同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Filtration

同©大学 Tongji University Lesson VI Filtration Tang Yulin 13 April 2017
Tongji University Lesson VI Filtration Tang Yulin 13 April 2017

同瘠大学 Mediaion Tongji University VI、Outline (1)History (2)Slow filtration (3)Rapid filtration (4)Media of filter (5)V-Type filter (6)Pressure Granular bed filter (7)Filtration theory
Tongji University VI、Outline (1) History (2) Slow filtration (3) Rapid filtration (4) Media of filter (5) V-Type filter (6) Pressure Granular bed filter (7) Filtration theory Media filtration

同©大学 Tongji University (1)History of the filtration Filtration is an ancient technology for cleaning water Sand and gravel filters used in India as early as 2000 B.C. Romans dug channels next to lakes to use natural filtration French began filtration around 1750 on small scale Filtration for municipal supply systems began in England and Scotland around 1800 First modern slow sand filtration system in London in 1829 Rapid filtration began in US in 1880s Rapid filtration began in China about 1895 in Shanghai)
Tongji University (1) History of the filtration Filtration is an ancient technology for cleaning water • Sand and gravel filters used in India as early as 2000 B.C. • Romans dug channels next to lakes to use natural filtration • French began filtration around 1750 on small scale • Filtration for municipal supply systems began in England and Scotland around 1800 • First modern slow sand filtration system in London in 1829 • Rapid filtration began in US in 1880s • Rapid filtration began in China about 1895 ( in Shanghai)

同©大学 Tongji University (2)Slow filtration This is the oldest form of filters,with fine sand loaded at low rate,0.05-0.2 m/hour. Slow sand filter treat the raw water by physical straining and biological degradation. There are 3-5 ft sand and form a layer of organic material and micro biofilm in the surface.Every few weeks or months,the top layer will be scrapped. This is a simple operation and no chemicals ones for small systems
Tongji University (2) Slow filtration This is the oldest form of filters, with fine sand loaded at low rate, 0.05-0.2 m/hour. Slow sand filter treat the raw water by physical straining and biological degradation. There are 3-5 ft sand and form a layer of organic material and micro biofilm in the surface. Every few weeks or months, the top layer will be scrapped. This is a simple operation and no chemicals ones for small systems
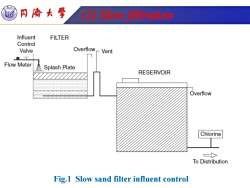
同©大学 2Sation Influent FILTER Control Valve Overflow -Vent Flow Meter Splash Plate RESERVOIR Overflow Chlorine To Distribution Fig.1 Slow sand filter influent control
Tongji University (2) Slow filtration Fig.1 Slow sand filter influent control
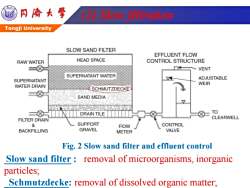
同©大学 2ation Tongji University SLOW SAND FILTER EFFLUENT FLOW RAW WATER HEAD SPACE CONTROL STRUCTURE VENT SUPERNATANT WATER SUPERNATANT ADJUSTABLE WATER DRAIN WEIR SCHMUTZDECKE SAND MEDIA DRAIN TILE TO FILTER DRAIN CLEARWELL & SUPPORT FIOW CONTROL BACKFILLING GRAVEL METER VALVE Fig.2 Slow sand filter and effluent control Slow sand filter removal of microorganisms,inorganic particles; Schmutzdecke:removal of dissolved organic matter;
Tongji University (2) Slow filtration Fig. 2 Slow sand filter and effluent control Slow sand filter : removal of microorganisms, inorganic particles; Schmutzdecke: removal of dissolved organic matter;

