中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Constraint Satisfaction Problems

Constraint Satisfaction Problems 吉建民 USTC jianminQustc.edu.cn 2022年3月21日 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Constraint Satisfaction Problems 吉建民 USTC jianmin@ustc.edu.cn 2022 年 3 月 21 日

Used Materials Disclaimer:本课件采用了S.Russell and P.Norvig's Artificial Intelligence-A modern approach slides,徐林莉老师课件和其他网 络课程课件,也采用了GitHub中开源代码,以及部分网络博客 内容 口卡4三4色进分QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Used Materials Disclaimer: 本课件采用了 S. Russell and P. Norvig’s Artificial Intelligence –A modern approach slides, 徐林莉老师课件和其他网 络课程课件,也采用了 GitHub 中开源代码,以及部分网络博客 内容

课程回顾 Best-first search Heuristic functions estimate costs of shortest paths Good heuristics can dramatically reduce search cost Greedy best-first search expands lowest h incomplete and not always optimal A*search expands lowest g+h complete and optimal also optimally efficient(up to tie-breaks,for forward search) Admissible heuristics can be derived from exact solution of relaxed problems 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 课程回顾 Best-first search ▶ Heuristic functions estimate costs of shortest paths ▶ Good heuristics can dramatically reduce search cost ▶ Greedy best-first search expands lowest h ▶ incomplete and not always optimal ▶ A* search expands lowest g + h ▶ complete and optimal ▶ also optimally efficient (up to tie-breaks, for forward search) ▶ Admissible heuristics can be derived from exact solution of relaxed problems

课程回顾 Local search algorithms the path to the goal is irrelevant;the goal state itself is the solution keep a single "current"state,try to improve it Hill-climbing search depending on initial state,can get stuck in local maxima Simulated annealing search escape local maxima by allowing some "bad"moves but gradually decrease their frequency Local beam search Keep track of k states rather than just one Genetic algorithms 口卡4三4色进分QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 课程回顾 Local search algorithms ▶ the path to the goal is irrelevant; the goal state itself is the solution ▶ keep a single “current” state, try to improve it ▶ Hill-climbing search ▶ depending on initial state, can get stuck in local maxima ▶ Simulated annealing search ▶ escape local maxima by allowing some “bad” moves but gradually decrease their frequency ▶ Local beam search ▶ Keep track of k states rather than just one ▶ Genetic algorithms

Table of Contents CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Table of Contents CSP examples Backtracking search for CSPs Problem structure and problem decomposition Local search for CSPs

Constraint satisfaction problems(CSPs) Standard search problem: state is a "black box"-any old data structure that supports goal test,eval,successor 任何可以由目标测试、评价函数、后继函数访问的数据结构 CSP: state is defined by Xi with values from domain (Di goal test is a set of constraints specifying allowable combinations of values for subsets of variables 每个约束包括一些变量的子集,并指定这些子集的值之间允 许进行的合并 Simple example of a formal representation language(形式化 表示方法) ~Allows useful general-purpose(通用的,而不是问题特定 algorithms with more power than standard search algorithms 口卡回t·三4色,是分Q0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) ▶ Standard search problem: ▶ state is a “black box” –– any old data structure that supports goal test, eval, successor 任何可以由目标测试、评价函数、后继函数访问的数据结构 ▶ CSP: ▶ state is defined by Xi with values from domain(值域) Di ▶ goal test is a set of constraints specifying allowable combinations of values for subsets of variables 每个约束包括一些变量的子集,并指定这些子集的值之间允 许进行的合并 ▶ Simple example of a formal representation language (形式化 表示方法) ▶ Allows useful general-purpose (通用的,而不是问题特定 的) algorithms with more power than standard search algorithms
Constraint satisfaction problems(CSPs) A constraint satisfaction problem(CSP)consists of three components,&D,and C: is a set of variables,{X1,...,Xn} D is a set of domains,[D1,...,Dn},one for each variable Each domain D;consists of a set of allowable values, [v1,...,vk}for variable Xi. C is a set of constraints that specify allowable combinations of values Each constraint Ci consists of a pair(scope,rel,where scope is a tuple of variables that participate in the constraint and rel is a relation that defines the values that those variables can take on A relation can be represented as an explicit list of all tuples of values that satisfy the constraint,or as an abstract relation that supports two operations:testing if a tuple is a member of the relation and enumerating the members of the relation 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) A constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) consists of three components, X , D, and C: ▶ X is a set of variables, {X1, . . . , Xn} ▶ D is a set of domains, {D1, . . . , Dn}, one for each variable ▶ Each domain Di consists of a set of allowable values, {v1, . . . , vk} for variable Xi . ▶ C is a set of constraints that specify allowable combinations of values ▶ Each constraint Ci consists of a pair ⟨scope,rel⟩, where scope is a tuple of variables that participate in the constraint and rel is a relation that defines the values that those variables can take on ▶ A relation can be represented as an explicit list of all tuples of values that satisfy the constraint, or as an abstract relation that supports two operations: testing if a tuple is a member of the relation and enumerating the members of the relation

