《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)26 Rotavirus Infection in Children
Rotavirus Infectionin Children
Rotavirus Infection in Children 1

Overview of Rotavirus infectionThe most common cause of severe diarrhea among infantsand young childrenAccounts for up to 50%ofhospitalizations for severediarrheaOne of several viruses that cause infections often calledstomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza.It is a double-stranded RNAvirus in the family ReoviridaeAlmost every child in the world has been infected withrotavirus at least once by the age of five. Adults are rarelyaffectedAbout 600,000 children under five years of age die fromrotavirus infection each year in whole world.Almost two million more become severely ill
2 Overview of Rotavirus infection • The most common cause of severe diarrhea among infants and young children. • Accounts for up to 50% ofhospitalizations for severe diarrhea. • One of several viruses that cause infections often called stomach flu, despite having no relation to influenza. • It is a double-stranded RNA virus in the family Reoviridae. • Almost every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Adults are rarely affected. • About 600,000 children under five years of age die from rotavirus infection each year in wholeworld. • Almost two million more become severely ill

History of RotavirusFirst identified as cause ofdiarrhea in 1973 by RuthBishop.Thomas Flewettsuggested the namerotavirus after observingthat.WheelRata(Latin)(E ng lish)
History of Rotavirus • • First identified as cause of diarrhea in 1973 by Ruth Bishop. Thomas Flewett suggested the name rotavirus after observing that. Rata (Latin) 3 Wheel = (E nglish)
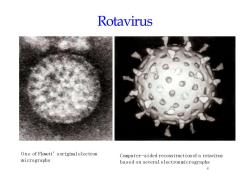
RotavirusOne of Flewett'soriginalelectronComputer-aidedreconstructionofarotavirusmicrographsbasedonseveralelectronmicrographs4
Rotavirus One of Flewett’soriginalelectron micrographs 4 Computer-aided reconstruction of a rotavirus based on several electronmicrographs

ElectronmicrographsDiameter75nmRotavirusAstrovirusCalicivirus-NVAdenovirusOCalicivirus-SvTorovirusPicobirnavirusEnterovirus22Harrison' s Principle of Internal Medicinge, 17th Ed
Electron micrographs Harrison’sPrinciple of InternalMedicin5 e,17th E d Diameter ≈75 n m
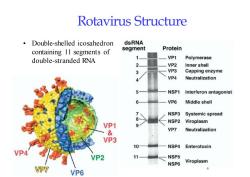
Rotavirus StructuredsRNADouble-shelledicosahedronProteinsegmentcontaining 11 segments of1VP1Polymerasedouble-stranded RNA2VP2InnershellVP3Capping enzyme3VP4Neutralization8-5NSP1Interferonantagonist6VP6Middleshell>NSP3Systemic spread8NSP2ViroplasmVP19VP7Neutralization&VP310NSP4EnterotoxinVP411NSP5VP2ViroplasmNSP66VP7VP6
Rotavirus Structure • Double-shelled icosahedron containing 11 segments of double-stranded RNA 6

Rotavirus ClassificationGroups: A, B, C,D,E, F, G.According to inner protein VP6: Most human illness is caused by group A, afew by groupsBand C. Group Bis reported in China and India onlySerotypes: G1-23, P1-31Defined by two outer-capsid protein VP7 (Gprotein) andVP4 (P protein): Only 10 Gtypes and 11 Ptypes found in human isolates
7 Rotavirus Classification Groups: A, B, C, D, E, F, G • According to inner proteinVP6 • Most human illness is caused by group A, a few by groups B and C. Group B is reported in China and India only. Serotypes: G1-23, P1-31 • Defined by two outer-capsid protein VP7 (G protein) and VP4 (P protein) • Only 10 G types and 11 P types found in human isolates

RotavirusDiseaseBurdenGlobally,estimated to cause 125million casesofdiarrhea.Ofthese, 18 million cases are considered at leastmoderately severe, with approximately 600,000 deathsper year.In china, estimated to cause more than 10 million casesofdiarrhea per year.:In U.S., estimated 3 million cases of diarrhea, 50,000hospitalizations, and 20-40 deaths annually in U.S
8 Rotavirus Disease Burden • Globally, estimated to cause 125 million cases of diarrhea. Of these, 18 million cases are considered at least moderately severe, with approximately 600,000 deaths per year. • In china, estimated to cause more than 10 million cases of diarrhea per year. • In U.S., estimated 3 million cases of diarrhea, 50,000 hospitalizations, and 20-40 deaths annually in U.S

Pathogens for acute gastroenteritis inchildrenFrequencyof enteropathogensinEuropeanchildren(O-5y)PathogenFrequency,%Rotavirus10-35Norovirus2-204-13Campylobacter2-10Adenovirus5-8Salmonella14.5EPECYersinia0.4-30.9-3Giardia0-3Cryptosporidium0-2EAggECShigella0.31.4STEC0-3ETEC0-0.50-4Entamoeba45-60No agent detectedEPEC=enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; EAggEC=enteroagenteroaggregative E coli; STEC-Shiga toxin-producing E coli,ETEC=enterotoxigenic strainsof Ecoli
Pathogens for acute gastroenteritis in children Frequency of enteropathogens in E u r o p e an children (0–5 y) 9
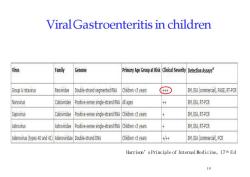
ViralGastroenteritis in childrenFamilyVirusPrimary Age Group at Risk Clnial Severty Detection AssaysGenomeReoviridaeDouble-strand segmented RNAChildren<5 years+EM,EIA(commercal),PAGERT-PCRGroup ArotavirusNorovrusCaliviridaeEM,EIA, RT-PCRPositive-sense single-strand RNA Allages++CaliviridaeEM,EIA,RT-PCRSapovirusPositive-sense single-strand RNA Children<5 yearsAstrovrusAstrovidaePositivesensesinglestrandRNhildrenyearsEM, EIA, RT-PCR+++chidren<5 earsAdenovirus (types 40 and 41)Adenovinidae Double-strand DNAEM, EIA (commercial,CRHarrison'sPrinciple of Internal Medicine,17th Ed10
Viral Gastroenteritis in children Harrison’sPrinciple of InternalMedicine, 17th E d 1 0
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)27 Inflammation Causes Cholesterol Redistribution by Diverting Cholesterol from Circulation to Tissue Tompartments.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 新生儿败血症 Neonatal Septicemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)07 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy(HIE).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷C卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷B卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷B卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷C卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)02 pneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)01 ABO incompatibility of neonates.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)03 congenital heart disease-TOF.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)07 congenital hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)05 purulent meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)04 iron deficiency anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)03 congenital heart disease-VSD.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)08 diarrhea.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 anute nepheritis-1.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)25 Scarlet Fever.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)24 Mumps(Epidemic parotitis).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)19 Pediatric Tuberculosis.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)18 Varicella.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)17 Measles.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)16 Growth Hormone Deficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)15 Congenital Hypothyroidism.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14 Immunodeficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)13 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 Acute Convulsion in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)10 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 Congenital Heart Disease.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)08 Respiratory Disorders.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)05 Neonatal Jaundice,Hemolytic Disease of Newborn.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)04 Nutrition During Childhood.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)03 Development.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)02 Growth.pptx
