北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Web Search

Outline Overview of web search Next generation search engines CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, 2 June25-27,2010
Outline • Overview of web search • Next generation search engines 2 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

Characteristics of Web Information "Infinite"size (Surface vs.deep Web) Surface static HTML pages Deep=dynamically generated HTML pages(DB) ·Semi-structured -Structured HTML tags,hyperlinks,etc Unstructured Text Different format (pdf,word,ps,...) 。Multi--media(Textual,,audio,images,…) High variances in quality(Many junks) "Universal"coverage(can be about any content) CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
Characteristics of Web Information • “Infinite” size (Surface vs. deep Web) – Surface = static HTML pages – Deep = dynamically generated HTML pages (DB) • Semi-structured – Structured = HTML tags, hyperlinks, etc – Unstructured = Text • Different format (pdf, word, ps, …) • Multi-media (Textual, audio, images, …) • High variances in quality (Many junks) • “Universal” coverage (can be about any content) 3 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

General Challenges in Web Information Management Handling the size of the Web How to ensure completeness of coverage? Efficiency issues Dealing with or tolerating errors and low quality information Addressing the dynamics of the Web Some pages may disappear permanently New pages are constantly created CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, 4 June25-27,2010
General Challenges in Web Information Management • Handling the size of the Web – How to ensure completeness of coverage? – Efficiency issues • Dealing with or tolerating errors and low quality information • Addressing the dynamics of the Web – Some pages may disappear permanently – New pages are constantly created 4 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

“Free text'"vs.“Structured text" So far,we've assumed "free text" Document word sequence -Query word sequence Collection a set of documents -Minimal structure .. But,we may have structures on text(e.g.,title, hyperlinks) Can we exploit the structures in retrieval? CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
“Free text” vs. “Structured text” • So far, we’ve assumed “free text” – Document = word sequence – Query = word sequence – Collection = a set of documents – Minimal structure … • But, we may have structures on text (e.g., title, hyperlinks) – Can we exploit the structures in retrieval? 5 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

Examples of Document Structures Intra-doc structures(=relations of components) Natural components:title,author,abstract, sections,references,.. Annotations:named entities,subtopics, markups,… Inter-doc structures (=relations between documents) Topic hierarchy Hyperlinks/citations (hypertext) CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010 6
Examples of Document Structures • Intra-doc structures (=relations of components) – Natural components: title, author, abstract, sections, references, … – Annotations: named entities, subtopics, markups, … • Inter-doc structures (=relations between documents) – Topic hierarchy – Hyperlinks/citations (hypertext) 6 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
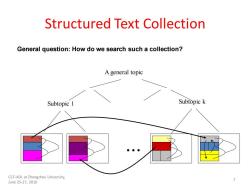
Structured Text Collection General question:How do we search such a collection? A general topic Subtopic 1 Subtopic k CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
Structured Text Collection ... Subtopic 1 Subtopic k A general topic General question: How do we search such a collection? 7 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
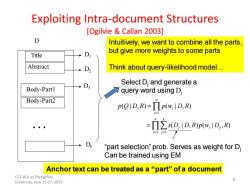
Exploiting Intra-document Structures [Ogilvie Callan 2003] D Intuitively,we want to combine all the parts. but give more weights to some parts Title D Abstract +D2 Think about query-likelihood model... Select D and generate a Body-Part1 +D3 query word using D; Body-Part2 p(QID.R)-TIp(w.ID.R) -TIEs(D,ID.R)pOID.R i=1j=1 D "part selection"prob.Serves as weight for D Can be trained using EM Anchor text can be treated as a "part"of a document CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University,June 25-27,2010
Exploiting Intra-document Structures [Ogilvie & Callan 2003] Title Abstract Body-Part1 Body-Part2 … D D1 D2 D3 Dk Intuitively, we want to combine all the parts, but give more weights to some parts Think about query-likelihood model… 1 1 1 ( | , ) ( | , ) ( | , ) ( | , ) n i i n k j i j i j p Q D R p w D R s D D R p w D R = = = = = “part selection” prob. Serves as weight for Dj Can be trained using EM Select Dj and generate a query word using Dj Anchor text can be treated as a “part” of a document 8 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

