同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF)

Water Resources Management Tool: Water Footprint (WF)
Water Resources Management Tool: Water Footprint (WF)

Outline -Concept of water footprint -The water footprint of a product -The water footprint of a nation -The water footprint of a business -Global water footprint -Groundwater footprint -From concept to practice
–Concept of water footprint –The water footprint of a product –The water footprint of a nation –The water footprint of a business –Global water footprint –Groundwater footprint –From concept to practice Outline

Concept of water footprint
Concept of water footprint

CONCEPT Water Footprint The total volume of freshwater that is used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business
CONCEPT Water Footprint The total volume of freshwater that is used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business

What is water footprint? The water footprint(WF)is an indicator of freshwater use that looks not only at direct water use of a consumer or producer,but also at the indirect water use. The water footprint can be regarded as a comprehensive indicator of freshwater resources appropriation, Hoekstra,2002 next to the traditional and restricted measure of water withdrawal. 2018/10/25
What is water footprint? 2018/10/25 ◼The water footprint (WF) is an indicator of freshwater use that looks not only at direct water use of a consumer or producer, but also at the indirect water use. ◼The water footprint can be regarded as a comprehensive indicator of freshwater resources appropriation, next to the traditional and restricted measure of water withdrawal. Hoekstra,2002

What is water footprint? Blue water consumption of blue water resources footprint (surface and groundwater)along the supply chain of a product. Green water consumption of green water resources (rainwater insofar as it does not become footprint run-off). volume of freshwater that is required to Gray water assimilate the load of pollutants given footprint natural background concentrations and existing ambient water quality standards. 2018/10/25
What is water footprint? 2018/10/25 • consumption of blue water resources (surface and groundwater) along the supply chain of a product. Blue water footprint • consumption of green water resources (rainwater insofar as it does not become run-off). Green water footprint • volume of freshwater that is required to assimilate the load of pollutants given natural background concentrations and existing ambient water quality standards. Gray water footprint

Categories Green Water Footprint volume of rainwater evaporated or incorporated into product volume of surface or groundwater Blue Water Footprint evaporated,incorporated into product or returned to other catchment or the sea. Grey Water Footprint volume of polluted water
Categories Green Water Footprint Blue Water Footprint Grey Water Footprint volume of polluted water. volume of rainwater evaporated or incorporated into product volume of surface or groundwater evaporated,incorporated into product or returned to other catchment or the sea
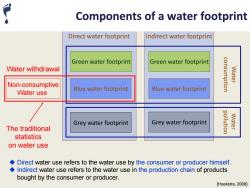
Components of a water footprint Direct water footprint Indirect water footprint Green water footprint Green water footprint Water withdrawal consumption Water Non-consumptive Blue water footprint Blue water footprint Water use Grey water footprint Grey water footprint pollution Water The traditional statistics on water use Direct water use refers to the water use by the consumer or producer himself. Indirect water use refers to the water use in the production chain of products bought by the consumer or producer. [Hoekstra,2008]
Direct water footprint Indirect water footprint Green water footprint Green water footprint Blue water footprint Blue water footprint Grey water footprint Grey water footprint Water consumption Water pollution [Hoekstra, 2008] Non-consumptive Water use Water withdrawal The traditional statistics on water use Components of a water footprint ◆ Direct water use refers to the water use by the consumer or producer himself. ◆ Indirect water use refers to the water use in the production chain of products bought by the consumer or producer

Why water footprint?
Why water footprint?

Shrinking Aral Sea ◆ The water footprint can make a link between consumption in one place and impacts on water systems elsewhere. ◆ Water use for cotton production can have major impacts on the environment. Particularly intensive irrigation schemes can have disastrous effects,as shown for example in the case of Uzbekistan and the desiccation of the Aral Sea. Shrinking Aral Sea
◆ The water footprint can make a link between consumption in one place and impacts on water systems elsewhere. ◆ Water use for cotton production can have major impacts on the environment. ◆ Particularly intensive irrigation schemes can have disastrous effects, as shown for example in the case of Uzbekistan and the desiccation of the Aral Sea. Shrinking Aral Sea Shrinking Aral Sea
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第5章 土壤质量监测 Soil Pollution Monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第3章 大气和废气监测 Atmosphere and flue waste gas monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第2章 水和废水监测.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 地球环境的基本特征.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 生态系统.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三章 人口与资源.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四章 资源短缺.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五章 环境污染 Environmental Pollution.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六章 生态破坏 Ecology Damage.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第七章 全球环境问题.doc
