同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas

Leachate and Landfill Gas
Leachate and Landfill Gas

Outline of the presentation 1.What are landfill gas and leachate? 2.How to anticipate their production? 3.Treatment and disposal technologies for leachate 4. How do we collect and recycle the landfill gas? 5.What can we do with GHG emissions from landfills?
1. What are landfill gas and leachate? 2. How to anticipate their production? 3. Treatment and disposal technologies for leachate 4. How do we collect and recycle the landfill gas? 5. What can we do with GHG emissions from landfills? Outline of the presentation

What are leachate and landfill gas?
What are leachate and landfill gas?

Leachate
Leachate

General definition >"Leachate is the term used for any liquid produced by the action of leaching which occurs when water percolates through any permeable material." >"Leachate is the liquid that drains or 'leaches'from a landfill;it varies widely in composition regarding the age of the landfill and the type of waste that it contains.It usually contains both dissolved and suspended material
“Leachate is the term used for any liquid produced by the action of leaching which occurs when water percolates through any permeable material.” “Leachate is the liquid that drains or ‘leaches’ from a landfill; it varies widely in composition regarding the age of the landfill and the type of waste that it contains. It usually contains both dissolved and suspended material.” General definition

Leachate
Leachate

Origin composition Water rainfall Decomposition >An important contributor to the >Some liquids exist already before water generation of leachate leakage in the landfill:inside garbage,food products and chemical waste. >Goes through the landfill and collects contaminants. Decomposition of material produces "Contaminants are leached from solid some water and a wide range of additional wastes” materials:methane,carbon dioxide,acids, -Leaching of inherent soluble materials in sugars,iron,heavy metals,pesticides,etc. the wastes -Leaching of soluble products of chemical >They produce a small quantity of reactions created by decomposition leachate by themselves,which,will be -Washout of fines and colloids collected by water,which,in turn,creates further leachate. >Aids bacteria in the process of decomposition:When organic matter decomposes it needs oxygen.Adding water to wastes makes the process faster
Water rainfall Decomposition An important contributor to the generation of leachate Goes through the landfill and collects contaminants. “Contaminants are leached from solid wastes” ‐Leaching of inherent soluble materials in the wastes ‐Leaching of soluble products of chemical reactions created by decomposition ‐Washout of fines and colloids Aids bacteria in the process of decomposition: When organic matter decomposes it needs oxygen. Adding water to wastes makes the process faster. Some liquids exist already before water leakage in the landfill: inside garbage, food products and chemical waste. Decomposition of material produces some water and a wide range of additional materials: methane, carbon dioxide, acids, sugars, iron, heavy metals, pesticides, etc. They produce a small quantity of leachate by themselves, which, will be collected by water, which, in turn, creates further leachate. Origin & composition

Factors influencing its composition >The characteristics of leachate are influenced by a wide range of factors: Composition of waste(e.g:batteries) Climate/season/Precipitations Site hydrology and soil composition Waste age Landfill design,cover design,sampling way,age of the landfill
The characteristics of leachate are influenced by a wide range of factors: ‐ Composition of waste (e.g: batteries) ‐ Climate / season /Precipitations ‐ Site hydrology and soil composition ‐ Waste age ‐ Landfill design, cover design, sampling way, age of the landfill Factors influencing its composition

Leachate escape >"Field capacity":the maximum moisture the soil can retain >In the unfinished landfill:When a landfill layer reaches its field capacity,more moisture will displace the moisture in the soil.The water will drop in the landfill the leachate will drop to the next lowest soil and refuse layer. >In the finished landfill:If the field capacity of the soil covering waste is exceeded,the water percolates through the soil and into the buried solid waste.If the field capacity of waste is exceeded,leachate flows into the collection system/into the ground
“Field capacity”: the maximum moisture the soil can retain In the unfinished landfill: When a landfill layer reaches its field capacity, more moisture will displace the moisture in the soil. The water will drop in the landfill & the leachate will drop to the next lowest soil and refuse layer. In the finished landfill: If the field capacity of the soil covering waste is exceeded, the water percolates through the soil and into the buried solid waste. If the field capacity of waste is exceeded, leachate flows into the collection system / into the ground. Leachate escape
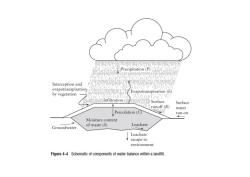
% Precipitation (P) Interception and evapotranspiration Evapotranspiration(E) by vegetation Infiltration Surface Surface runoff(R) 明 water Percolation(C】 run-on Moisture content of waste (S) Leachate Groundwater Leachate escape to environment Flgure 4-4 Schematic of components of water balance within a landfill
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第5章 土壤质量监测 Soil Pollution Monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第3章 大气和废气监测 Atmosphere and flue waste gas monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第2章 水和废水监测.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验8 生化需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验7 化学需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验5 碘量法测定水中溶解氧.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验6 水中铬的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验4 水中氟化物的测定(离子选择电极法).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验3 氨氮的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验2 颜色的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验1 废水悬浮固体和浊度的测定.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