Exploiting Inter-document Structures Document collection has links (e.g.,Web, citations of literature) ·Query:text query Results:ranked list of documents Challenge:how to exploit links to improve ranking? CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, 9 June25-27,2010
Exploiting Inter-document Structures • Document collection has links (e.g., Web, citations of literature) • Query: text query • Results: ranked list of documents • Challenge: how to exploit links to improve ranking? 9 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
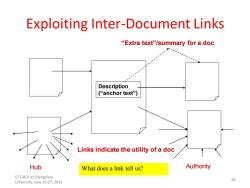
Exploiting Inter-Document Links "Extra text"/summary for a doc Description (“anchor text") Links indicate the utility of a doc Hub What does a link tell us? Authority CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University,June 25-27,2010 10
Exploiting Inter-Document Links Description (“anchor text”) Hub Authority “Extra text”/summary for a doc Links indicate the utility of a doc What does a link tell us? 10 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

PageRank:Capturing Page "Popularity" [Page Brin 98] 。Intuitions Links are like citations in literature -A page that is cited often can be expected to be more useful in general ·PageRank is essentially“citation counting”,but improves over simple counting -Consider "indirect citations"(being cited by a highly cited paper counts a lot...) Smoothing of citations(every page is assumed to have a non-zero citation count) PageRank can also be interpreted as random surfing (thus capturing popularity) CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
PageRank: Capturing Page “Popularity” [Page & Brin 98] • Intuitions – Links are like citations in literature – A page that is cited often can be expected to be more useful in general • PageRank is essentially “citation counting”, but improves over simple counting – Consider “indirect citations” (being cited by a highly cited paper counts a lot…) – Smoothing of citations (every page is assumed to have a non-zero citation count) • PageRank can also be interpreted as random surfing (thus capturing popularity) 11 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Course Overview(主讲:闫宏飞).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Introdution(主讲:吉建民).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 15 智能机器人系统介绍.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 14 Reinforcement Learning.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 13 神经网络与深度学习.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 09 AI Planning.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 08 First-Order Logic and Inference in FOL.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 11 马尔可夫决策过程.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Uncertainty and Bayesian Networks.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 07 Logical Agents.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Game Playing.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Constraint Satisfaction Problems.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Informed Search.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Solving Problems by Searching.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《人工智能基础》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Intelligent Agents.pdf
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 9-Inference in first-order logic.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 8-First-Order Logic.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 7-Logical Agents.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 6-Adversarial Search.ppt
- 《Artificial Intelligence:A Modern Approach》教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)Chapter 5-Constraint Satisfaction Problems.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Crawling the Web.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Retrieval Models.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Essential Background.ppt
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)文本分类 Text Categorization(主讲:刘挺).pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)信息过滤(主讲:刘挺).pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)信息检索模型 IRModel.pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)信息检索概述.pdf
- 哈尔滨工业大学:《信息检索》课程教学资源(课件讲义)搜索引擎技术 SearchEngine.pdf
- 《统计自然语言处理》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第7章 汉语自动分词与词性标注.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程PPT课件讲稿(自然语言处理)01 Introduction(主讲:彭波)The CCF Advanced Disciplines Lectures.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程PPT课件讲稿(自然语言处理)02 Link Analysis.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程PPT课件讲稿(自然语言处理)03 Web Spam.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程PPT课件讲稿(自然语言处理)04 Recommendation System.ppt
- 北京大学:《信息检索》课程PPT课件讲稿(自然语言处理)05 Infrastructure and Cloud.ppt
- 河南科技学院:信息工程学院本科课程教学大纲汇编(计算机科学与技术专业).pdf
- 广东茂名农林科技职业学院:计算机网络技术人才培养方案(2020级).pdf
- 广东茂名农林科技职业学院:计算机网络技术专业人才培养方案(2021级).pdf
- 广东茂名农林科技职业学院:动漫制作技术专业人才培养方案(2020级).pdf
- 南京农业大学:《面向对象程序设计实验》课程教学大纲 Experiment in Object-Oriented Programming.pdf
- 广东茂名农林科技职业学院:电子商务专业人才培养方案(2019级).pdf
