Davis)答案.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Midterm Examination 4(UC Davis)试题.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(UC Davis)试题.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(Fuzhou University)试题.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(UC Davis)答案.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)Final Examination(Fuzhou University)答案.pdf
- 《食品化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)BET理论在食品吸湿研究中的若干应用.pdf
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Cocoa Butter.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Polymorphism.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)油脂类物质的理化性质.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论(负责人:倪莉).ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 水.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 碳水化合物 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 脂肪 Lipids.ppt
- 福州大学:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 色素.ppt
