广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system
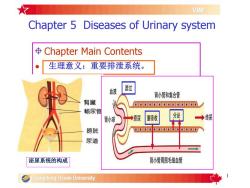
VIMChapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system$Chapter Main Contents生理意义:重要排泄系统。滤过血液肾小管和集合管臀藏aoapncddpdan输尿管分泌重吸收终尿原尿肾小球nondonbdbnno膀胱尿道肾小管周围毛细血管泌尿系统的构成Guangdong Ocean University
1 Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system Chapter Main Contents • Conspectus • Section 1 Glomerulonephritis • Section 2 Cystitis • Section 3 Urolithiasis 生理意义:重要排泄系统。 泌尿系统的构成

★Chapter5DiseasesofUrinarysystemVIM$ConspectusPrimaryfunctions1) excretion of waste products of metabolism;2) maintenance of a constant extracellular environmentthroughconservationandexcretion of waterandelectrolytes;3)productionof thehormones erythropoietinandrenin,whichregulatehematopoiesis造血作用,bloodpressure,andsodium reabsorption;4)metabolismofvitaminDtoitsactiveform(1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol),Guangdong OceanUniversity
2 Conspectus 1) excretion of waste products of metabolism; 2) maintenance of a constant extracellular environment through conservation and excretion of water and electrolytes; 3) production of the hormones erythropoietin and renin, which regulate hematopoiesis造血作用, blood pressure, and sodium reabsorption; 4) metabolism of vitamin D to its active form (1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol). Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system
★Chapter5DiseasesofUrinarysystemVIMDiagnoses>Many abnormalities of the urinary system can be diagnosed fromthe signalmentofthe patient, historyand physical examinationfindings,serumchemistryprofile,urinalysis,andaerobicbacterialurine culture.犬膀胱结石Guangdong Ocean University
3 uDiagnoses ØMany abnormalities of the urinary system can be diagnosed from the signalment of the patient, history and physical examination findings, serum chemistry profile, urinalysis, and aerobic bacterial urine culture. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system
★Chapter5DiseasesofUrinarysystemVIMPrinciplesof Therapy>Diseases of the urinarysystem can result from a variety ofpathologic processes, and appropriate therapy depends on thelocation, severity, and etiology of the problem.>Diuretics are used to remove inappropriate water in animals withedema or volume overlcad..correct.snecific ian imhalang2anCorteprontnVeterimary Colleyreducebloodpressure.RIORenalcalculus肾结Guangdong Ocean University
4 lPrinciples of Therapy ØDiseases of the urinary system can result from a variety of pathologic processes, and appropriate therapy depends on the location, severity, and etiology of the problem. ØDiuretics are used to remove inappropriate water in animals with edema or volume overload, correct specific ion imbalances, and reduce blood pressure. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system
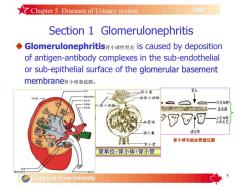
★Chapter5Diseases of Urinary systemVIMSection 1 GlomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritis肾小球性肾炎iscausedbydepositionof antigen-antibodycomplexes in the sub-endothelialor sub-epithelial surface of theglomerularbasementmembrane肾小球基底膜.窗肾小管精质育机出球小动脉肾包摄肾皮膜内皮细胞舒养人球小动脉基底膜国四酒土皮细胞次级足卖滤过陈肾小袭肾小球毛细血管滤过膜肾小管肾单位-肾小体+肾小管得机Guangdong Ocean University
5 Section 1 Glomerulonephritis uGlomerulonephritis肾小球性肾炎 is caused by deposition of antigen-antibody complexes in the sub-endothelial or sub-epithelial surface of the 肾小球基底膜. uSecondary glomerulonephritis occurs as a side effect of chronic infectious, neoplastic瘤的, or immunologic disorders, it is apparently more common in dogs than cats. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system 肾小球毛细血管滤过膜 肾单位=肾小体+肾小管
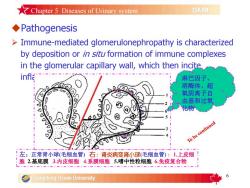
★Chapter5Diseases of Urinary systemDAIMPathogenesis>Immune-mediated glomerulonephropathyischaracterizedbydepositionor insituformationof immunecomplexesin the glomerular capillary wall, which then inciteinfl淋巴因子溶酶体、超氧阴离子自由基和过氧左:正常肾小球(毛细血管)右:肾炎病变肾小球(毛细血管):1.上皮细胞2.基底膜3.内皮细胞4.系膜细胞5.嗜中性粒细胞6.免疫复合物Guangdong OceanUniversity
6 uPathogenesis Ø Immune-mediated glomerulonephropathy is characterized by deposition or in situ formation of immune complexes in the glomerular capillary wall, which then incite inflammatory changes. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system 正常肾小球(毛细血管) :肾炎病变肾小球(毛细血管) :1.上皮细 胞 2.基底膜 3.内皮细胞 4.系膜细胞 5.嗜中性粒细胞 6.免疫复合物 淋巴因子、 溶酶体、超 氧阴离子自 由基和过氧 化物

