《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Fast Sampling Constraint Satisfaction Solutions via the Lovász Local Lemma

Fast Sampling Constraint Satisfaction Solutions via the Lovasz Local Lemma Yitong Yin Nanjing University International Joint Conference On Theoretical Computer Science(IJTCS)2021 融 Frontiers of Algorithmics Workshop(FAW)2021
Fast Sampling Constraint Satisfaction Solutions via the Lovász Local Lemma Yitong Yin Nanjing University International Joint Conference On Theoretical Computer Science (IJTCS) 2021 Frontiers of Algorithmics Workshop (FAW) 2021

Constraint Satisfaction Problem Φ=(V,Q,C) Variables:V={,..}with finite domains ... (local)Constraints:C=[C1,C2,...,Cm} each cC is defined on a subset vbl(c)of variables c:⑧g,→{True,False} iEvbl(c) ·CSP formula:Hx∈Q1×Q2×…×2n x)=∧c(o Example (k-SAT):Boolean variables V=[x1,x2.x3x,} k-CNFΦ=(:1VxV)A(x1VVx4)AxVx4Vx5) clause
• Variables: with finite domains • (local) Constraints: • each is defined on a subset vbl(c) of variables • CSP formula: • Example (k-SAT): Boolean variables V = {x1, x2,…, xn} Q1,…, Qn C = {c1, c2,…, cm} c ∈ C c : i∈ ⨂ 𝗏𝖻𝗅(c) Qi → {𝚃𝚛𝚞𝚎, 𝙵𝚊𝚕𝚜𝚎} ∀x ∈ Q1 × Q2 × ⋯ × Qn Φ(x) = ⋀ c∈C c (x𝗏𝖻𝗅(c)) V = {x1, x2, x3, x4, x5} Φ = (x1 ∨ ¬x2 ∨ x3) ∧ (x1 ∨ x2 ∨ x4) ∧ (x3 ∨ ¬x4 ∨ ¬x5) Constraint Satisfaction Problem Φ = (V, Q,C) k-CNF clause

Lovasz Local Lemma (LLL) Variables take independent random values X1,X2,...,X ·Violation Probability:each c∈C is violated with prob.≤p Dependency Degree:each c e C shares variables with s D other constraints c'∈C,i.e.vbl(c)nvbl(c)≠⑦ LLL [Erdos,Lovasz,1975]: epD≤I→solution exists .Constructive LLL [Moser,Tardos,2010]: epD≤I→solution can be found very efficiently
• Variables take independent random values • Violation Probability: each is violated with prob. ≤ p • Dependency Degree: each shares variables with ≤ D other constraints , i.e. • LLL [Erdős, Lovász, 1975]: ⟹ solution exists • Constructive LLL [Moser, Tardos, 2010]: ⟹ solution can be found very efficiently X1, X2,…, Xn c ∈ C c ∈ C c′∈ C 𝗏𝖻𝗅(c) ∩ 𝗏𝖻𝗅(c′) ≠ ∅ epD ≤ 1 epD ≤ 1 Lovász Local Lemma (LLL)
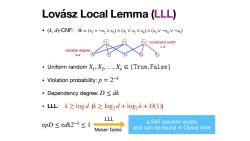
Lovasz Local Lemma(LLL) ·(k,d)-CNF:Φ=(x1Vx2V3)∧(x1Vx2Vx4)A(x3Vx4Vx5) constraint width =k variable degree sd ·Uniform random X1,X,,Xn∈{True,False} Violation probability:p=2-k ·Dependency degree:D≤dk ·LLL:k之logd (k≥1og2d+log2k+O(1) LLL epD≤edk2-k≤1 a SAT solution exists Moser-Tados and can be found in O(dkn)time
Lovász Local Lemma (LLL) • (k, d)-CNF: • Uniform random • Violation probability: • Dependency degree: • LLL: ( ) Φ = (x1 ∨ ¬x2 ∨ x3) ∧ (x1 ∨ x2 ∨ x4) ∧ (x3 ∨ ¬x4 ∨ ¬x5) X1, X2, …, Xn ∈ {𝚃𝚛𝚞𝚎, 𝙵𝚊𝚕𝚜𝚎} p = 2−k D ≤ dk k ≳ log d k ≥ log2 d + log2 k + O(1) c1 c2 c3 x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 constraint width = k variable degree ≤ d a SAT solution exists and can be found in O(dkn) time epD ≤ edk2−k ≤ 1 LLL Moser-Tados

