《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia

NUTRITIONAIIRONDEFICIENCYANEMIA
N U T R IT IO N A L IRON D E F I C I E N C Y ANEMIA

WCONTENTSINDUCTIONIRONMETABOLISMETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESISMANIFESTATIONSLABORATORYFINDINGSDIAGNOSIS&DIFFERENTIAL口PREVENTION& TREATMENT
C O N T E N T S □ I N D U C T I O N □ IRON METABOLISM □ E T I O L O G Y / P A T H O G E N E S I S □ MANIFESTATIONS □ LABORATORY FINDINGS □ D I A G N O S I S & DIFFERENTIAL □ PREVENTION & TREATMENT

INTRODUCTION Definition for N-IDA-The anemia caused by insufficientdietary ironuptake, inwhich the ironstorage and hemoglobin synthesisdecreased.HEMATOLOGYLONCOLOGY.CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
INTRODUCTION □ Definition for N - IDA –The anemia caused by insufficient dietary iron uptake, in which the iron storage and hemoglobin synthesis decreased. HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L

·INTRODUCTION Clinical characteristicsserum iron (SI),iron stores (SF),transferrin saturation (Ts)hemoglobin concentration,microcytichypochromic anemia, good response to iron therapy.- 6mo to 3 yrs. IncidenceHEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGYCHILDRENS HOSPITAL
□ Clinical characteristics – iron stores (SF), serum iron (SI), transferrin saturation(TS) – hemoglobin concentration , microcytic hypochromic anemia, –good response to iron therapy. –6mo to 3 yrs. □ Incidence INTRODUCTION HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L
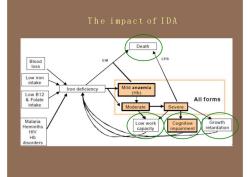
TheimpactofIDADeathCFRGMBloodlossLowironintakeMildanaemiaIrondeficiency(Hb)LowB12Allforms&FolateintakeModerateSevereMalariaGrowthCognitiveLowworkHeminthsretardationcapacityimpairmentHIVHbdisorders
The impact of IDA

