同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification

Incineration,pyrolysis gasification Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn
Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn

Table of content ODefinitions o Incineration systems oPyrolysis systems oGasification systems
Table of content Definitions Incineration systems Pyrolysis systems Gasification systems

Definition o Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials.[11 "thermal treatment". o Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash,flue gas,and heat. o The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste,and may take the form of sol id lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas
Definition Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials.[1] "thermal treatment". Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas, and heat. The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste, and may take the form of solid lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas
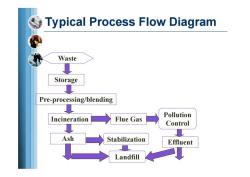
Typical Process Flow Diagram Waste Storage Pre-processing/blending Pollution Incineration Flue Gas Control Ash Stabilization Effluent Landfill
Typical Process Flow Diagram Waste Storage Pre-processing/blending Incineration Flue Gas Pollution Control Ash Stabilization Landfill Effluent

Heating value oThe heating value or calorific value of a substance, usual ly a fuel or food (see food energy),is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it. oa characteristic for each substance. ounits kcal/kg,kJ/kg,J/mol
Heating value The heating value or calorific value of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it. a characteristic for each substance. units : kcal/kg, kJ/kg, J /mol

Heating value Heating value is commonly determined by use of a bomb calor imeter. OThe heat of combustion for fuels is expressed as the HHV,LHV,or GHV
Heating value Heating value is commonly determined by use of a bomb calorimeter. The heat of combustion for fuels is expressed as the HHV, LHV, or GHV

Higher heating value odetermined by bringing all the products of combustion back to the or iginal pre-combustion temperature, and in particular condensing any vapor produced. 25°C. 1 o hhV assumes all the water component is in liquid state at the end of combustion (in product of combust ion)
Higher heating value determined by bringing all the products of combustion back to the original pre-combustion temperature, and in particular condensing any vapor produced. 25 °C. HHV assumes all the water component is in liquid state at the end of combustion (in product of combustion)

Lower heating value odetermined by subtracting the heat of vaporization of the water v vapor from the higher heating value. OThis treats any H20 formed as a vapor. OThe energy required to vaporize the water therefore is not real ized as heat
Lower heating value determined by subtracting the heat of vaporization of the water vapor from the higher heating value. This treats any H 2O formed as a vapor. The energy required to vaporize the water therefore is not realized as heat

Heating value w=r-2Ho4-8】 式中LHV一低位热值,kJkg: HHV一高位热值,kJkg; H,O一焚烧产物中水的质量百分率,%; H、C、F一分别为废物中氢、氯、氟含量的质量 百分率,%
Heating value 式中 LHV—低位热值,kJ/kg; HHV—高位热值,kJ/kg; H2O—焚烧产物中水的质量百分率, %; H、Cl、F—分别为废物中氢、氯、氟含量的质量 百分率,%。 35.5 19 2420 2 9 Cl F LHV HHV H O H
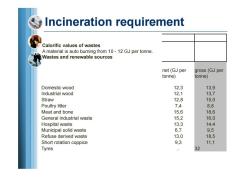
Incineration requirement Calorific values of wastes A material is auto burning from 10-12 GJ per tonne. Wastes and renewable sources net(GJ per gross(GJ per tonne) tonne) Domestic wood 12,3 13,9 Industrial wood 12,1 13,7 Straw 12,8 15,0 Poultry litter 7,4 8,8 Meat and bone 15,6 18,6 General industrial waste 15,2 16,0 Hospital waste 13,3 14,4 Municipal solid waste 6,7 9,5 Refuse derived waste 13,0 18,5 Short rotation coppice 9,3 11,1 Tyres … 32
Incineration requirement Calorific values of wastes A material is auto burning from 10 - 12 GJ per tonne. Wastes and renewable sources net (GJ per tonne) gross (GJ per tonne) Domestic wood 12,3 13,9 Industrial wood 12,1 13,7 Straw 12,8 15,0 Poultry litter 7,4 8,8 Meat and bone 15,6 18,6 General industrial waste 15,2 16,0 Hospital waste 13,3 14,4 Municipal solid waste 6,7 9,5 Refuse derived waste 13,0 18,5 Short rotation coppice 9,3 11,1 Tyres .. 32
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第5章 土壤质量监测 Soil Pollution Monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第3章 大气和废气监测 Atmosphere and flue waste gas monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第2章 水和废水监测.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验8 生化需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验7 化学需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验5 碘量法测定水中溶解氧.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验6 水中铬的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验4 水中氟化物的测定(离子选择电极法).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验3 氨氮的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验2 颜色的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验1 废水悬浮固体和浊度的测定.pdf
- 《环境监测》课程教学资源(作业习题)问答题(打印版,含答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
