《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)08 Respiratory Disorders

Respiratory Disorders
Respiratory Disorders

TopicsRespiratory disordersRespiratory infectionsPneumonia
Top ics □ Respiratory disorders □ Respiratory infections □ Pneumonia

TopicsRespiratorydisordersRespiratory infectionsPneumonia
Top ics □ Respiratory disorders □ Respiratory infections □ Pneumonia

RespiratoryDisorders50% of consultation with general practitioners or acuteillness in young children and a third of consultations inolder children20-35% of acute pediatric admissions tohospital, some ofwhich are life-threateningAsthma is the most common chronic illness of childhoodCystic fibrosis isthemost common inherited disorder inCaucasians causing chronicdisease
Respiratory Disorders □ 5 0 % of consultation with general practitioners or acute illness in young children and a third of consultations in older children □ 2 0-35% of acute pediatric admissions to hospital,some of which are life-threatening □ Asthma is the most common chronic illness of childhood □ Cystic fibrosis is the most common inherited disorder in Caucasians causing chronic disease

TopicsRespiratory disordersRespiratoryinfectionsPneumonia
Top ics □ Respiratory disorders □ Respiratory infections □ Pneumonia

RespiratoryInfectionsThe most frequent infections ofchildhood: 6-8/yearPathogens: viruses, bacterial, otherpathogensHost and environmental factorsClassification of respiratory infections
Respiratory Infections □ The most frequent infections of childhood: 6-8/year □ Pathogens: viruses,bacterial, other pathogens □ Host and environmental factors □ Classification of respiratory infections
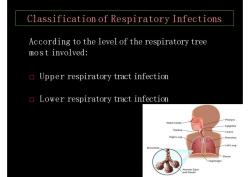
ClassificationofRespiratoryInfectionsAccording to the level of the respiratory treemost involved:Upper respiratory tract infectionLower respiratory tract infection-PharynxNasal CaEpiglottisFrachLarynxRight LungBronchusLettLungBronchPlelDiaphragm86dAe
Classification of Respiratory Infections According to the level of the respiratory tree most involved: □ Upper respiratory tract infection □ Lower respiratory tract infection

Case-lJack, age four months, is sent at home by his generalpractitioner because of two days of rapid, labouredbreathing and poor feeding. He was born at 27 weeksgestation, birth weight 979g and was discharged home atthree months of age. On examination he was a fever of37.4 C and a respiratory rate of 60 breaths/min. His chestis hyperinflated with marked intercoatal recession. Onauscultation there are generalized fine crackles andwheezes
Case -1 Jack, age four months, is sent at home by his general practitioner because of two days of rapid, laboured breathing and poor feeding. H e was born at 27 weeks’ gestation, birth weight 979g and was discharged home at three months of age. O n examination he was a fever of 37.4 C and a respiratory rate of 60 breaths/min. His chest is hyperinflated with marked intercoatal recession. O n auscultation there are generalized fine crackles and wheezes

QuestionDo you have any comments or what doyou conclude anything fromthiscase?
Qu e stion Do you have any comments or what d o you conclude anything from this case?

Case -lJack, age four months, is sent at home by his generalpractitioner because of two days of rapid. labouredbreathing and poor feeding. He was born at 27 weeksgestation, birth weight 979g and was discharged home atthree months of age. On examination he was a fever of37. 4 C and a respiratory rate of 60 breaths/min. His chestis hyperinflated with marked intercoatal recession. Ongeneralized fine crackles andauscultation there arewheezes
Case -1 Jack, age four months, is sent at home by his general practitioner because of two days of rapid, laboured breathing and poor feeding. H e was born at 27 weeks’ gestation, birth weight 979g and was discharged home at three months of age. O n examination he was a fever of 37.4 C and a respiratory rate of 60 breaths/min. His chest is hyperinflated with marked intercoatal recession. O n auscultation there are generalized fine crackles and wheezes
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 Congenital Heart Disease.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)10 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 Acute Convulsion in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)13 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14 Immunodeficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)15 Congenital Hypothyroidism.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)16 Growth Hormone Deficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)17 Measles.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)18 Varicella.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)19 Pediatric Tuberculosis.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)24 Mumps(Epidemic parotitis).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)25 Scarlet Fever.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)26 Rotavirus Infection in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)27 Inflammation Causes Cholesterol Redistribution by Diverting Cholesterol from Circulation to Tissue Tompartments.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 新生儿败血症 Neonatal Septicemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)05 Neonatal Jaundice,Hemolytic Disease of Newborn.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)04 Nutrition During Childhood.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)03 Development.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)02 Growth.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.pptx
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程教学大纲 A Teaching Outline for Obstetrics and Gynecology Course(中英文双语).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)06 妊娠期高血压疾病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)04 异位妊娠.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)05 正常分娩.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)03 流产.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)01 月经生理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)02 妊娠生理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)09 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)07 妊娠合并心脏病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)08 妊娠合并糖尿病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)10 妊娠合并病毒性肝炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)11 前置胎盘.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)12 胎盘早期剥离.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)13 胎儿窘迫.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《妇产科学》课程授课教案(中文)14 产后出血.doc
