《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)15 Congenital Hypothyroidism

Congenital Hypothyroidism(Cretinism)
(Cretinism) Congenital Hypothyroidism

LearningobjectivesYoushould know:The clinical features of congenitalhypothyroidism in neonates and childrenBe able to discussthe diagnosis andmanagement
Learning objectives You should know: The clinical features of congenital hypothyroidism in neonates and children Be able to discuss the diagnosis and management

Major contentsOverview of congenitalhypothroidismEtiologyClinical manifestationLaboratory examinationDiagnosis and differential diagnosisTreatment
Major contents Overview of congenital hypothroidism Etiology Clinical manifestation Laboratory examination Diagnosis and differential diagnosis Treatment

AbbreviationCHcongenital hypothyroidismTRHthyrotropin-releasing hormoneTSHthyrotropic-stimulatinghormoneT4thyroxineT3triiodothyronineMITmonoiodotyrosineDITdiiodotyrosineTGthyroglobulinTBGthyroxine-binding globulin
Abbreviation CH congenital hypothyroidism TRH thyrotropin-releasing hormone TSH thyrotropic-stimulating hormone T4 thyroxine T3 triiodothyronine MIT monoiodotyrosine DIT diiodotyrosine TG thyroglobulin TBG thyroxine-binding globulin

OverviewHypothyroidismCongenital hypothyroidismacquired hypothyroidismIodine deficiencyAutoimmunediseaseHashimoto thyroiditis
Overview Hypothyroidism Congenital hypothyroidism acquired hypothyroidism Iodine deficiency Autoimmune disease— Hashimoto thyroiditis

OverviewHypothyroidismCongenital hypothyroidismacquiredhypothyroidismIodine deficiencyAutoimmunediseaseHashimotothyroiditis
Overview Hypothyroidism Congenital hypothyroidism acquired hypothyroidism Iodine deficiency Autoimmune disease— Hashimoto thyroiditis

OverviewCongenitalHypothyroidismiscommondisease of pediatric endocrinology.Congenital factors cause the insufficiency of thyroidhormone, which result in the low metabolism,growth retardation, and mental impairment.The onset during inborn or newborn period, canlead to irreversible mentalimpairment.One of the few preventable disease, earlytreatment can improve prognosisthoroughly
Overview Congenital Hypothyroidism is common disease of pediatric endocrinology. Congenital factors cause the insufficiency of thyroid hormone, which result in the low metabolism, growth retardation, and mental impairment. The onset during inborn or newborn period, can lead to irreversible mentalimpairment. One of the few preventable disease, early treatment can improve prognosisthoroughly

Incidence1 in 4000livebirths(AmericaandEurope)Females 2: Male 1InChinaIncidenceofCongenital hypothyroidismFromthe neonatalscreening): 1 in 3624-----the nationwide neonatal screening fromclinical examination center of Health Bureau in1999
Incidence 1 in 4000 live births (America and Europe) Females 2: Male 1 In China: Incidence of Congenital hypothyroidism (From the neonatalscreening): 1 in 3624 -the nationwide neonatal screening from clinical examination center of Health Bureau in1999
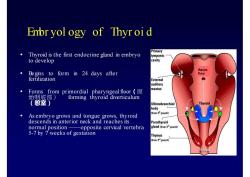
Enbr yol ogy of Thyr oidPrimaryThyroid is the first endocrine gland in embryotympaniccavityto developPharyrxBegins toform in 24days afterfloorfertilizationExternalauditorymeatusFormsfromprimordialpharyngealfloor(原始咽底部)forming thyroid diverticulum(憩室)UItimobranchialbody(from4pouch)As embryo grows and tongue grows, thyroiddescendsinanteriorneck and reaches itsParathyroidgland (trom 3"pouch)normalposition--opposite cervical vertebra5-7by7weeksof gestationThymus(from3"pouch)
Embr yol ogy of Thyr oi d • Thyroid is the first endocrine gland in embryo to develop • Begins to form in 24 days after fertilization • Forms from primordial pharyngealfloor(原 始咽底部) forming thyroid diverticulum (憩室) • As embryo grows and tongue grows, thyroid descends in anterior neck and reaches its normal position ——opposite cervical vertebra 5-7 by 7 weeks of gestation Pharynx floor
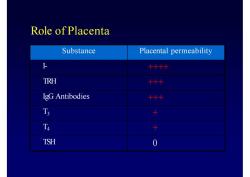
RoleofPlacentaSubstancePlacental permeabilityI-++++TRH+++IgG Antibodies+++T3+T4TSH0
Role of Placenta Substance Placental permeability I- ++++ TRH +++ IgG Antibodies +++ T3 + T4 + TSH 0
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)16 Growth Hormone Deficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)17 Measles.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)18 Varicella.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)19 Pediatric Tuberculosis.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)24 Mumps(Epidemic parotitis).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)25 Scarlet Fever.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)26 Rotavirus Infection in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)27 Inflammation Causes Cholesterol Redistribution by Diverting Cholesterol from Circulation to Tissue Tompartments.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 新生儿败血症 Neonatal Septicemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)07 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy(HIE).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷C卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷B卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷B卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷C卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14 Immunodeficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)13 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 Acute Convulsion in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)10 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 Congenital Heart Disease.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)08 Respiratory Disorders.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)05 Neonatal Jaundice,Hemolytic Disease of Newborn.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)04 Nutrition During Childhood.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)03 Development.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)02 Growth.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.pptx
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程教学大纲 A Teaching Outline for Obstetrics and Gynecology Course(中英文双语).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)06 妊娠期高血压疾病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)04 异位妊娠.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)05 正常分娩.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)03 流产.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)01 月经生理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)02 妊娠生理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)09 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症.doc