★Chapter5Diseases ofUrinary systemVIMPathogenesis> Familial glomerulopathies肾小球疾病 as a primary cause ofchronickidney diseasehavebeenreported in severalbreeds of dogs.These arenot immunecomplexdiseases, although some are characterized byproteinuria and associated clinical abnormalities thatresemblethosecaused byimmune-mediatedglomerulonephropathy.In one study of dogs, the mean age of presentation for glomerulonephritis was 4-8yr;55% weremales.Guangdong Ocean University
7 uPathogenesis Ø Familial glomerulopathies肾小球疾病 as a primary cause of chronic kidney disease have been reported in several breeds of dogs. These are not immune complex diseases, although some are characterized by proteinuria and associated clinical abnormalities that resemble those caused by immune-mediated glomerulonephropathy. Ø In one study of dogs, the mean age of presentation for glomerulonephritis was 4-8 yr; 55% were males. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system

Chapter5Diseases ofUrinarysystemDAIMClinical Findings>Glomerulopathy often leads to proteinuria (primarilyalbuminuria)and canproduce hypoproteinemia, ascites, dyspnea (due to pleural effusion orpulmonary edema), and/or peripheral edema, which may be referred to asthe nephrotic syndrome.Protein wasting can produce preferential loss ofleanbodymass thatmaybeapparent oncareful physical examination.Systemichypertensionmaybemoreprevalent inproteinuricchronickidney disease and may observed at any stage.Proteinuria may result in loss of antithrombin抗凝血酶 IIthrough the glomerular basementmembrane, leading to a hypercoagulable state高凝状态 in dogs,generally when plasmaalbumin levels are ≤1.0 g/dLGuangdong Ocean University
8 uClinical Findings Ø Glomerulopathy often leads to proteinuria (primarily albuminuria) and can produce hypoproteinemia, ascites, dyspnea (due to pleural effusion or pulmonary edema), and/or peripheral edema, which may be referred to as the nephrotic syndrome. Protein wasting can produce preferential loss of lean body mass that may be apparent on careful physical examination. Systemic hypertension may be more prevalent in proteinuric chronic kidney disease and may observed at any stage. Ø Proteinuria may result in loss of antithrombin抗凝血酶 III through the glomerular basement membrane, leading to a 高凝状态 in dogs, generally when plasma albumin levels are ≤1.0 g/dL. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system

★Chapter5DiseasesofUrinarysystemVIMDiagnosisTheserumureanitrogen,creatinine肌氨酸酐,andphosphorusconcentrations are usually increased.Marked proteinuria with edemamaybeobservedinthepresenceorabsenceofazotemia氮血质症.Physicalfindings are usually nonspecificexcept thatascites,pleuraleffusion,and/orperipheral,pitting麻点,nonpainful,subcutaneousedema,areevident insomeanimals(75%of cats and15%of dogs)Renal biopsy isoften required to determinethetypeof glomerulardisease.Membranousglomerulonephritis is reported most frequently in cats;there isaroughly equal distribution of histologic findings in dogs,with glomerularamyloidosis and membranous,proliferative,and membranoproliferativeglomerulonephritisall represented.Systemic hypertension develops in an unusually large proportion of animals withprotein-losing glomerulonephritis;therefore, blood pressure should bedetermined in all animals with evidence of glomerulardiseaseGuangdong Ocean University
9 uDiagnosis Ø The serum urea nitrogen, creatinine肌氨酸酐, and phosphorus concentrations are usually increased. Marked proteinuria with edema may be observed in the presence or absence of azotemia氮血质症. Ø Physical findings are usually nonspecific except that ascites, pleural effusion, and/or peripheral, pitting麻点, nonpainful, subcutaneous edema, are evident in some animals (75% of cats and 15% of dogs). Ø Renal biopsy is often required to determine the type of glomerular disease. Membranous glomerulonephritis is reported most frequently in cats; there is a roughly equal distribution of histologic findings in dogs, with glomerular amyloidosis and membranous, proliferative, and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis all represented. Ø Systemic hypertension develops in an unusually large proportion of animals with protein-losing glomerulonephritis; therefore, blood pressure should be determined in all animals with evidence of glomerular disease. Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system

