同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology

同©大学 Tongji University Lesson X Membrane technology Tang Yulin 25May2017
Tongji University Lesson X Membrane technology Tang Yulin 25 May 2017
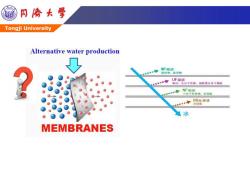
酒 同©大号 Tongji University Alternative water production MF微这 固形物、品浮物 UF超返 出白,大分千色蒸,黑胶等大分子物质 NF纳滤 小分子有机物、芳香能 RO反渗透 无机盐 水 MEMBRANES
Tongji University
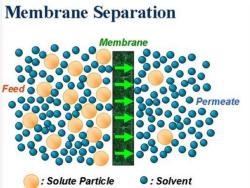
Membrane Separation Membrane Feed Permeate Solute Particle O:Solvent
Tongji University

g© 同©大学 Tongji University Introduction to membrane 。Classification of membrane processes Characteristics of membrane processes 用下
Tongji University Introduction to membrane Classification of membrane processes Characteristics of membrane processes

同燎大学 rocesses Tongji University A membrane is a selective barrier that permits the separation of certain species i in a a fluid by combination of sieving and diffusion mechanisms. Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights Membrane processes are becoming popular because they are considered "Green"technology -no chemicals are used in the process
Tongji University A membrane is a selective barrier that permits the separation of certain species in a fluid by combination of sieving and diffusion mechanisms. Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights . Membrane processes are becoming popular because they are considered “Green” technology - no chemicals are used in the process. Membrane Processes
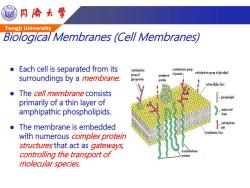
同©大学 Tongji University Biological Membranes (Cell Membranes) Each cell is separated from its carbobydrate carbohydrate group of protein oyrateoufid surroundings by a membrane. group of peripheral glycoprotein protein extracellular face The cell membrane consists -phospholipid primarily of a thin layer of amphipathic phospholipids. amino acid chain carbohydrate The membrane is embedded unit cytoplasmie face with numerous complex protein structures that act as gateways, controlling the transport of t女ansmembrane proteins molecular species
Tongji University Biological Membranes (Cell Membranes) Each cell is separated from its surroundings by a membrane. The cell membrane consists primarily of a thin layer of amphipathic phospholipids. The membrane is embedded with numerous complex protein structures that act as gateways, controlling the transport of molecular species

同海大学 Tongji University Synthetic Membranes 1956 -early 1980s:RO desalination,no commercial MF/UF for drinking water mid-1980 -early 1990s:Development of Memcor(MF), Aquasource (UF),clean waters small capacities mid-1990-2002:Start of market growth,new competitors (Zenon,Xflow,Hydranautics,Pall,lonics)with second generation membranes/modules Use on not so clean waters,start of immersed MBR products Now:Large plants 200000m3/d;Strong growth of RO desalination market
Tongji University Synthetic Membranes 1956 -early 1980s: RO desalination, no commercial MF/UF for drinking water mid-1980 -early 1990s: Development of Memcor (MF), Aquasource (UF), clean waters & small capacities mid-1990 -2002: Start of market growth, new competitors (Zenon, Xflow, Hydranautics, Pall, Ionics) with second generation membranes/modules ; Use on not so clean waters, start of immersed MBR products Now: Large plants > 200000m3 /d; Strong growth of RO desalination market

同海大学 Tongji U Source The McILVAINE COMPANY (2004) Chemical 5.6% 40%for water Desalination 20.4% Food&Bev.12.9% Metals 4.9% Mining 1.4% Oil&Gas 1.5% Water 15.4% Other industries 9.6% Wastewater 4.3% Pharmaceutical 10.4% Semiconductor 5.1% Power 3.8% Refineries1.4% Pulp&paper 3.1% GVEOUA Global Market Share
Tongji University Global Market Share
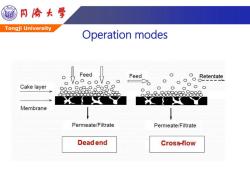
G 同©大号 Tongji University Operation modes Feed Feed O Retentate Cake layer Membrane Permeate/Filtrate Permeate/Filtrate Dead end Cross-flow
Tongji University Operation modes
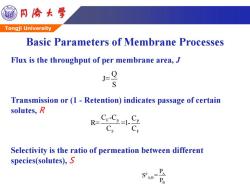
同©大学 Tongji University Basic Parameters of Membrane Processes Flux is the throughput of per membrane area,J J= S Transmission or (1 Retention)indicates passage of certain solutes,R R-Cr Selectivity is the ratio of permeation between different species(solutes),S =PA
Tongji University Flux is the throughput of per membrane area, J Transmission or (1 - Retention) indicates passage of certain solutes, R Selectivity is the ratio of permeation between different species(solutes), S F p P F F C -C C R= =1- C C Q J= S p A A,B B P S = P Basic Parameters of Membrane Processes
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第5章 土壤质量监测 Soil Pollution Monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第3章 大气和废气监测 Atmosphere and flue waste gas monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第2章 水和废水监测.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验8 生化需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验7 化学需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验5 碘量法测定水中溶解氧.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验6 水中铬的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验4 水中氟化物的测定(离子选择电极法).pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 地球环境的基本特征.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 生态系统.doc
