同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management

Question What is a trans-boundary river/lake? A transboundary river/lake is a river/lake that crosses at least one political borders
Question What is a trans-boundary river/lake? Atransboundary river/lake is a river/lake that crosses at least one political borders

Outline 1.Transboundary river basins of the world 2.Current water stress in major river basins of the world transboundary water agreements 3.Benefits from the cooperative management of transboundary water resources 4.Case:Senegal River Basin:Cooperative Management
1. Transboundary river basins of the world 2. Current water stress in major river basins of the world transboundary water agreements 3. Benefits from the cooperative management of transboundary water resources 4. Case: Senegal River Basin: Cooperative Management Outline

Water "There is a water crisis, and there is an increasing understanding that it is a Water crisis of governance rather than one of ash国ed resp0n5ltW physical scarcity of Te United Nifiors g脚g0 icpmeet water”(UNEP2008) Biport 2
“There is awater crisis, and there is an increasing understanding that it is a crisis of governance rather than one of physical scarcity of water” (UNEP, 2008)

"I urge Governments to recognize the urban water crisis for what it is a crisis of governance,weak policies and poor management,rather than one of scarcity."UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon,2011 "This crisis is one of water governance,essentially caused by the ways in which we mismanage water,"UNWWDR.2006
“I urge Governments to recognize the urban water crisis for what it is — a crisis of governance, weak policies and poor management, rather than one of scarcity.” UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon, 2011 "This crisis is one of water governance, essentially caused by the ways in which we mismanage water,” UNWWDR, 2006

Introduction Almost 40%of the world's population lives in more than 200 river basins that are shared by more than two countries. 22 countries around the world are heavily dependent upon the flow of water originating in other upstream nations for a large part of their supply. Cooperative management of shared watercourses can optimize regional benefits,mitigate water-related disasters, and minimize tensions. It can also help maintain shared ecosystems and improve water productivity in agriculture
Introduction • Almost 40% of the world’s population lives in more than 200 river basins that are shared by more than two countries. • 22 countries around the world are heavily dependent upon the flow of water originating in other upstream nations for a large part of their supply. • Cooperative management of shared watercourses can optimize regional benefits, mitigate water-related disasters, and minimize tensions. • It can also help maintain shared ecosystems and improve water productivity in agriculture

Transboundary river basins of the world 263 international river basins cover 45%of earth's surface 145 international treaties since 1814 established to deal with some non-navigational use aspect 12 states have more than 95%of their territory within one or more transboundary basin(s) Global Figures on Transboundary Waters 148 countries include territory within one or more transboundary river basins 39 countries have more than 90%of their territory within one or more transboundary river basins 21 lie entirely within one or more of these watersheds There are numerous examples where transboundary waters have proved to be a source of cooperation rather than conflict
◆263 international river basins cover 45% of earth’s surface ◆145 international treaties since 1814 established to deal with some non-navigational use aspect ◆12 states have more than 95% of their territory within one or more transboundary basin(s) Transboundary river basins of the world
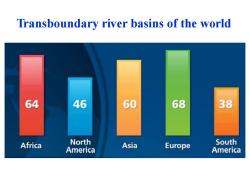
Transboundary river basins of the world 64 46 60 68 38 Africa North America Asia Europe South America
Transboundary river basins of the world
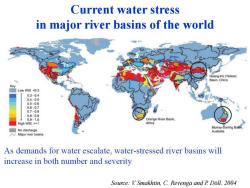
Current water stress in major river basins of the world Huang-Ho (Yellow) Basin,China Key Low WSI =1 Africa Murray-Darling Bas No discharge Australia Major river basins As demands for water escalate,water-stressed river basins will increase in both number and severity Source:V.Smakhtin,C.Revenga and P Doll.2004
Current water stress in major river basins of the world As demands for water escalate, water-stressed river basins will increase in both number and severity Source: V. Smakhtin, C. Revenga and P. Döll. 2004
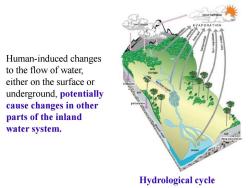
cloud forme EVAPORATION Human-induced changes to the flow of water, either on the surface or underground,potentially cause changes in other parts of the inland water system. Hydrological cycle
Human-induced changes to the flow of water, either on the surface or underground, potentially cause changes in other parts of the inland water system. Hydrological cycle
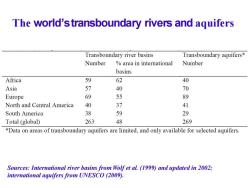
The world'stransboundary rivers and aquifers Transboundary river basins Transboundary aquifers* Number area in international Number basins Africa 59 62 40 Asia 57 40 70 Europe 69 55 89 North and Central America 40 37 41 South America 38 59 29 Total (global) 263 48 269 *Data on areas of transboundary aquifers are limited,and only available for selected aquifers. Sources:International river basins from Wolf et al.(1999)and updated in 2002; international aquifers from UNESCO(2009)
The world’stransboundary rivers and aquifers Sources: International river basins from Wolf et al. (1999) and updated in 2002; international aquifers from UNESCO (2009)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 地球环境的基本特征.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 生态系统.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三章 人口与资源.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四章 资源短缺.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五章 环境污染 Environmental Pollution.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六章 生态破坏 Ecology Damage.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第七章 全球环境问题.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第八章 可持续发展的基本理论.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第九章 可持续发展战略的实施途径.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第十章 环境伦理观.doc