Sampling Counting Input:a CSP formula =(V,C) Output .(sampling)uniform random satisfying solution .(counting)#of satisfying solutions .u:uniform distribution over all satisfying solutions of Rejection Sampling generate a uniform random Vx∈Q1×Q2×…×2mi if (x)=True then accept else reject; u is the distribution of accept) SAT solutions may be exponentially rare!
• μ: uniform distribution over all satisfying solutions of Φ Sampling & Counting generate a uniform random ; if then accept else reject; is the distribution of ∀x ∈ Q1 × Q2 × ⋯ × Qm Φ(x) = 𝚃𝚛𝚞𝚎 μ (x ∣ accept) Rejection Sampling SAT solutions may be exponentially rare! Input: a CSP formula Output : • (sampling) uniform random satisfying solution • (counting) # of satisfying solutions Φ = (V, Q,C)

Sampling Counting Input:a CSP formula=(V,O,C) Output: .(sampling)almost uniform random satisfying solution .(counting)an estimation of of satisfying solutions exact counting is #P-hard self-reduction Almost Uniform [Jerrum,Valiant,Vazirani 1986] Approximate Sampling adaptive simulated annealing Counting [Stefankovic,Vempala,Vigoda 2009] Application:inference in probabilistic graphical models Gibbs distribution cw=Πc(a) where each c:&g→Ro iEvbl(c) Inference:Pr [X;=IXs =xs] X~u
• exact counting is #P-hard • • Application: inference in probabilistic graphical models Sampling & Counting Input: a CSP formula Output : • (sampling) uniform random satisfying solution • (counting) # of satisfying solutions Φ = (V, Q,C) an estimation of almost Almost Uniform Sampling Approximate Counting self-reduction [Jerrum, Valiant, Vazirani 1986] adaptive simulated annealing [Štefankovič, Vempala, Vigoda 2009] c : i∈ ⨂ 𝗏𝖻𝗅(c) μ Qi → ℝ≥0 (x) ∝ Φ(x) = ∏ c∈C c (x𝗏𝖻𝗅(c)) Inference: Pr X∼μ [Xi = ⋅ ∣ XS = xS] Gibbs where each distribution
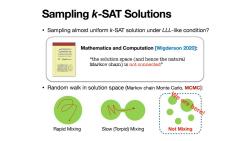
Sampling k-SAT Solutions Sampling almost uniform k-SAT solution under LLL-like condition? Mathematics and Computation [Wigderson 2020]: COAFU7A0米 Ar Myeason "the solution space (and hence the natural Markov chain)is not connected" Random walk in solution space (Markov chain Monte Carlo,MCMC): e ere here! Rapid Mixing Slow (Torpid)Mixing Not Mixing
• Sampling almost uniform k-SAT solution under LLL-like condition? • Random walk in solution space (Markov chain Monte Carlo, MCMC): Sampling k-SAT Solutions “the solution space (and hence the natural Markov chain) is not connected” Mathematics and Computation [Wigderson 2020]: Rapid Mixing Slow (Torpid) Mixing Not Mixing We ere here!

Sampling k-SAT Solutions Sampling almost uniform SAT solution under LLL-like condition? constraint width =k LLL cond.: variable degree sd k之logd (k,d)-CNF Condition Complexity Technique Hermon,Sly,Zhang'16 monotone CNF [1] k之21ogd (dk)o(n log n MCMC Guo,Jerrum,Liu'17 s≥min(log dk/2)☒ (dk)o(n Partial Rejection Sampling k之21ogd Bezakova et al '16 k≤2logd-C NP-hard lower bound [1]Monotone CNF:all variables appear positively,e.g.=(x V2 VX)(x VX2Vx)A (x3 Vx V xs) [2]s:two dependent clauses share at least s variables. Moitra STOC'17 JACM'19 k之60logd nO(dk) Coupling LP Feng,Guo,Y.,Zhang'20 k之20logd 0(d2k3n1.000001 Projected MCMC
• Sampling almost uniform SAT solution under LLL-like condition? Sampling k-SAT Solutions (k,d)-CNF Condition Complexity Technique Hermon, Sly, Zhang ’16 monotone CNF [1] MCMC Guo, Jerrum, Liu ’17 s ≥ min(log dk, k/2) [2] Partial Rejection Sampling Bezáková et al ’16 NP-hard lower bound k ≳ 2 log d (dk) O(1) n log n k ≳ 2 log d (dk) O(1) n k ≤ 2 log d − C [1] Monotone CNF: all variables appear positively, e.g. [2] s: two dependent clauses share at least 𝑠 variables. Φ = (x1 ∨ x2 ∨ x3) ∧ (x1 ∨ x2 ∨ x4) ∧ (x3 ∨ x4 ∨ x5) Moitra STOC’17 JACM’19 k ≳ 60 log d Coupling + LP nO(d2 k2 ) Feng, Guo, Y., Zhang ’20 k ≳ 20 log d O ˜ (d2k3 n1.000001) Projected MCMC c1 c2 c3 x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 constraint width = k variable degree ≤ d LLL cond.: k ≳ log d