25th International Congress25-30AugustofPediatricsAthens-GreeceATHENS2OOZThe incidence:-In China (2004)an investigationfrom9118children in 15 provinces and 26 cities reveledthat the incidenceis30.1% vs 16.8%for the childrenwith7~12mos.and15.5%vs4.4%forthechildrenwith13~36mos- In the US.It isabout3% of 1-2yr-oldsare irondeficientanemia.: Of adolescent girls, 2% are iron deficient anemia
• The incidence: –In China (2004),an investigation from 9118 children in 15 provinces and 2 6 cities reveled that the incidence • is 30.1% vs 16.8% for the children with 7~12mos • and 15.5% vs 4.4% for the children with 13~36mos –In the U S • It is about 3 % of 1-2 yr-olds are iron deficient anemia. • O f adolescent girls,2 % are iron deficient anemia
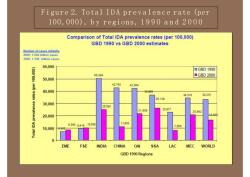
Figure 2.TotalIDA prevalence rate (per100,000),byregions,1990and2000Comparison of TotalIDAprevalence rates (per 100,000)GBD1990vsGBD2000estimatesNumbetofcasesalobalily2000:1.026bilfioncases1990:1750billion cases60,000GBD1990oGBD200050.36950,00042.79342.05440,0000.0033,2154B30,00025.0362281721,60920.68220,00011,0238.3609.41910.0367.85810.000OAIEMEFSEINDIACHINASSALACMECWORLDGBD1990Regions
Figure 2. Total IDA p r e v a lenc e rate (per 100,000), b y regions, 1990 and 2000
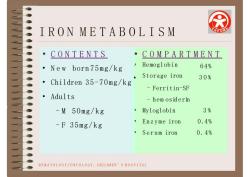
IRONMETABOLISMCUCONTENTSCOMPARTMENTHemoglobin64%Newborn75mg/kgStorage iron30%Chi1dren 35-70mg/kg-Ferritin-SFAdults- hemosiderin3%-M 50mg/kgMyloglobin0.4%Enzyme iron-F35mg/kg0.4%Serum ironHEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY.CHILDREN SHOSPITAL
IRON METABOLISM • Hemoglobin Storage iron 6 4% 30% –Ferritin-SF –hem osiderin • Myloglobin • Enzyme iron • Serum iron 3 % 0.4% 0.4% HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L • CONTENTS • C O M P A R T M E N T • New born 75mg/kg • Children 35-70mg/kg • • Adults –M 50mg/kg –F 35mg/kg
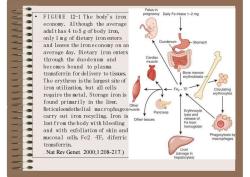
Fetus inDailyFe intake1-2mgpregnancyFIGURE12-1The body s ironAlthough the averageeconomy.adult has 4 to5 g of body iron,Tonly 1 m g of dietary iron entersDuodenumStomachand leaves theironeconomy onanaverage day. Dietary iron entersCardiacthrough the duodenum andmusclebecomes bound to plasmaBonemarrowtransferrin for delivery to tissues.erythroblastsThe erythron is the largest site ofiron utilization, but all cellsFea-TFCirculatingerythrocytesrequire the metal. Storage iron isfound primarily in the liver.OtherReticuloendothelial macrophagesmuscleErythrocytePancreaslysisandcarry out iron recycling.Iron isreleaseofOthertissueslostfrom thebody with bleedingFefromhemoglobinand with exfoliationof skin andPhagocytosis bymucosal cells Fe2 -TF, diferricmacrophagestransferrin.Liver,Nat Rev Genet.2000;1:208-217.)(storageinhepatocytes)
• FIGURE 12-1 The body's iron economy. Although the average adult has 4 to 5 g of body iron, only 1 m g of dietary iron enters and leaves the iron economy on an average day. Dietary iron enters through the duodenum and becomes bound to plasma transferrin for delivery to tissues. The erythron isthe largest site of iron utilization, but all cells require the metal.Storage iron is found primarily in the liver. Reticuloendothelial macrophages carry out iron recycling. Iron is lostfrom the body with bleeding and with exfoliation of skin and mucosal cells. Fe2 –TF, diferric transferrin. . Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:208-217.)
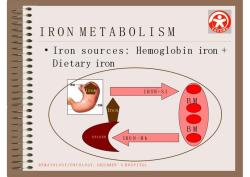
IRONMETABOLISM Iron sources: Hemoglobin iron +Dietary ironIRON-SIBMIronBMSPLEENIRON-HbHEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY,CHILDREN'SHOSPITAL
• Iron sources: Hemoglobin iron + Dietary iron IRON METABOLISM iron B M B M IRON - S I IR O N - H b S P L E E N HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L Iro n
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 Acute Convulsion in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)13 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14 Immunodeficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)15 Congenital Hypothyroidism.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)16 Growth Hormone Deficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)17 Measles.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)18 Varicella.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)19 Pediatric Tuberculosis.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)24 Mumps(Epidemic parotitis).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)25 Scarlet Fever.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)26 Rotavirus Infection in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)27 Inflammation Causes Cholesterol Redistribution by Diverting Cholesterol from Circulation to Tissue Tompartments.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 新生儿败血症 Neonatal Septicemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)07 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy(HIE).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)10 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 Congenital Heart Disease.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)08 Respiratory Disorders.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)05 Neonatal Jaundice,Hemolytic Disease of Newborn.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)04 Nutrition During Childhood.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)03 Development.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)02 Growth.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.pptx
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程教学大纲 A Teaching Outline for Obstetrics and Gynecology Course(中英文双语).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)06 妊娠期高血压疾病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)04 异位妊娠.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)05 正常分娩.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)03 流产.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)01 月经生理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)02 妊娠生理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)09 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)07 妊娠合并心脏病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)08 妊娠合并糖尿病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)10 妊娠合并病毒性肝炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)11 前置胎盘.doc