★ Chapter5Diseases of Urinary systemVIMTreatmentThere are 5 basic principles to therapy inglomerulonephropathies:1) If a cause of immune-complex disease can be identified, itshould be treated.2) Manifestations of the nephrotic syndrome, if present, shouldbe managed with dietary salt restriction and judicious use ofdiuretics.3)Antithrombotics抗血栓药 (eg,aspirin) should be considered forhypoalbuminemic (plasma albumin <1.0 g/dL) animals aswell as those with low serumlevels of antithrombin III(<30% of normal).becoTo10Guangdong Ocean University
10 uTreatment Ø There are 5 basic principles to therapy in glomerulonephropathies: 1) If a cause of immune-complex disease can be identified, it should be treated. 2) Manifestations of the nephrotic syndrome, if present, should be managed with dietary salt restriction and judicious use of diuretics. 3) Antithrombotics抗血栓药 (eg, aspirin) should be considered for hypoalbuminemic (plasma albumin <1.0 g/dL) animals as well as those with low serum levels of antithrombin III (<30% of normal). Chapter 5 Diseases of Urinary system
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 4 Diseases of cardiovascular system.pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 3 Diseases of Respiratory System.pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 2 Diseases of Digestive System.pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction to VIM.pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,共六章,任课教师:陈进军、康丹菊).doc
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》实验课程教学大纲 Veterinary Internal Medicine.doc
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程实验指导(讲义)实验四 血液丙酮酸的测定.doc
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程实验指导(讲义)实验三 血清谷丙、谷草转氨酶活力测定(赖氏法).doc
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程实验指导(讲义)实验二 氢氰酸的定性与定量检验.doc
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程实验指导(讲义)实验一 血清总钙含量的测定.doc
- 塔里木大学:《兽医临床诊断学》课程实验课教案.docx
- 塔里木大学:《兽医临床诊断学》课程实验教学大纲.pdf
- 塔里木大学:《兽医临床诊断学》课程理论课教案.docx
- 塔里木大学:《兽医临床诊断学》课程教学大纲 Veterinary Clinical Diagnostics.pdf
- 《兽医外科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十五章 小动物牙病.ppt
- 《兽医外科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十四章 四肢疾病.ppt
- 《兽医外科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十三章 跛行诊断.ppt
- 《兽医外科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十二章 泌尿生殖系统疾病.ppt
- 《兽医外科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十一章 直肠及肛门疾病.ppt
- 《兽医外科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 头部疾病.ppt
- 广东海洋大学:《兽医内科学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Chapter 6 Diseases of the nervous system.pdf
- 西昌学院:《动物遗传学》实验课程教学大纲.docx
- 西昌学院:《家畜解剖学》实验课程教学指导(共十八个实验).doc
- 龙岩学院:《预防兽医学》实验课程教学大纲.docx
- 龙岩学院:《基础兽医学》实验课程教学大纲.docx
- 龙岩学院:《临床兽医学》实验课程教学大纲.docx
- 南京农业大学:《兽医内科学》实验课程教学大纲(强化).doc
- 南京农业大学:《兽医内科学》实验课程教学大纲(动医).doc
- 南京农业大学:《兽医内科学》实验课程教学大纲.doc
- 南京农业大学:《兽医临床诊断学》实验课程教学大纲(动医、实验).doc
- 南京农业大学:《动物解剖学》课程II教学大纲(动医).pdf
- 南京农业大学:《动物解剖学》课程II教学大纲(动物实验).pdf
- 南京农业大学:《宠物解剖学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《中兽医学》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《兽医药理学》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《兽医药代动力学》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《药物化学》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《兽医毒理学》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《药物分析》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《兽药制剂学》实验课程教学大纲.pdf
