同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City

Contents Part 1:Overview:concepts,principles, methodologies and applications Part 2:Stormwater quantity management programs,methodologies Part 3:Stormwater quality management programs,methodologies;Rainwater Harvesting
Contents • Part 1: Overview: concepts, principles, methodologies and applications • Part 2: Stormwater quantity management programs, methodologies • Part 3: Stormwater quality management programs, methodologies; Rainwater Harvesting

References Debo,Thomas N.Municipal stormwater management/2nd ed.Lewis Publishers,c2003 Scott Slaney.Stormwater Management for Sustainable Urban Environments,images Publishing,2017. Municipal Stormwater Stormwater Management 基础施 Management Second Edition for Sustainable Urban Environments Stormwater 器兴 海绵城市基础设施 Management 雨洪管理手册 for Sustainable Thomas N.DeboFindrew )Reese Urban Environments LEWIS PUBLISHERS M家智
References • Debo,Thomas N. Municipal stormwater management/ 2nd ed. Lewis Publishers, c2003. • Scott Slaney. Stormwater Management for Sustainable Urban Environments, images Publishing, 2017

PART 1 > What is a Sponge City? What are the key issues the Sponge City wants to solve? >What does a Sponge City need in practise? What are the benefits of a Sponge City? > Progress of the Sponge City construction in China
PART 1 ➢ What is a Sponge City? ➢ What are the key issues the Sponge City wants to solve? ➢ What does a Sponge City need in practise? ➢ What are the benefits of a Sponge City? ➢ Progress of the Sponge City construction in China
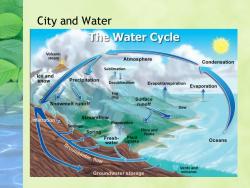
City and Water The Water Cycle Volcanic steam Atmosphere Condensation Sublimation Ice and f snow Precipitation Desublimation Evapotranspiration Evaporation Fog drip Surface Snowmelt runoff runoff Dew ation Streamflow Evaporation epage 个 Spring Flora and fauna Fresh- Plant water uptake Oceans Groundwater flow Vents and Groundwater storage volcanos
City and Water
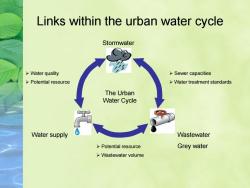
Links within the urban water cycle Stormwater >Water quality >Sewer capacities >Potential resource >Water treatment standards The Urban Water Cycle Water supply Wastewater >Potential resource Grey water >Wastewater volume
Links within the urban water cycle Stormwater Wastewater Grey water Water supply ➢ Water quality ➢ Potential resource ➢ Sewer capacities ➢ Water treatment standards ➢ Potential resource ➢ Wastewater volume The Urban Water Cycle

Impacts of Urbanization on the Water Environment Decrease in forest and grass cover Decrease in water conservation and storage capability Decrease in paddy and pond area>Decrease in rainfall storage capacity Increase in nonpermeable land surface>Decrease in infiltration and increase in runoff Population growth and concentration>Increase in demand for water supply and wastewater treatment Before Urbanization After Urbanization
Before Urbanization After Urbanization Decrease in forest and grass cover ➔ Decrease in water conservation and storage capability Decrease in paddy and pond area ➔ Decrease in rainfall storage capacity Increase in nonpermeable land surface ➔ Decrease in infiltration and increase in runoff Population growth and concentration ➔ Increase in demand for water supply and wastewater treatment Impacts of Urbanization on the Water Environment
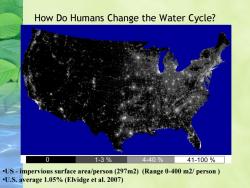
How Do Humans Change the Water Cycle? 0 1-3% 4-40% 41-100% .US-impervious surface area/person (297m2)(Range 0-400 m2/person U.S.average 1.05%(Elvidge et al.2007)
How Do Humans Change the Water Cycle? •US - impervious surface area/person (297m2) (Range 0-400 m2/ person ) •U.S. average 1.05% (Elvidge et al. 2007)
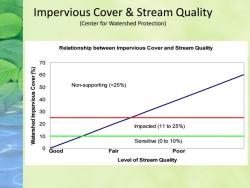
Impervious Cover Stream Quality (Center for Watershed Protection) Relationship between Impervious Cover and Stream Quality 70 60 50 Non-supporting (>25%) 40 20 Impacted (11 to 25%) 10 Sensitive (0 to 10%) 0 Good Fair Poor Level of Stream Quality
Impervious Cover & Stream Quality (Center for Watershed Protection) Relationship between Impervious Cover and Stream Quality 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Level of Stream Quality Watershed Impervious Cover (%) Good Fair Poor Non-supporting (>25%) Impacted (11 to 25%) Sensitive (0 to 10%)

Urbanization and Water Water resource scarcity 。Vater pollution 。Urban Waterlogging
Urbanization and Water • Water resource scarcity • Water pollution • Urban Waterlogging

按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 地球环境的基本特征.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 生态系统.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三章 人口与资源.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四章 资源短缺.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五章 环境污染 Environmental Pollution.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六章 生态破坏 Ecology Damage.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第七章 全球环境问题.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第八章 可持续发展的基本理论.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第九章 可持续发展战略的实施途径.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第十章 环境伦理观.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第十一章 环境规划与管理.doc
