同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛)
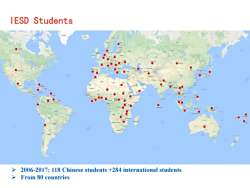
IESD Students 2006-2017:118 Chinese students +284 international students >From 80 countries
IESD Students ➢ 2006-2017: 118 Chinese students +284 international students ➢ From 80 countries

General Introduction to water resources
General Introduction to water resources

Outline -1.1 Water resources -1.2 Win-win solutions to mitigate water scarcity -1.3 Climate Change and Water Scarcity -1.4 Solutions to reduce water consumption -1.5 Sustainable water use -1.6 Sustainable water resources management
– 1.1 Water resources – 1.2 Win-win solutions to mitigate water scarcity – 1.3 Climate Change and Water Scarcity – 1.4 Solutions to reduce water consumption – 1.5 Sustainable water use – 1.6 Sustainable water resources management Outline

1.1 Water Resources
1.1 Water Resources

Properties of Water ● Composed of 2 Hydrogen and (a) 1 Oxygen Exists as solid,liquid or gas (b) ·High heat capacity 。Polar -One end has (+charge,one end has (-)charge ·Forms Hydrogen bond between 2 water molecules -H-bonds define water's physical properties
Properties of Water • Composed of 2 Hydrogen and 1 Oxygen • Exists as solid, liquid or gas • High heat capacity • Polar – One end has (+) charge, one end has (-) charge • Forms Hydrogen bond between 2 water molecules – H-bonds define water’s physical properties

Definition Water resources Water resources are sources of water that are potentially useful -Wikipedia Water resources management Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing,distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources It is a sub-set of water cycle management. Ideally,water resource management planning has regard to all the competing demands for water and seeks to allocate water on an equitable basis to satisfy all uses and demands. As with other resource management,this is rarely possible in practice
Definition Water resources • Water resources are sources of water that are potentially useful. - Wikipedia Water resources management • Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the optimum use of water resources. • It is a sub-set of water cycle management. • Ideally, water resource management planning has regard to all the competing demands for water and seeks to allocate water on an equitable basis to satisfy all uses and demands. • As with other resource management, this is rarely possible in practice

Global Water resources Total amount of water at the Earth's surface:1408.7X 106 km3 unevenly distribution of fresh water in the world. China with 21%of world's population has only 7%of the water resources. ● However,Canada,with only 0.5%of the world population,has 20% of world's fresh water. The world's fresh water supply is continuously collected,purified, recycled,and distributed in the solar powered hydraulic cycle
• Total amount of water at the Earth’s surface: 1408.7×106 km3 • unevenly distribution of fresh water in the world. • China with 21% of world’s population has only 7% of the water resources. • However, Canada, with only 0.5% of the world population, has 20% of world’s fresh water. • The world’s fresh water supply is continuously collected, purified, recycled, and distributed in the solar powered hydraulic cycle. Global Water Resources
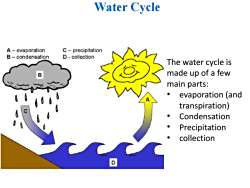
Water Cycle A-evaporation C-precipitation B-condensation D-collection The water cycle is made up of a few main parts: ● evaporation (and transpiration) ● Condensation Precipitation collection
Water Cycle The water cycle is made up of a few main parts: • evaporation (and transpiration) • Condensation • Precipitation • collection
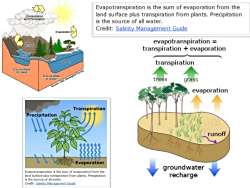
公 Evapotranspiration is the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants.Precipitation is the source of all water. Credit:Salinity Management Guide Evaporation evapotranspiration transpiration evaporation ake Ocean transpiration Source:Utah Geologicai Survey trees grass evaporation Transpiration Precipitation runoff 公外分公 泰Evaporation groundwater Evapotranspiration is the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants.Precipitation recharge is the source of all water. Credit:Salinity Management Guide
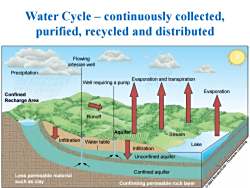
Water Cycle-continuously collected, purified,recycled and distributed Flowing artesian well Precipitation Evaporation and transpiration Well requiring a pump Confined Evaporation Recharge Area Runoff Aquifer Stream Infiltration Water table Lake Infiltration Unconfined aquifer ole Confined aquifer Less permeable material such as clay Confirming permeable rock layer 2002 Brooks
Evaporation and transpiration Evaporation Stream Infiltration Water table Infiltration Unconfined aquifer Confined aquifer Lake Well requiring a pump Flowing artesian well Runoff Precipitation Confined Recharge Area Aquifer Less permeable material such as clay Confirming permeable rock layer Water Cycle – continuously collected, purified, recycled and distributed
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第5章 土壤质量监测 Soil Pollution Monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第3章 大气和废气监测 Atmosphere and flue waste gas monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第2章 水和废水监测.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验8 生化需氧量的测定.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 地球环境的基本特征.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 生态系统.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三章 人口与资源.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四章 资源短缺.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五章 环境污染 Environmental Pollution.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六章 生态破坏 Ecology Damage.doc