Constraint satisfaction problems(CSPs) To solve a CSP,we need to define a state space and the notion of a solution Each state in a CSP is defined by an assignment of values to some or all of the variables,Xi=vi,Xj=vj,... An assignment that does not violate any constraints is called a consistent or legal assignment A complete assignment is one in which every variable is assigned A partial assignment is one that assigns values to only some of the variables A solution to a CSP is a consistent,complete assignment 口卡回t·三4色,是分Q0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) To solve a CSP, we need to define a state space and the notion of a solution ▶ Each state in a CSP is defined by an assignment of values to some or all of the variables, {Xi = vi , Xj = vj , . . .} ▶ An assignment that does not violate any constraints is called a consistent or legal assignment ▶ A complete assignment is one in which every variable is assigned ▶ A partial assignment is one that assigns values to only some of the variables ▶ A solution to a CSP is a consistent, complete assignment
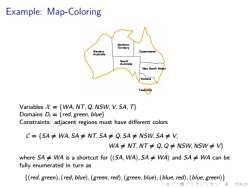
Example:Map-Coloring unne Variables={WA,NT,Q,NSW,V,SA,T} Domains D;=red,green,blue Constraints:adjacent regions must have different colors C={SA≠WA,5A≠NT,SA≠Q,5A≠NSW,SA≠V, WA≠NT,NT≠Q,Q≠NSw,NSW≠ where SA≠WA is a shortcut for(SA,WA),SA≠WA)and SA≠WA can be fully enumerated in turn as (red,green),(red,blue),(green,red),(green,blue),(blue,red),(blue,green)) 2ac
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Example: Map-Coloring Variables X = {WA, NT, Q, NSW, V, SA, T} Domains Di = {red, green, blue} Constraints: adjacent regions must have different colors C = {SA ̸= WA, SA ̸= NT, SA ̸= Q, SA ̸= NSW, SA ̸= V, WA ̸= NT, NT ̸= Q, Q ̸= NSW, NSW ̸= V} where SA ̸= WA is a shortcut for ⟨(SA, WA), SA ̸= WA⟩ and SA ̸= WA can be fully enumerated in turn as {(red, green),(red, blue),(green,red),(green, blue),(blue,red),(blue, green)}
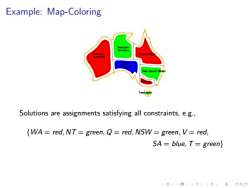
Example:Map-Coloring Ta呼 Solutions are assignments satisfying all constraints,e.g., {WA=red,NT=green,Q=red,NSW=green,V=red, SA=blue,T=green} 口·三色,进分双0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Example: Map-Coloring Solutions are assignments satisfying all constraints, e.g., {WA = red, NT = green, Q = red, NSW = green, V = red, SA = blue,T = green}
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Informed Search.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Solving Problems by Searching.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Intelligent Agents.pdf
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 9-Inference in first-order logic.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 8-First-Order Logic.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 7-Logical Agents.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 6-Adversarial Search.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 5-Constraint Satisfaction Problems.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 4-Informed search algorithms.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 3-Solving problems by searching.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 2-Intelligent Agents.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 18-Learning from Observations.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 14-Bayesian networks.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 13-Uncertainty.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 1-Introduction.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(讲义,英文版)chapter25.pdf
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(讲义,英文版)chapter25-6pp.pdf
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(讲义,英文版)chapter22.pdf
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(讲义,英文版)chapter22-6pp.pdf
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(讲义,英文版)chapter20b.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Game Playing.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Logical Agents.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Uncertainty and Bayesian Networks.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 11 马尔可夫决策过程.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 First-Order Logic and Inference in FOL.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 AI Planning.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 13 神经网络与深度学习.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 14 Reinforcement Learning.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 15 智能机器人系统介绍.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introdution(主讲:吉建民).pdf
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Course Overview(主讲:闫宏飞).ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Web Search.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Crawling the Web.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Retrieval Models.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Essential Background.ppt
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)文本分类 Text Categorization(主讲:刘挺).pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)信息过滤(主讲:刘挺).pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)信息检索模型 IRModel.pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)信息检索概述.pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)搜索引擎技术 SearchEngine.pdf