同海大学 inlet pipe used to introduce backwater for Tongji University sand cleaning filter gravel 3)Rapid filtration outlet under drain Replaced slow sand filters in 20th century; Much higher loading rate than slow sand filters,more than 100 X,typically 5-15 m/hour; Media are coarser,more uniform,(often multiple); Removal is not by physical straining on the surface as primary mechanism; Conceptually,rapid filtration is like sedimentation; Particles need pre-treatment with a coagulant to destabilize electrical charge;Destabilized particles adhere to grains in filter medium and are removed; Turbidity of outflow changes with time;
Tongji University (3) Rapid filtration • Replaced slow sand filters in 20th century; • Much higher loading rate than ; slow sand filters, more than 100 X, typically 5-15 m/hour; • Media are coarser, more uniform, (often multiple); • Removal is not by physical straining on the surface as primary mechanism; • Conceptually, rapid filtration is like sedimentation; • Particles need pre-treatment with a coagulant to destabilize electrical charge; Destabilized particles adhere to grains in filter medium and are removed; • Turbidity of outflow changes with time;
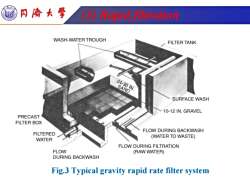
同燎大学 ③)ration WASH-WATER TROUGH FILTER TANK 24-301N. SAND SURFACE WASH 10-12 IN.GRAVEL PRECAST FILTER BOX FLOW DURING BACKWASH FILTERED WATER (WATER TO WASTE) FLOW DURING FILTRATION FLOW (RAW WATER) DURING BACKWASH Fig.3 Typical gravity rapid rate filter system
Tongji University (3) Rapid filtration Fig.3 Typical gravity rapid rate filter system
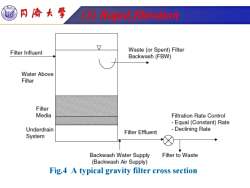
同©大学 ③ration Filter Influent Waste(or Spent)Filter Backwash(FBW) Water Above Filter Filter Media Filtration Rate Control Equal(Constant)Rate Underdrain Filter Effluent Declining Rate System Backwash Water Supply Filter to Waste (Backwash Air Supply) Fig.4 A typical gravity filter cross section
Tongji University (3) Rapid filtration Fig.4 A typical gravity filter cross section
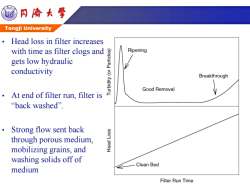
同海大学 Tongji University Head loss in filter increases with time as filter clogs and Ripening gets low hydraulic conductivity Breakthrough Good Removal At end of filter run,filter is "back washed". Strong flow sent back through porous medium, mobilizing grains,and washing solids off of Clean Bed medium Filter Run Time
Tongji University • Head loss in filter increases with time as filter clogs and gets low hydraulic conductivity • At end of filter run, filter is “back washed”. • Strong flow sent back through porous medium, mobilizing grains, and washing solids off of medium
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Sedimentation.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Leachate and Landfill Gas.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Incineration, pyrolysis & gasification.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Biogas – a way to solve sanitation problems.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Waste processing technologies application.pdf
- 同济大学:《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(讲稿)Introduction on Solid Waste.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)LANDFILL MANUALS LANDFILL SITE DESIGN.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste - Prospects and constraints.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting.pdf
- 《固体废物处理与资源化》课程教学资源(文献资料)A feasibility assessment of an integrated plastic waste system adopting.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第9章 环境监测质量保证.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第5章 土壤质量监测 Soil Pollution Monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第3章 大气和废气监测 Atmosphere and flue waste gas monitoring.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第2章 水和废水监测.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验8 生化需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验7 化学需氧量的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验5 碘量法测定水中溶解氧.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验6 水中铬的测定.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验4 水中氟化物的测定(离子选择电极法).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《环境监测》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)实验3 氨氮的测定.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Membrane technology.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Municipal Water Purification Plant.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Advanced Oxidation.pdf
- 同济大学:《给水工程原理与技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Mixing Coagulation - Flocculation.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)01 Introduction to water resources(负责人:王洪涛).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)02 Water Resources Management Tool - Water Footprint(WF).pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)03 Energy-water nexus in urban water systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)04 Water Quality Modeling、Reactions & Transport、Dissolved Oxygen Modeling in Rivers、Eutrophication.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)05 Trans-boundary water resources management.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)06 Water Resource Management - Sponge City.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)08 Case in Lake Victoria, East Africa.pdf
- 同济大学:《水资源管理》课程教学资源(教案讲义)07 Brief Introduction to Integrated Water Environment Rehabilitation、A Big Picture:China City’s Effort to Improve River Water Quality with Shanghai as a Case、River water quality assessment and water pollution sources survey.pdf
- 上海海洋大学:海洋生态与环境学院课程教学大纲汇编(2018版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(大纲讲义)教学大纲 Environmental protection and sustainable development.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷1.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷2.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷3.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷4.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷5.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《环境保护与可持续发展》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 地球环境的基本特征.doc