Main Theorem (for CNF) [Feng,Guo,Y.,Zhang '20] For any sufficiently small 2-20,any (k,d)-CNF satisfying k≥201ogd+201ogk+31o 1 。Sampling algorithm: draw almost uniform SAT solution in time (d23+5) ·Counting algorithm: count SAT solutions approximately in time (d2k3n2+5)
Main Theorem (for CNF) For any sufficiently small , any (k,d)-CNF satisfying • Sampling algorithm: draw almost uniform SAT solution in time • Counting algorithm: count # SAT solutions approximately in time ζ ≤ 2−20 k ≥ 20 log d + 20 log k + 3 log 1 ζ O ˜ (d2 k3 n1+ζ ) O ˜ (d2 k3 n2+ζ ) [Feng, Guo, Y., Zhang ’20]
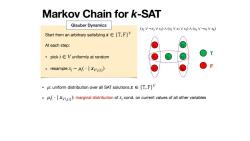
Markov Chain for k-SAT Glauber Dynamics (X]VX2VX3)A(VXV x5)A (x4 Vx5VX6) Start from an arbitrary satisfyingx[T,F)V At each step: ·pick i∈V uniformly at random resamplex~以(·|x) A:uniform distribution over all SAT solutionsx[T,F]V .(marginal distribution ofcond.on current values of all other variables
Markov Chain for k-SAT Start from an arbitrary satisfying At each step: • pick uniformly at random • resample x ∈ {𝚃, 𝙵}V i ∈ V xi ∼ μi ( ⋅ ∣ xV∖{i}) !" !# !$ !% !& !' !( (x1 ∨ ¬x2 ∨ x3) ∧ (x2 ∨ x7 ∨ x5) ∧ (x4 ∨ ¬x5 ∨ x6) T F • : uniform distribution over all SAT solutions • : marginal distribution of cond. on current values of all other variables μ x ∈ {𝚃, 𝙵}V μi ( ⋅ ∣ xV∖{i}) xi Glauber Dynamics
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Dynamic and Distributed Algorithms for Sampling from Gibbs Distributions.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Ranged hash functions and the price of churn.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Fast construction of overlay networks.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Cell-Probe Proofs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Cell-probe proofs and nondeterministic cell-probe complexity.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Improved FPTAS for Multi-Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Correlation Decay up to Uniqueness in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Assigning Tasks for Efficiency in Hadoop.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Approximate Counting via Correlation Decay on Planar Graphs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Approximate Counting via Correlation Decay in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Spatial Mixing of Coloring Random Graphs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Spatial mixing and the connective constant - Optimal bounds.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Simple average-case lower bounds for approximate near-neighbor from isoperimetric inequalities.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Counting hypergraph matchings up to uniqueness threshold.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Convergence of MCMC and Loopy BP in the Tree Uniqueness Region for the Hard-Core Model.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)What can be sampled locally?.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)On Local Distributed Sampling and Counting.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Dynamic Sampling from Graphical Models.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Dynamic inference in probabilistic graphical models.pdf
- 中国计算机学会学术著作丛书:《对等网络——结构、应用与设计 Peer-to-Peer Network Structure, Application and Design》PDF电子书(正文,共九章).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Distributed Algorithms for MCMC Sampling.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Dynamic Sampling from Graphical Models.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Sampling & Counting for Big Data.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Introduction to the Correlation Decay Method.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Local Distributed Sampling from Locally-Defined Distribution.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Rectangle Inequalities for Data Structure Lower Bounds.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Sampling up to the Uniqueness Threshold.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)What can be sampled locally?.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Correlation Decay up to Uniqueness in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Phase transition of hypergraph matchings.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:Beautiful Journey of Theoretical Computer Science(理论计算机科学的美丽旅程).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:Quest for Artificial Intelligence(人工智能探秘).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源:The Magical Wild Animals(神奇的动物).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Counting with Bounded Treewidth.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Decay of Correlation in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)POMP:Protocol Oblivious SDN Programming with Automatic Multi-Table Pipelining.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Progress of Concurrent Objects with Partial Methods.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Practical Verification Framework for Preemptive OS Kernels.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)A Program Logic for Concurrent Objects under Fair Scheduling.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Compositional Verification of Termination-Preserving Refinement of Concurrent Programs.pdf
